本文分析Spark on k8s项目静态恢复机制也即SAR(相关源码可能不是最新,仅供参考)
一、前言
spark on k8s项目SAR并不健壮和完善,主要体现在如下方面(参考这里):
- 1、如果
executor挂掉,则driver不会产生新的 替换executor - 2、如果
executor全部挂掉,driver依然运行——bug(原因待查……) - 3、
executor产生过程存在问题——如果某些executor因为某些原因始终无法起来,则driver不会继续产生新的executor
最终想要的结果是在spark应用程序正确的情况下,始终产生并维持用户指定数目的executor数目,并采用某种机制保障(检测)运行的executor是"健康状态",最终保证应用程序的成功运行
解决方案调研
官方有开源解决方案Changes to support executor recovery behavior during static allocation.,基本是参考spark on yarn的静态恢复方案
改进方案解析
What changes were proposed in this pull request?
Added initial support for driver to ask for more executors in case of framework faults.
Reviewer notes: This is WIP and currently being tested. Seems to work for simple smoke-tests. Looking for feedback on
- Any major blindspots in logic or functionality
- General flow. Potential issues with control/data flows.
- Are style guidelines followed.
Potential issues/Todos:
- Verify that no deadlocks are possible.
- May be explore message passing between threads instead of using synchronization
- Any uncovered issues in further testing
Reviewer notes
Main business logic is in removeFailedAndRequestNewExecutors()
Overall executor recovery logic at a high-level:
- On executor disconnect, we immediately disable the executor.
- Delete/Error Watcher actions will trigger a capture of executor loss reasons. This happens on a separate thread.
- There is another dedicated recovery thread, which looks at all previously disconnected executors and their loss reasons to remove those executors with the right loss reasons or keep trying till the loss reasons’ are discovered. If the loss reason of a lost executors is not discovered within a sufficient time window, then we give up and still remove the executor. For all removed executors, we request new executors on this recovery thread.
How was this patch tested?
Manually tested that on deleting a pod, new pods were being requested.
参考如下三个Commits(SAR):
- Changes to support executor recovery behavior during static allocation.
- Unit Tests for KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend
- Code enhancement: Replaced explicit synchronized access to a hashmap with a concurrent map.
下面从源码分析SAR解决方案:
数据结构:
private val RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK = new Object
// Indexed by executor IDs and guarded by RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.
private val runningExecutorsToPods = new mutable.HashMap[String, Pod]
// Indexed by executor pod names and guarded by RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.
private val runningPodsToExecutors = new mutable.HashMap[String, String]
// TODO(varun): Get rid of this lock object by my making the underlying map a concurrent hash map.
private val EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK = new Object
// Indexed by executor IP addrs and guarded by EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK
private val executorPodsByIPs = new mutable.HashMap[String, Pod]
private val podsWithKnownExitReasons: concurrent.Map[String, ExecutorExited] =
new ConcurrentHashMap[String, ExecutorExited]().asScala
private val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval =
new ConcurrentHashMap[String, Pod]().asScala
allocatorRunnable线程执行具体分配executor逻辑(核心函数):
override def start(): Unit = {
super.start()
executorWatchResource.set(kubernetesClient.pods().withLabel(SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL, applicationId())
.watch(new ExecutorPodsWatcher()))
allocator.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
allocatorRunnable, 0, podAllocationInterval, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
if (!Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(sc.conf)) {
doRequestTotalExecutors(initialExecutors)
} else {
shufflePodCache = shuffleServiceConfig
.map { config => new ShufflePodCache(
kubernetesClient, config.shuffleNamespace, config.shuffleLabels) }
shufflePodCache.foreach(_.start())
kubernetesExternalShuffleClient.foreach(_.init(applicationId()))
}
}
private val allocatorRunnable: Runnable = new Runnable {
// Maintains a map of executor id to count of checks performed to learn the loss reason
// for an executor.
private val executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts = new mutable.HashMap[String, Int]
override def run(): Unit = {
handleDisconnectedExecutors()
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
if (totalRegisteredExecutors.get() < runningExecutorsToPods.size) {
logDebug("Waiting for pending executors before scaling")
} else if (totalExpectedExecutors.get() <= runningExecutorsToPods.size) {
logDebug("Maximum allowed executor limit reached. Not scaling up further.")
} else {
for (i <- 0 until math.min(
totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorsToPods.size, podAllocationSize)) {
val (executorId, pod) = allocateNewExecutorPod()
runningExecutorsToPods.put(executorId, pod)
runningPodsToExecutors.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, executorId)
logInfo(
s"Requesting a new executor, total executors is now ${runningExecutorsToPods.size}")
}
}
}
}
def handleDisconnectedExecutors(): Unit = {
// For each disconnected executor, synchronize with the loss reasons that may have been found
// by the executor pod watcher. If the loss reason was discovered by the watcher,
// inform the parent class with removeExecutor.
val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy =
Map.empty ++ disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy.foreach { case (executorId, executorPod) =>
val knownExitReason = podsWithKnownExitReasons.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
knownExitReason.fold {
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
} { executorExited =>
logDebug(s"Removing executor $executorId with loss reason " + executorExited.message)
removeExecutor(executorId, executorExited)
// We keep around executors that have exit conditions caused by the application. This
// allows them to be debugged later on. Otherwise, mark them as to be deleted from the
// the API server.
if (!executorExited.exitCausedByApp) {
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
}
}
}
}
def removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId: String): Unit = {
val reasonCheckCount = executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts.getOrElse(executorId, 0)
if (reasonCheckCount >= MAX_EXECUTOR_LOST_REASON_CHECKS) {
removeExecutor(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor lost for unknown reasons."))
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
} else {
executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts.put(executorId, reasonCheckCount + 1)
}
}
def deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId: String): Unit = {
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval -= executorId
executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts -= executorId
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
runningExecutorsToPods.remove(executorId).map { pod =>
kubernetesClient.pods().delete(pod)
runningPodsToExecutors.remove(pod.getMetadata.getName)
}.getOrElse(logWarning(s"Unable to remove pod for unknown executor $executorId"))
}
}
}
allocatorRunnable线程首先创建executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts(executorId,executorCountCheckPerformed),如下:
// Maintains a map of executor id to count of checks performed to learn the loss reason
// for an executor.
private val executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts = new mutable.HashMap[String, Int]
...
根据注释可以知道该结构体保存了executor已经被执行removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount的次数
run函数首先执行handleDisconnectedExecutors如下:
def handleDisconnectedExecutors(): Unit = {
// For each disconnected executor, synchronize with the loss reasons that may have been found
// by the executor pod watcher. If the loss reason was discovered by the watcher,
// inform the parent class with removeExecutor.
val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy =
Map.empty ++ disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy.foreach { case (executorId, executorPod) =>
val knownExitReason = podsWithKnownExitReasons.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
knownExitReason.fold {
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
} { executorExited =>
logDebug(s"Removing executor $executorId with loss reason " + executorExited.message)
removeExecutor(executorId, executorExited)
// We keep around executors that have exit conditions caused by the application. This
// allows them to be debugged later on. Otherwise, mark them as to be deleted from the
// the API server.
if (!executorExited.exitCausedByApp) {
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
}
}
}
}
handleDisconnectedExecutors执行逻辑如下:
- 1、从
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval(executorId,executorPod)获取disconnected Pod,如下:
private val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval =
new ConcurrentHashMap[String, Pod]().asScala
def handleDisconnectedExecutors(): Unit = {
// For each disconnected executor, synchronize with the loss reasons that may have been found
// by the executor pod watcher. If the loss reason was discovered by the watcher,
// inform the parent class with removeExecutor.
val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy =
Map.empty ++ disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy.foreach { case (executorId, executorPod) =>
val knownExitReason = podsWithKnownExitReasons.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
knownExitReason.fold {
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
} { executorExited =>
logDebug(s"Removing executor $executorId with loss reason " + executorExited.message)
removeExecutor(executorId, executorExited)
// We keep around executors that have exit conditions caused by the application. This
// allows them to be debugged later on. Otherwise, mark them as to be deleted from the
// the API server.
if (!executorExited.exitCausedByApp) {
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
}
}
}
}
- 2、遍历
disconnected Pod判断knownExitReason(executorName,ExecutorExited)中是否已经存在Poddisconnected的原因ExecutorExited:
private val podsWithKnownExitReasons: concurrent.Map[String, ExecutorExited] =
new ConcurrentHashMap[String, ExecutorExited]().asScala
def handleDisconnectedExecutors(): Unit = {
// For each disconnected executor, synchronize with the loss reasons that may have been found
// by the executor pod watcher. If the loss reason was discovered by the watcher,
// inform the parent class with removeExecutor.
val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy =
Map.empty ++ disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy.foreach { case (executorId, executorPod) =>
val knownExitReason = podsWithKnownExitReasons.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
knownExitReason.fold {
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
} { executorExited =>
logDebug(s"Removing executor $executorId with loss reason " + executorExited.message)
removeExecutor(executorId, executorExited)
// We keep around executors that have exit conditions caused by the application. This
// allows them to be debugged later on. Otherwise, mark them as to be deleted from the
// the API server.
if (!executorExited.exitCausedByApp) {
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
}
}
}
}
- 3、若不存在对应Pod
disconnected的原因,则执行:
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
看removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)函数,如下:
def removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId: String): Unit = {
val reasonCheckCount = executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts.getOrElse(executorId, 0)
if (reasonCheckCount >= MAX_EXECUTOR_LOST_REASON_CHECKS) {
removeExecutor(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor lost for unknown reasons."))
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
} else {
executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts.put(executorId, reasonCheckCount + 1)
}
}
该函数执行逻辑是:
- 根据
executorId从executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts中获取(默认为0)count of checks performed(已经执行removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount的次数) - 如果
reasonCheckCount还没有达到最大check上限MAX_EXECUTOR_LOST_REASON_CHECKS,则添加对应executorId次数 - 如果
reasonCheckCount达到最大check上限MAX_EXECUTOR_LOST_REASON_CHECKS,则执行removeExecutor,如下:
...
removeExecutor(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor lost for unknown reasons."))
...
/**
* Called by subclasses when notified of a lost worker. It just fires the message and returns
* at once.
*/
protected def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
// Only log the failure since we don't care about the result.
driverEndpoint.ask[Boolean](RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason)).onFailure { case t =>
logError(t.getMessage, t)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
...
case class RemoveExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason)
extends CoarseGrainedClusterMessage
...
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {
executorRef.send(RegisterExecutorFailed("Duplicate executor ID: " + executorId))
context.reply(true)
} else {
// If the executor's rpc env is not listening for incoming connections, `hostPort`
// will be null, and the client connection should be used to contact the executor.
val executorAddress = if (executorRef.address != null) {
executorRef.address
} else {
context.senderAddress
}
logInfo(s"Registered executor $executorRef ($executorAddress) with ID $executorId")
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorId
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorRef.address, hostname,
cores, cores, logUrls)
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)
if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {
currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt
}
if (numPendingExecutors > 0) {
numPendingExecutors -= 1
logDebug(s"Decremented number of pending executors ($numPendingExecutors left)")
}
}
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the map
context.reply(true)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))
makeOffers()
}
case StopDriver =>
context.reply(true)
stop()
case StopExecutors =>
logInfo("Asking each executor to shut down")
for ((_, executorData) <- executorDataMap) {
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor)
}
context.reply(true)
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
// We will remove the executor's state and cannot restore it. However, the connection
// between the driver and the executor may be still alive so that the executor won't exit
// automatically, so try to tell the executor to stop itself. See SPARK-13519.
executorDataMap.get(executorId).foreach(_.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor))
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
context.reply(true)
case RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId) =>
val reply = SparkAppConfig(sparkProperties,
SparkEnv.get.securityManager.getIOEncryptionKey())
context.reply(reply)
}
...
// Remove a disconnected slave from the cluster
private def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
logDebug(s"Asked to remove executor $executorId with reason $reason")
executorDataMap.get(executorId) match {
case Some(executorInfo) =>
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
val killed = CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
addressToExecutorId -= executorInfo.executorAddress
executorDataMap -= executorId
executorsPendingLossReason -= executorId
executorsPendingToRemove.remove(executorId).getOrElse(false)
}
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(-executorInfo.totalCores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(-1)
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, if (killed) ExecutorKilled else reason)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorRemoved(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, reason.toString))
case None =>
// SPARK-15262: If an executor is still alive even after the scheduler has removed
// its metadata, we may receive a heartbeat from that executor and tell its block
// manager to reregister itself. If that happens, the block manager master will know
// about the executor, but the scheduler will not. Therefore, we should remove the
// executor from the block manager when we hit this case.
scheduler.sc.env.blockManager.master.removeExecutorAsync(executorId)
logInfo(s"Asked to remove non-existent executor $executorId")
}
}
removeExecutor执行如下:
// Remove a disconnected slave from the cluster
private def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
logDebug(s"Asked to remove executor $executorId with reason $reason")
executorDataMap.get(executorId) match {
case Some(executorInfo) =>
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
val killed = CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
addressToExecutorId -= executorInfo.executorAddress
executorDataMap -= executorId
executorsPendingLossReason -= executorId
executorsPendingToRemove.remove(executorId).getOrElse(false)
}
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(-executorInfo.totalCores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(-1)
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, if (killed) ExecutorKilled else reason)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorRemoved(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, reason.toString))
case None =>
// SPARK-15262: If an executor is still alive even after the scheduler has removed
// its metadata, we may receive a heartbeat from that executor and tell its block
// manager to reregister itself. If that happens, the block manager master will know
// about the executor, but the scheduler will not. Therefore, we should remove the
// executor from the block manager when we hit this case.
scheduler.sc.env.blockManager.master.removeExecutorAsync(executorId)
logInfo(s"Asked to remove non-existent executor $executorId")
}
}
// Accessing `executorDataMap` in `DriverEndpoint.receive/receiveAndReply` doesn't need any
// protection. But accessing `executorDataMap` out of `DriverEndpoint.receive/receiveAndReply`
// must be protected by `CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this`. Besides, `executorDataMap` should
// only be modified in `DriverEndpoint.receive/receiveAndReply` with protection by
// `CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this`.
private val executorDataMap = new HashMap[String, ExecutorData]
/**
* Grouping of data for an executor used by CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.
*
* @param executorEndpoint The RpcEndpointRef representing this executor
* @param executorAddress The network address of this executor
* @param executorHost The hostname that this executor is running on
* @param freeCores The current number of cores available for work on the executor
* @param totalCores The total number of cores available to the executor
*/
private[cluster] class ExecutorData(
val executorEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef,
val executorAddress: RpcAddress,
override val executorHost: String,
var freeCores: Int,
override val totalCores: Int,
override val logUrlMap: Map[String, String]
) extends ExecutorInfo(executorHost, totalCores, logUrlMap)
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* Stores information about an executor to pass from the scheduler to SparkListeners.
*/
@DeveloperApi
class ExecutorInfo(
val executorHost: String,
val totalCores: Int,
val logUrlMap: Map[String, String]) {
def canEqual(other: Any): Boolean = other.isInstanceOf[ExecutorInfo]
override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match {
case that: ExecutorInfo =>
(that canEqual this) &&
executorHost == that.executorHost &&
totalCores == that.totalCores &&
logUrlMap == that.logUrlMap
case _ => false
}
override def hashCode(): Int = {
val state = Seq(executorHost, totalCores, logUrlMap)
state.map(_.hashCode()).foldLeft(0)((a, b) => 31 * a + b)
}
}
转到removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount函数,执行完removeExecutor后,执行deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures如下:
def deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId: String): Unit = {
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval -= executorId
executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts -= executorId
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
runningExecutorsToPods.remove(executorId).map { pod =>
kubernetesClient.pods().delete(pod)
runningPodsToExecutors.remove(pod.getMetadata.getName)
}.getOrElse(logWarning(s"Unable to remove pod for unknown executor $executorId"))
}
}
- 将
executorId从disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval(executorId,executorPod)中剔除:disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval -= executorId - 将
executorId从executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts(executorId,executorCountCheckPerformed)中剔除:executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts -= executorId - 将
executorId从runningExecutorsToPods(executorId,executorPod)中剔除:runningExecutorsToPods.remove(executorId) - 将
executorPod从集群中物理上删除:kubernetesClient.pods().delete(pod) - 将
executorName从runningPodsToExecutors(executorName,executorId)中剔除:runningPodsToExecutors.remove(pod.getMetadata.getName)
总结removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount函数逻辑也即:若executorId对应的check次数没有到达阈值:MAX_EXECUTOR_LOST_REASON_CHECKS,则增加check次数;否则删除集群中executorId对应的Pod以及相应的结构
- 4、若存在对应Pod
disconnected的原因,执行如下:
def handleDisconnectedExecutors(): Unit = {
// For each disconnected executor, synchronize with the loss reasons that may have been found
// by the executor pod watcher. If the loss reason was discovered by the watcher,
// inform the parent class with removeExecutor.
val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy =
Map.empty ++ disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy.foreach { case (executorId, executorPod) =>
val knownExitReason = podsWithKnownExitReasons.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
knownExitReason.fold {
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
} { executorExited =>
logDebug(s"Removing executor $executorId with loss reason " + executorExited.message)
removeExecutor(executorId, executorExited)
// We keep around executors that have exit conditions caused by the application. This
// allows them to be debugged later on. Otherwise, mark them as to be deleted from the
// the API server.
if (!executorExited.exitCausedByApp) {
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
}
}
}
}
- 执行
removeExecutor将executorId从scheduler和block manager中删除 - 若该
executorId对应的Poddisconnected不是由spark内部原因造成的,而是由外部原因造成的(比如从k8s master执行kubectl delete pods/xxx等外部命令),则执行deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures将该executorId对应的Pod从集群中删除(也即内部原因造成的disconnected对应的Pod在集群中保留,以便后续debug;否则从集群中删除,不保留)
这里保留一个疑问:executorExited.exitCausedByApp具体可能是哪些?同时!executorExited.exitCausedByApp具体可能又是哪些?
回到allocatorRunnable线程的run函数:
private val allocatorRunnable: Runnable = new Runnable {
// Maintains a map of executor id to count of checks performed to learn the loss reason
// for an executor.
private val executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts = new mutable.HashMap[String, Int]
override def run(): Unit = {
handleDisconnectedExecutors()
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
if (totalRegisteredExecutors.get() < runningExecutorsToPods.size) {
logDebug("Waiting for pending executors before scaling")
} else if (totalExpectedExecutors.get() <= runningExecutorsToPods.size) {
logDebug("Maximum allowed executor limit reached. Not scaling up further.")
} else {
for (i <- 0 until math.min(
totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorsToPods.size, podAllocationSize)) {
val (executorId, pod) = allocateNewExecutorPod()
runningExecutorsToPods.put(executorId, pod)
runningPodsToExecutors.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, executorId)
logInfo(
s"Requesting a new executor, total executors is now ${runningExecutorsToPods.size}")
}
}
}
}
}
修改前allocatorRunnable线程如下:
private val runningExecutorPods = new mutable.HashMap[String, Pod] // Indexed by executor IDs.
private val allocatorRunnable: Runnable = new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
if (totalRegisteredExecutors.get() < runningExecutorPods.size) {
logDebug("Waiting for pending executors before scaling")
} else if (totalExpectedExecutors.get() <= runningExecutorPods.size) {
logDebug("Maximum allowed executor limit reached. Not scaling up further.")
} else {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
for (i <- 0 until math.min(
totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorPods.size, podAllocationSize)) {
runningExecutorPods += allocateNewExecutorPod()
logInfo(
s"Requesting a new executor, total executors is now ${runningExecutorPods.size}")
}
}
}
}
}
这是创建executor的主要函数,逻辑很清晰:
- 1、若已经成功创建(
executor注册了自己(register itself),则视为成功创建)的executorpod数量(totalRegisteredExecutors) < 已经发出创建请求的数量(runningExecutorsToPods),则等待k8s创建executorpod(或者等待executorregister itself),直到两者相等为止 - 2、若需要创建的
executorpod数量(totalExpectedExecutors)= 已经发出创建请求的数量(runningExecutorsToPods),则不再发出新的创建请求 - 3、否则,按照策略:
math.min(totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorsToPods.size, podAllocationSize)批量发出executorpod 创建请求allocateNewExecutorPod,并同时增加runningExecutorsToPods(executorId,executorPod)和runningPodsToExecutors(executorName,executorId)数值
接下来主要看ExecutorPodsWatcher class,由该类的eventReceived函数负责executor的监控工作……
private class ExecutorPodsWatcher extends Watcher[Pod] {
private val DEFAULT_CONTAINER_FAILURE_EXIT_STATUS = -1
override def eventReceived(action: Action, pod: Pod): Unit = {
if (action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Running"
&& pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null) {
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
val clusterNodeName = pod.getSpec.getNodeName
logDebug(s"Executor pod $pod ready, launched at $clusterNodeName as IP $podIP.")
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs += ((podIP, pod))
}
} else if ((action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp != null) ||
action == Action.DELETED || action == Action.ERROR) {
val podName = pod.getMetadata.getName
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
logDebug(s"Executor pod $podName at IP $podIP was at $action.")
if (podIP != null) {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs -= podIP
}
}
if (action == Action.ERROR) {
logInfo(s"Received pod $podName exited event. Reason: " + pod.getStatus.getReason)
handleErroredPod(pod)
} else if (action == Action.DELETED) {
logInfo(s"Received delete pod $podName event. Reason: " + pod.getStatus.getReason)
handleDeletedPod(pod)
}
}
}
override def onClose(cause: KubernetesClientException): Unit = {
logDebug("Executor pod watch closed.", cause)
}
def getExecutorExitStatus(pod: Pod): Int = {
val containerStatuses = pod.getStatus.getContainerStatuses
if (!containerStatuses.isEmpty) {
// we assume the first container represents the pod status. This assumption may not hold
// true in the future. Revisit this if side-car containers start running inside executor
// pods.
getExecutorExitStatus(containerStatuses.get(0))
} else DEFAULT_CONTAINER_FAILURE_EXIT_STATUS
}
def getExecutorExitStatus(containerStatus: ContainerStatus): Int = {
Option(containerStatus.getState).map(containerState =>
Option(containerState.getTerminated).map(containerStateTerminated =>
containerStateTerminated.getExitCode.intValue()).getOrElse(UNKNOWN_EXIT_CODE)
).getOrElse(UNKNOWN_EXIT_CODE)
}
def isPodAlreadyReleased(pod: Pod): Boolean = {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
!runningPodsToExecutors.contains(pod.getMetadata.getName)
}
}
def handleErroredPod(pod: Pod): Unit = {
val containerExitStatus = getExecutorExitStatus(pod)
// container was probably actively killed by the driver.
val exitReason = if (isPodAlreadyReleased(pod)) {
ExecutorExited(containerExitStatus, exitCausedByApp = false,
s"Container in pod " + pod.getMetadata.getName +
" exited from explicit termination request.")
} else {
val containerExitReason = containerExitStatus match {
case VMEM_EXCEEDED_EXIT_CODE | PMEM_EXCEEDED_EXIT_CODE =>
memLimitExceededLogMessage(pod.getStatus.getReason)
case _ =>
// Here we can't be sure that that exit was caused by the application but this seems
// to be the right default since we know the pod was not explicitly deleted by
// the user.
s"Pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName}'s executor container exited with exit status" +
s" code $containerExitStatus."
}
ExecutorExited(containerExitStatus, exitCausedByApp = true, containerExitReason)
}
podsWithKnownExitReasons.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, exitReason)
}
def handleDeletedPod(pod: Pod): Unit = {
val exitMessage = if (isPodAlreadyReleased(pod)) {
s"Container in pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName} exited from explicit termination request."
} else {
s"Pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName} deleted or lost."
}
val exitReason = ExecutorExited(
getExecutorExitStatus(pod), exitCausedByApp = false, exitMessage)
podsWithKnownExitReasons.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, exitReason)
}
}
回到最开始的start函数如下:
private val executorWatchResource = new AtomicReference[Closeable]
...
override def start(): Unit = {
super.start()
executorWatchResource.set(kubernetesClient.pods().withLabel(SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL, applicationId())
.watch(new ExecutorPodsWatcher()))
allocator.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
allocatorRunnable, 0, podAllocationInterval, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
if (!Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(sc.conf)) {
doRequestTotalExecutors(initialExecutors)
} else {
shufflePodCache = shuffleServiceConfig
.map { config => new ShufflePodCache(
kubernetesClient, config.shuffleNamespace, config.shuffleLabels) }
shufflePodCache.foreach(_.start())
kubernetesExternalShuffleClient.foreach(_.init(applicationId()))
}
}
eventReceived watch executor action,如下:
// Indexed by executor IP addrs and guarded by EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK
private val executorPodsByIPs = new mutable.HashMap[String, Pod]
def getExecutorPodByIP(podIP: String): Option[Pod] = {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs.get(podIP)
}
}
...
override def eventReceived(action: Action, pod: Pod): Unit = {
if (action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Running"
&& pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null) {
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
val clusterNodeName = pod.getSpec.getNodeName
logDebug(s"Executor pod $pod ready, launched at $clusterNodeName as IP $podIP.")
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs += ((podIP, pod))
}
} else if ((action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp != null) ||
action == Action.DELETED || action == Action.ERROR) {
val podName = pod.getMetadata.getName
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
logDebug(s"Executor pod $podName at IP $podIP was at $action.")
if (podIP != null) {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs -= podIP
}
}
if (action == Action.ERROR) {
logInfo(s"Received pod $podName exited event. Reason: " + pod.getStatus.getReason)
handleErroredPod(pod)
} else if (action == Action.DELETED) {
logInfo(s"Received delete pod $podName event. Reason: " + pod.getStatus.getReason)
handleDeletedPod(pod)
}
}
}
这里分析之前介绍一下k8s中Pod Watch 的几种状态:
io.fabric8.kubernetes.client.Watcher.Action Action 如下:
package io.fabric8.kubernetes.client;
import io.fabric8.kubernetes.api.model.Status;
public interface Watcher<T> {
void eventReceived(Action action, T resource);
/**
* Run when the watcher finally closes.
*
* @param cause What caused the watcher to be closed. Null means normal close.
*/
void onClose(KubernetesClientException cause);
enum Action {
ADDED, MODIFIED, DELETED, ERROR
}
}
k8s Watch event 如下:
// EventType defines the possible types of events.
type EventType string
const (
Added EventType = "ADDED"
Modified EventType = "MODIFIED"
Deleted EventType = "DELETED"
Error EventType = "ERROR"
DefaultChanSize int32 = 100
)
// Event represents a single event to a watched resource.
type Event struct {
Type EventType
// Object is:
// * If Type is Added or Modified: the new state of the object.
// * If Type is Deleted: the state of the object immediately before deletion.
// * If Type is Error: *api.Status is recommended; other types may make sense
// depending on context.
Object runtime.Object
}
// Add sends an add event.
func (f *FakeWatcher) Add(obj runtime.Object) {
f.result <- Event{Added, obj}
}
// Modify sends a modify event.
func (f *FakeWatcher) Modify(obj runtime.Object) {
f.result <- Event{Modified, obj}
}
// Delete sends a delete event.
func (f *FakeWatcher) Delete(lastValue runtime.Object) {
f.result <- Event{Deleted, lastValue}
}
// Error sends an Error event.
func (f *FakeWatcher) Error(errValue runtime.Object) {
f.result <- Event{Error, errValue}
}
测试如下:
- step1:创建
test_dnsPod
#kubectl create -f test_dns.yml
test_dns.yml如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dns-test
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- image: centos:6
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- sleep
args:
- "9999999"
name: dns-test
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: 800Mi
requests:
cpu: "1"
memory: 800Mi
- step2:
Watchtest_dnsPod
#curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/watch/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test
watch 如下:
{"type":"ADDED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"71998352","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Pending"}}}
{"type":"MODIFIED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"71998353","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Pending","conditions":[{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}]}}}
{"type":"MODIFIED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"71998355","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Pending","conditions":[{"type":"Initialized","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},{"type":"Ready","status":"False","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","reason":"ContainersNotReady","message":"containers with unready status: [dns-test]"},{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}],"hostIP":"x.x.x.x","startTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","containerStatuses":[{"name":"dns-test","state":{"waiting":{"reason":"ContainerCreating"}},"lastState":{},"ready":false,"restartCount":0,"image":"centos:6","imageID":""}]}}}
{"type":"MODIFIED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"71998362","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Running","conditions":[{"type":"Initialized","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},{"type":"Ready","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:31Z"},{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}],"hostIP":"x.x.x.x","podIP":"192.168.22.112","startTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","containerStatuses":[{"name":"dns-test","state":{"running":{"startedAt":"2017-12-13T03:49:30Z"}},"lastState":{},"ready":true,"restartCount":0,"image":"centos:6","imageID":"docker://sha256:38255ae1ae4375616b659950294364918d8079bb352dcf858d5053c7223b5e3e","containerID":"docker://42fed22e555dd83e8837d8211b352062dfda8b5e2a0d5b64aaf3cc80a6044342"}],"cpuSet":"7"}}}
- step3: 制造
ERROR
如果手动kill -9 sleep_pid,则Watch到发现如下Action:
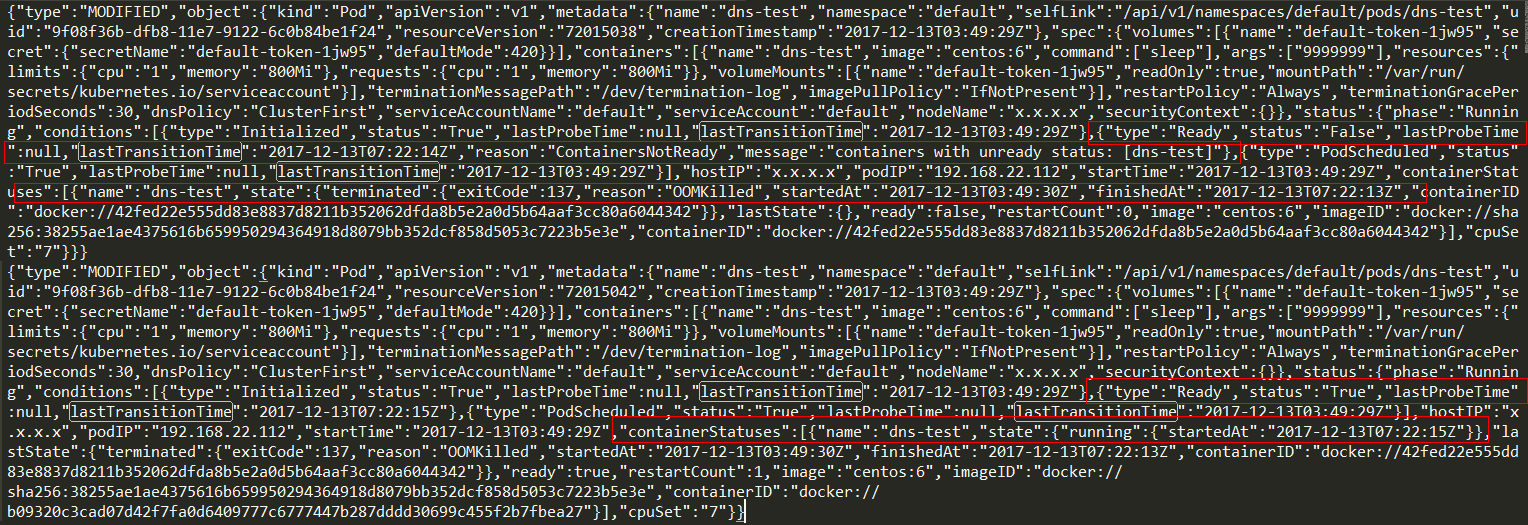
重新创建一个Pod,设置restartPolicy为Never,如下:
#kubectl create -f test_dns2.yml
test_dns2.yml如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dns-test2
namespace: default
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- image: centos:6
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- sleep
args:
- "9999999"
name: dns-test2
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: 800Mi
requests:
cpu: "1"
memory: 800Mi
手动kill -9 sleep_pid,Watch到发现如下Action:
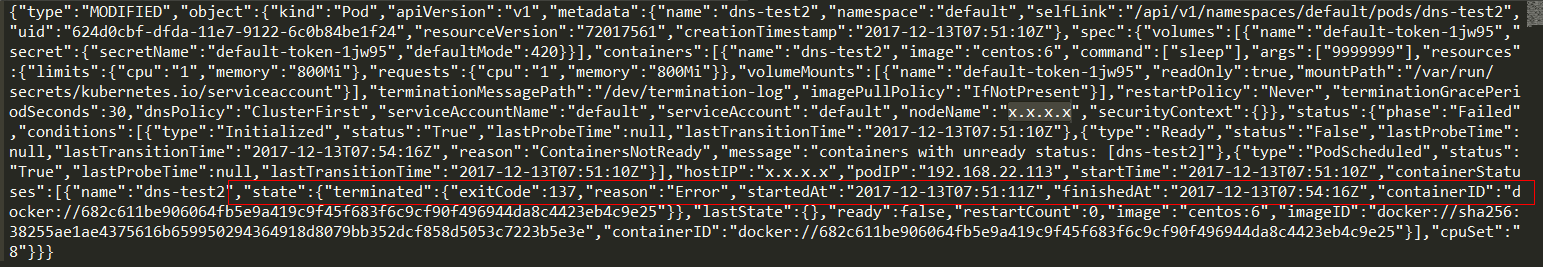
并没有ERROR Action出现,那么ERROR Action什么时候触发???
func newErrWatcher(err error) *errWatcher {
// Create an error event
errEvent := watch.Event{Type: watch.Error}
switch err := err.(type) {
case runtime.Object:
errEvent.Object = err
case *errors.StatusError:
errEvent.Object = &err.ErrStatus
default:
errEvent.Object = &unversioned.Status{
Status: unversioned.StatusFailure,
Message: err.Error(),
Reason: unversioned.StatusReasonInternalError,
Code: http.StatusInternalServerError,
}
}
// Create a watcher with room for a single event, populate it, and close the channel
watcher := &errWatcher{result: make(chan watch.Event, 1)}
watcher.result <- errEvent
close(watcher.result)
return watcher
}
...
// Implements storage.Interface.
func (c *Cacher) Watch(ctx context.Context, key string, resourceVersion string, pred SelectionPredicate) (watch.Interface, error) {
watchRV, err := ParseWatchResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
c.ready.wait()
// We explicitly use thread unsafe version and do locking ourself to ensure that
// no new events will be processed in the meantime. The watchCache will be unlocked
// on return from this function.
// Note that we cannot do it under Cacher lock, to avoid a deadlock, since the
// underlying watchCache is calling processEvent under its lock.
c.watchCache.RLock()
defer c.watchCache.RUnlock()
initEvents, err := c.watchCache.GetAllEventsSinceThreadUnsafe(watchRV)
if err != nil {
// To match the uncached watch implementation, once we have passed authn/authz/admission,
// and successfully parsed a resource version, other errors must fail with a watch event of type ERROR,
// rather than a directly returned error.
return newErrWatcher(err), nil
}
triggerValue, triggerSupported := "", false
// TODO: Currently we assume that in a given Cacher object, any <predicate> that is
// passed here is aware of exactly the same trigger (at most one).
// Thus, either 0 or 1 values will be returned.
if matchValues := pred.MatcherIndex(); len(matchValues) > 0 {
triggerValue, triggerSupported = matchValues[0].Value, true
}
// If there is triggerFunc defined, but triggerSupported is false,
// we can't narrow the amount of events significantly at this point.
//
// That said, currently triggerFunc is defined only for Pods and Nodes,
// and there is only constant number of watchers for which triggerSupported
// is false (excluding those issues explicitly by users).
// Thus, to reduce the risk of those watchers blocking all watchers of a
// given resource in the system, we increase the sizes of buffers for them.
chanSize := 10
if c.triggerFunc != nil && !triggerSupported {
// TODO: We should tune this value and ideally make it dependent on the
// number of objects of a given type and/or their churn.
chanSize = 1000
}
c.Lock()
defer c.Unlock()
forget := forgetWatcher(c, c.watcherIdx, triggerValue, triggerSupported)
watcher := newCacheWatcher(watchRV, chanSize, initEvents, filterFunction(key, pred), forget)
c.watchers.addWatcher(watcher, c.watcherIdx, triggerValue, triggerSupported)
c.watcherIdx++
return watcher, nil
}
...
func (w *watchCache) GetAllEventsSinceThreadUnsafe(resourceVersion uint64) ([]watchCacheEvent, error) {
size := w.endIndex - w.startIndex
oldest := w.resourceVersion
if size > 0 {
oldest = w.cache[w.startIndex%w.capacity].resourceVersion
}
if resourceVersion == 0 {
// resourceVersion = 0 means that we don't require any specific starting point
// and we would like to start watching from ~now.
// However, to keep backward compatibility, we additionally need to return the
// current state and only then start watching from that point.
//
// TODO: In v2 api, we should stop returning the current state - #13969.
allItems := w.store.List()
result := make([]watchCacheEvent, len(allItems))
for i, item := range allItems {
elem, ok := item.(*storeElement)
if !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("not a storeElement: %v", elem)
}
result[i] = watchCacheEvent{
Type: watch.Added,
Object: elem.Object,
Key: elem.Key,
ResourceVersion: w.resourceVersion,
}
}
return result, nil
}
if resourceVersion < oldest-1 {
return nil, errors.NewGone(fmt.Sprintf("too old resource version: %d (%d)", resourceVersion, oldest-1))
}
// Binary search the smallest index at which resourceVersion is greater than the given one.
f := func(i int) bool {
return w.cache[(w.startIndex+i)%w.capacity].resourceVersion > resourceVersion
}
first := sort.Search(size, f)
result := make([]watchCacheEvent, size-first)
for i := 0; i < size-first; i++ {
result[i] = w.cache[(w.startIndex+first+i)%w.capacity].watchCacheEvent
}
return result, nil
}
...
// NewGone returns an error indicating the item no longer available at the server and no forwarding address is known.
func NewGone(message string) *StatusError {
return &StatusError{unversioned.Status{
Status: unversioned.StatusFailure,
Code: http.StatusGone,
Reason: unversioned.StatusReasonGone,
Message: message,
}}
}
...
// StatusError is an error intended for consumption by a REST API server; it can also be
// reconstructed by clients from a REST response. Public to allow easy type switches.
type StatusError struct {
ErrStatus unversioned.Status
}
// Status is a return value for calls that don't return other objects.
type Status struct {
TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// Standard list metadata.
// More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
// +optional
ListMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// Status of the operation.
// One of: "Success" or "Failure".
// More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
// +optional
Status string `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=status"`
// A human-readable description of the status of this operation.
// +optional
Message string `json:"message,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=message"`
// A machine-readable description of why this operation is in the
// "Failure" status. If this value is empty there
// is no information available. A Reason clarifies an HTTP status
// code but does not override it.
// +optional
Reason StatusReason `json:"reason,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=reason,casttype=StatusReason"`
// Extended data associated with the reason. Each reason may define its
// own extended details. This field is optional and the data returned
// is not guaranteed to conform to any schema except that defined by
// the reason type.
// +optional
Details *StatusDetails `json:"details,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=details"`
// Suggested HTTP return code for this status, 0 if not set.
// +optional
Code int32 `json:"code,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,6,opt,name=code"`
}
从上述k8s watch代码可以看出ERROR Action是watch失败时产生的
- step4: 删除Pod
删除test_dns Pod,如下:
#kubectl delete pods/dns-test
watch 如下:
{"type":"MODIFIED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"72018227","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","deletionTimestamp":"2017-12-13T08:03:16Z","deletionGracePeriodSeconds":30},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Running","conditions":[{"type":"Initialized","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},{"type":"Ready","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T07:41:10Z"},{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}],"hostIP":"x.x.x.x","podIP":"192.168.22.112","startTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","containerStatuses":[{"name":"dns-test","state":{"running":{"startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:10Z"}},"lastState":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:22:15Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:08Z","containerID":"docker://b09320c3cad07d42f7fa0d6409777c6777447b287dddd30699c455f2b7fbea27"}},"ready":true,"restartCount":2,"image":"centos:6","imageID":"docker://sha256:38255ae1ae4375616b659950294364918d8079bb352dcf858d5053c7223b5e3e","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}],"cpuSet":"7"}}}
{"type":"MODIFIED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"72018272","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","deletionTimestamp":"2017-12-13T08:03:16Z","deletionGracePeriodSeconds":30},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Running","conditions":[{"type":"Initialized","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},{"type":"Ready","status":"False","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T08:03:17Z","reason":"ContainersNotReady","message":"containers with unready status: [dns-test]"},{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}],"hostIP":"x.x.x.x","startTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","containerStatuses":[{"name":"dns-test","state":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:10Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T08:03:16Z","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}},"lastState":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:22:15Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:08Z","containerID":"docker://b09320c3cad07d42f7fa0d6409777c6777447b287dddd30699c455f2b7fbea27"}},"ready":false,"restartCount":2,"image":"centos:6","imageID":"docker://sha256:38255ae1ae4375616b659950294364918d8079bb352dcf858d5053c7223b5e3e","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}],"cpuSet":"7"}}}
{"type":"MODIFIED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"72018273","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","deletionTimestamp":"2017-12-13T08:02:46Z","deletionGracePeriodSeconds":0},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Running","conditions":[{"type":"Initialized","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},{"type":"Ready","status":"False","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T08:03:17Z","reason":"ContainersNotReady","message":"containers with unready status: [dns-test]"},{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}],"hostIP":"x.x.x.x","startTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","containerStatuses":[{"name":"dns-test","state":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:10Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T08:03:16Z","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}},"lastState":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:22:15Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:08Z","containerID":"docker://b09320c3cad07d42f7fa0d6409777c6777447b287dddd30699c455f2b7fbea27"}},"ready":false,"restartCount":2,"image":"centos:6","imageID":"docker://sha256:38255ae1ae4375616b659950294364918d8079bb352dcf858d5053c7223b5e3e","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}],"cpuSet":"7"}}}
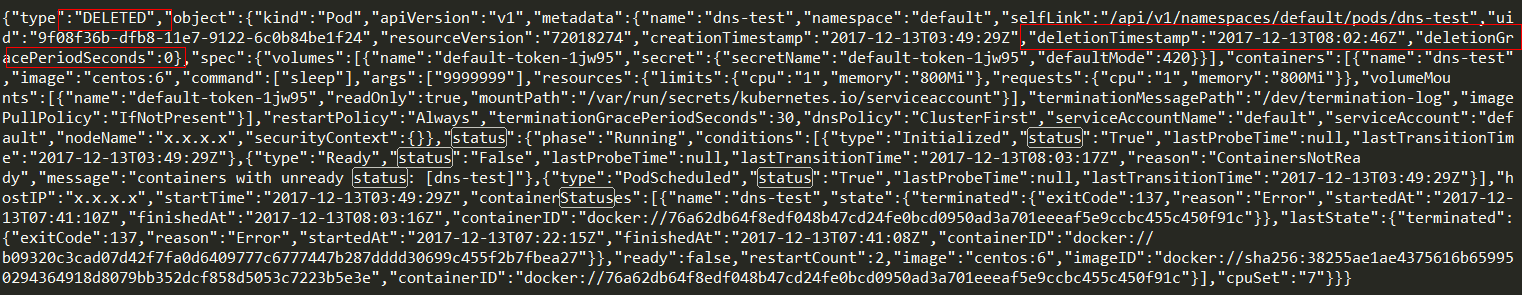
{"type":"DELETED","object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1","metadata":{"name":"dns-test","namespace":"default","selfLink":"/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/dns-test","uid":"9f08f36b-dfb8-11e7-9122-6c0b84be1f24","resourceVersion":"72018274","creationTimestamp":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","deletionTimestamp":"2017-12-13T08:02:46Z","deletionGracePeriodSeconds":0},"spec":{"volumes":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","secret":{"secretName":"default-token-1jw95","defaultMode":420}}],"containers":[{"name":"dns-test","image":"centos:6","command":["sleep"],"args":["9999999"],"resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"1","memory":"800Mi"}},"volumeMounts":[{"name":"default-token-1jw95","readOnly":true,"mountPath":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"}],"terminationMessagePath":"/dev/termination-log","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent"}],"restartPolicy":"Always","terminationGracePeriodSeconds":30,"dnsPolicy":"ClusterFirst","serviceAccountName":"default","serviceAccount":"default","nodeName":"x.x.x.x","securityContext":{}},"status":{"phase":"Running","conditions":[{"type":"Initialized","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"},{"type":"Ready","status":"False","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T08:03:17Z","reason":"ContainersNotReady","message":"containers with unready status: [dns-test]"},{"type":"PodScheduled","status":"True","lastProbeTime":null,"lastTransitionTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z"}],"hostIP":"x.x.x.x","startTime":"2017-12-13T03:49:29Z","containerStatuses":[{"name":"dns-test","state":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:10Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T08:03:16Z","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}},"lastState":{"terminated":{"exitCode":137,"reason":"Error","startedAt":"2017-12-13T07:22:15Z","finishedAt":"2017-12-13T07:41:08Z","containerID":"docker://b09320c3cad07d42f7fa0d6409777c6777447b287dddd30699c455f2b7fbea27"}},"ready":false,"restartCount":2,"image":"centos:6","imageID":"docker://sha256:38255ae1ae4375616b659950294364918d8079bb352dcf858d5053c7223b5e3e","containerID":"docker://76a62db64f8edf048b47cd24fe0bcd0950ad3a701eeeaf5e9ccbc455c450f91c"}],"cpuSet":"7"}}}
总结如下:
ADDED:向k8s master发出了Pod创建请求,但是还没有分配nodeName和hostIP

MODIFIED:k8s scheduler从etcd中获取了该请求,并为该Pod分配nodeName和hostIP,之后kubelet从etcd中获取请求,在相应IP上启动相应container,注意这是一个持续的过程,会不断有MODIFIED Action
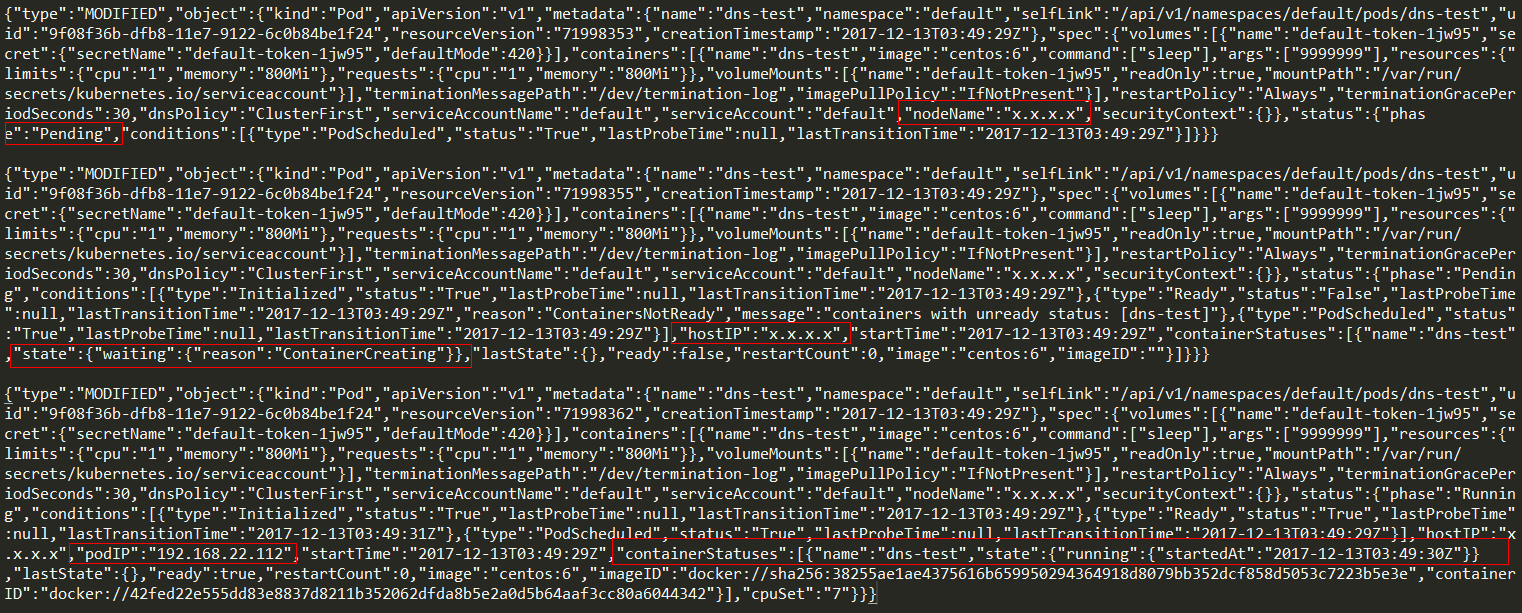
ERROR:执行watch失败
DELETED:Pod从集群中被删除了
// DeletionTimestamp is RFC 3339 date and time at which this resource will be deleted. This
// field is set by the server when a graceful deletion is requested by the user, and is not
// directly settable by a client. The resource is expected to be deleted (no longer visible
// from resource lists, and not reachable by name) after the time in this field. Once set,
// this value may not be unset or be set further into the future, although it may be shortened
// or the resource may be deleted prior to this time. For example, a user may request that
// a pod is deleted in 30 seconds. The Kubelet will react by sending a graceful termination
// signal to the containers in the pod. After that 30 seconds, the Kubelet will send a hard
// termination signal (SIGKILL) to the container and after cleanup, remove the pod from the
// API. In the presence of network partitions, this object may still exist after this
// timestamp, until an administrator or automated process can determine the resource is
// fully terminated.
// If not set, graceful deletion of the object has not been requested.
//
// Populated by the system when a graceful deletion is requested.
// Read-only.
// More info: http://releases.k8s.io/HEAD/docs/devel/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
DeletionTimestamp *unversioned.Time `json:"deletionTimestamp,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,9,opt,name=deletionTimestamp"`
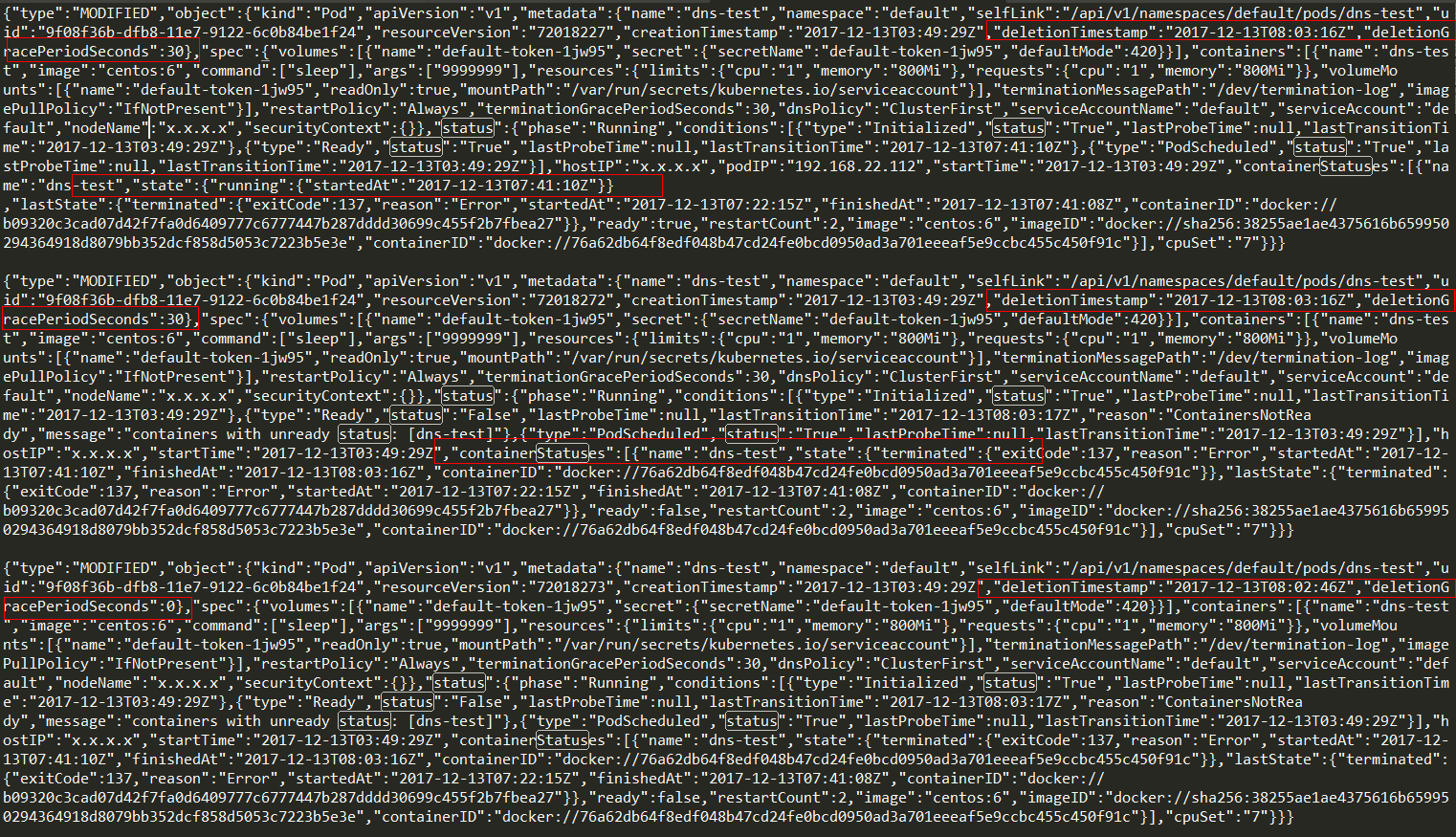
回到eventReceived函数,如下:
// Indexed by executor IP addrs and guarded by EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK
private val executorPodsByIPs = new mutable.HashMap[String, Pod]
def getExecutorPodByIP(podIP: String): Option[Pod] = {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs.get(podIP)
}
}
...
override def eventReceived(action: Action, pod: Pod): Unit = {
if (action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Running"
&& pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null) {
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
val clusterNodeName = pod.getSpec.getNodeName
logDebug(s"Executor pod $pod ready, launched at $clusterNodeName as IP $podIP.")
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs += ((podIP, pod))
}
} else if ((action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp != null) ||
action == Action.DELETED || action == Action.ERROR) {
val podName = pod.getMetadata.getName
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
logDebug(s"Executor pod $podName at IP $podIP was at $action.")
if (podIP != null) {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs -= podIP
}
}
if (action == Action.ERROR) {
logInfo(s"Received pod $podName exited event. Reason: " + pod.getStatus.getReason)
handleErroredPod(pod)
} else if (action == Action.DELETED) {
logInfo(s"Received delete pod $podName event. Reason: " + pod.getStatus.getReason)
handleDeletedPod(pod)
}
}
}
修改前eventReceived如下:
private class ExecutorPodsWatcher extends Watcher[Pod] {
override def eventReceived(action: Action, pod: Pod): Unit = {
if (action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Running"
&& pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null) {
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
val clusterNodeName = pod.getSpec.getNodeName
logDebug(s"Executor pod $pod ready, launched at $clusterNodeName as IP $podIP.")
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs += ((podIP, pod))
}
} else if ((action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp != null) ||
action == Action.DELETED || action == Action.ERROR) {
val podName = pod.getMetadata.getName
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
logDebug(s"Executor pod $podName at IP $podIP was at $action.")
if (podIP != null) {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs -= podIP
}
}
}
}
override def onClose(cause: KubernetesClientException): Unit = {
logDebug("Executor pod watch closed.", cause)
}
}
修改前后相同处理逻辑(same)如下:
- 1、如果watch到action为
MODIFIED且Pod状态(pod.getStatus.getPhase)为Running,同时Pod没有被删除pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null,则认为Pod成功产生了,取该Pod信息添加到executorPodsByIPs(PodIP,Pod) - 2、如果watch到action为
MODIFIED且Pod没有被删除pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null,或者action为DELETE或者action为ERROR,则从executorPodsByIPs中剔除该Pod:executorPodsByIPs -= podIP
修改后新增处理逻辑(added)如下:
- 1、如果watch到action为
ERROR则单独调用handleErroredPod(pod)进行处理 - 2、如果watch到action为
DELETE则单独调用handleDeletedPod(pod)进行处理
分析到这里,有一些疑问:
- 1、正常Pod产生错误,Pod状态(
pod.getStatus.getPhase)为Failed,这在上述中不会得到处理 - 2、有一些处理函数的作用以及它们之间的联系没搞清楚:
doKillExecutors、removeExecutor以及新添加的onDisconnected?
保留疑问,我们先按照改进方案逻辑 分析action为ERROR or DELETE的情况:
1、如果watch到action为ERROR则单独调用handleErroredPod(pod)进行处理,如下:
def handleErroredPod(pod: Pod): Unit = {
val containerExitStatus = getExecutorExitStatus(pod)
// container was probably actively killed by the driver.
val exitReason = if (isPodAlreadyReleased(pod)) {
ExecutorExited(containerExitStatus, exitCausedByApp = false,
s"Container in pod " + pod.getMetadata.getName +
" exited from explicit termination request.")
} else {
val containerExitReason = containerExitStatus match {
case VMEM_EXCEEDED_EXIT_CODE | PMEM_EXCEEDED_EXIT_CODE =>
memLimitExceededLogMessage(pod.getStatus.getReason)
case _ =>
// Here we can't be sure that that exit was caused by the application but this seems
// to be the right default since we know the pod was not explicitly deleted by
// the user.
s"Pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName}'s executor container exited with exit status" +
s" code $containerExitStatus."
}
ExecutorExited(containerExitStatus, exitCausedByApp = true, containerExitReason)
}
podsWithKnownExitReasons.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, exitReason)
}
首先调用getExecutorExitStatus获取Pod退出码,如下:
private val DEFAULT_CONTAINER_FAILURE_EXIT_STATUS = -1
def getExecutorExitStatus(pod: Pod): Int = {
val containerStatuses = pod.getStatus.getContainerStatuses
if (!containerStatuses.isEmpty) {
// we assume the first container represents the pod status. This assumption may not hold
// true in the future. Revisit this if side-car containers start running inside executor
// pods.
getExecutorExitStatus(containerStatuses.get(0))
} else DEFAULT_CONTAINER_FAILURE_EXIT_STATUS
}
def getExecutorExitStatus(containerStatus: ContainerStatus): Int = {
Option(containerStatus.getState).map(containerState =>
Option(containerState.getTerminated).map(containerStateTerminated =>
containerStateTerminated.getExitCode.intValue()).getOrElse(UNKNOWN_EXIT_CODE)
).getOrElse(UNKNOWN_EXIT_CODE)
}
对应Pod containerStatuses 结构如下:
"containerStatuses": [
{
"containerID": "docker://682c611be906064fb5e9a419c9f45f683f6c9cf90f496944da8c4423eb4c9e25",
"image": "centos:6",
"imageID": "docker://sha256:38255ae1ae4375616b659950294364918d8079bb352dcf858d5053c7223b5e3e",
"lastState": {},
"name": "dns-test2",
"ready": false,
"restartCount": 0,
"state": {
"terminated": {
"containerID": "docker://682c611be906064fb5e9a419c9f45f683f6c9cf90f496944da8c4423eb4c9e25",
"exitCode": 137,
"finishedAt": "2017-12-13T07:54:16Z",
"reason": "Error",
"startedAt": "2017-12-13T07:51:11Z"
}
}
}
]
接着根据isPodAlreadyReleased(pod)构造ExecutorExited返回,isPodAlreadyReleased如下:
def isPodAlreadyReleased(pod: Pod): Boolean = {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
!runningPodsToExecutors.contains(pod.getMetadata.getName)
}
}
def handleErroredPod(pod: Pod): Unit = {
val containerExitStatus = getExecutorExitStatus(pod)
// container was probably actively killed by the driver.
val exitReason = if (isPodAlreadyReleased(pod)) {
ExecutorExited(containerExitStatus, exitCausedByApp = false,
s"Container in pod " + pod.getMetadata.getName +
" exited from explicit termination request.")
} else {
val containerExitReason = containerExitStatus match {
case VMEM_EXCEEDED_EXIT_CODE | PMEM_EXCEEDED_EXIT_CODE =>
memLimitExceededLogMessage(pod.getStatus.getReason)
case _ =>
// Here we can't be sure that that exit was caused by the application but this seems
// to be the right default since we know the pod was not explicitly deleted by
// the user.
s"Pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName}'s executor container exited with exit status" +
s" code $containerExitStatus."
}
ExecutorExited(containerExitStatus, exitCausedByApp = true, containerExitReason)
}
podsWithKnownExitReasons.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, exitReason)
}
private val podsWithKnownExitReasons: concurrent.Map[String, ExecutorExited] =
new ConcurrentHashMap[String, ExecutorExited]().asScala
private[spark]
case class ExecutorExited(exitCode: Int, exitCausedByApp: Boolean, reason: String)
extends ExecutorLossReason(reason)
private[spark] object ExecutorExited {
def apply(exitCode: Int, exitCausedByApp: Boolean): ExecutorExited = {
ExecutorExited(
exitCode,
exitCausedByApp,
ExecutorExitCode.explainExitCode(exitCode))
}
}
判断runningPodsToExecutors(executorName,executorId)中是否不包含该Pod。如果不包含该Pod,则认为exited from explicit termination request;否则认为:pod was not explicitly deleted
这里不明白什么意思???
最后将ExecutorExited添加到podsWithKnownExitReasons(executorName,ExecutorExited)
2、如果watch到action为DELETE则单独调用handleDeletedPod(pod)进行处理,如下:
def handleDeletedPod(pod: Pod): Unit = {
val exitMessage = if (isPodAlreadyReleased(pod)) {
s"Container in pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName} exited from explicit termination request."
} else {
s"Pod ${pod.getMetadata.getName} deleted or lost."
}
val exitReason = ExecutorExited(
getExecutorExitStatus(pod), exitCausedByApp = false, exitMessage)
podsWithKnownExitReasons.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, exitReason)
}
这里和handleErroredPod处理逻辑类似,也是:判断runningPodsToExecutors(executorName,executorId)中是否不包含该Pod。如果不包含该Pod,则认为exited from explicit termination request;否则认为:pod was not explicitly deleted
不同点是将exitCausedByApp统一设置为false,why???
重新理一下思路,有几个问题:
1、disassociated executor到底怎么发现的?
是通过onDisconnected进行发现的:
override def createDriverEndpoint(properties: Seq[(String, String)]): DriverEndpoint = {
new KubernetesDriverEndpoint(rpcEnv, properties)
}
private class KubernetesDriverEndpoint(
rpcEnv: RpcEnv,
sparkProperties: Seq[(String, String)])
extends DriverEndpoint(rpcEnv, sparkProperties) {
private val externalShufflePort = conf.getInt("spark.shuffle.service.port", 7337)
override def onDisconnected(rpcAddress: RpcAddress): Unit = {
addressToExecutorId.get(rpcAddress).foreach { executorId =>
if (disableExecutor(executorId)) {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
runningExecutorsToPods.get(executorId).foreach { pod =>
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval.put(executorId, pod)
logInfo(s"executor $executorId Disconnected")
}
}
}
}
}
override def receiveAndReply(
context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
new PartialFunction[Any, Unit]() {
override def isDefinedAt(msg: Any): Boolean = {
msg match {
case RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId) =>
Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(sc.conf)
case _ => false
}
}
override def apply(msg: Any): Unit = {
msg match {
case RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId) =>
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
var resolvedProperties = sparkProperties
val runningExecutorPod = kubernetesClient
.pods()
.withName(runningExecutorsToPods(executorId).getMetadata.getName)
.get()
val nodeName = runningExecutorPod.getSpec.getNodeName
val shufflePodIp = shufflePodCache.get.getShufflePodForExecutor(nodeName)
// Inform the shuffle pod about this application so it can watch.
kubernetesExternalShuffleClient.foreach(
_.registerDriverWithShuffleService(shufflePodIp, externalShufflePort))
resolvedProperties = resolvedProperties ++ Seq(
(SPARK_SHUFFLE_SERVICE_HOST.key, shufflePodIp))
val reply = SparkAppConfig(
resolvedProperties,
SparkEnv.get.securityManager.getIOEncryptionKey())
context.reply(reply)
}
}
}
}.orElse(super.receiveAndReply(context))
}
}
消息处理逻辑???
由SparkContext实例初始化:_env = createSparkEnv(_conf, isLocal, listenerBus):
try {
_conf = config.clone()
_conf.validateSettings()
if (!_conf.contains("spark.master")) {
throw new SparkException("A master URL must be set in your configuration")
}
if (!_conf.contains("spark.app.name")) {
throw new SparkException("An application name must be set in your configuration")
}
// System property spark.yarn.app.id must be set if user code ran by AM on a YARN cluster
if (master == "yarn" && deployMode == "cluster" && !_conf.contains("spark.yarn.app.id")) {
throw new SparkException("Detected yarn cluster mode, but isn't running on a cluster. " +
"Deployment to YARN is not supported directly by SparkContext. Please use spark-submit.")
}
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.logConf", false)) {
logInfo("Spark configuration:\n" + _conf.toDebugString)
}
// Set Spark driver host and port system properties. This explicitly sets the configuration
// instead of relying on the default value of the config constant.
_conf.set(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS, _conf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS))
_conf.setIfMissing("spark.driver.port", "0")
_conf.set("spark.executor.id", SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER)
_jars = Utils.getUserJars(_conf)
_files = _conf.getOption("spark.files").map(_.split(",")).map(_.filter(_.nonEmpty))
.toSeq.flatten
_eventLogDir =
if (isEventLogEnabled) {
val unresolvedDir = conf.get("spark.eventLog.dir", EventLoggingListener.DEFAULT_LOG_DIR)
.stripSuffix("/")
Some(Utils.resolveURI(unresolvedDir))
} else {
None
}
_eventLogCodec = {
val compress = _conf.getBoolean("spark.eventLog.compress", false)
if (compress && isEventLogEnabled) {
Some(CompressionCodec.getCodecName(_conf)).map(CompressionCodec.getShortName)
} else {
None
}
}
if (master == "yarn" && deployMode == "client") System.setProperty("SPARK_YARN_MODE", "true")
// "_jobProgressListener" should be set up before creating SparkEnv because when creating
// "SparkEnv", some messages will be posted to "listenerBus" and we should not miss them.
_jobProgressListener = new JobProgressListener(_conf)
listenerBus.addListener(jobProgressListener)
// Create the Spark execution environment (cache, map output tracker, etc)
_env = createSparkEnv(_conf, isLocal, listenerBus)
SparkEnv.set(_env)
// If running the REPL, register the repl's output dir with the file server.
_conf.getOption("spark.repl.class.outputDir").foreach { path =>
val replUri = _env.rpcEnv.fileServer.addDirectory("/classes", new File(path))
_conf.set("spark.repl.class.uri", replUri)
}
_statusTracker = new SparkStatusTracker(this)
_progressBar =
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.showConsoleProgress", true) && !log.isInfoEnabled) {
Some(new ConsoleProgressBar(this))
} else {
None
}
_ui =
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.enabled", true)) {
Some(SparkUI.createLiveUI(this, _conf, listenerBus, _jobProgressListener,
_env.securityManager, appName, startTime = startTime))
} else {
// For tests, do not enable the UI
None
}
// Bind the UI before starting the task scheduler to communicate
// the bound port to the cluster manager properly
_ui.foreach(_.bind())
_hadoopConfiguration = SparkHadoopUtil.get.newConfiguration(_conf)
// Add each JAR given through the constructor
if (jars != null) {
jars.foreach(addJar)
}
if (files != null) {
files.foreach(addFile)
}
_executorMemory = _conf.getOption("spark.executor.memory")
.orElse(Option(System.getenv("SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY")))
.orElse(Option(System.getenv("SPARK_MEM"))
.map(warnSparkMem))
.map(Utils.memoryStringToMb)
.getOrElse(1024)
// Convert java options to env vars as a work around
// since we can't set env vars directly in sbt.
for { (envKey, propKey) <- Seq(("SPARK_TESTING", "spark.testing"))
value <- Option(System.getenv(envKey)).orElse(Option(System.getProperty(propKey)))} {
executorEnvs(envKey) = value
}
Option(System.getenv("SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES")).foreach { v =>
executorEnvs("SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES") = v
}
// The Mesos scheduler backend relies on this environment variable to set executor memory.
// TODO: Set this only in the Mesos scheduler.
executorEnvs("SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY") = executorMemory + "m"
executorEnvs ++= _conf.getExecutorEnv
executorEnvs("SPARK_USER") = sparkUser
// We need to register "HeartbeatReceiver" before "createTaskScheduler" because Executor will
// retrieve "HeartbeatReceiver" in the constructor. (SPARK-6640)
_heartbeatReceiver = env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(
HeartbeatReceiver.ENDPOINT_NAME, new HeartbeatReceiver(this))
// Create and start the scheduler
val (sched, ts) = SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master, deployMode)
_schedulerBackend = sched
_taskScheduler = ts
_dagScheduler = new DAGScheduler(this)
_heartbeatReceiver.ask[Boolean](TaskSchedulerIsSet)
// start TaskScheduler after taskScheduler sets DAGScheduler reference in DAGScheduler's
// constructor
_taskScheduler.start()
_applicationId = _taskScheduler.applicationId()
_applicationAttemptId = taskScheduler.applicationAttemptId()
_conf.set("spark.app.id", _applicationId)
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.reverseProxy", false)) {
System.setProperty("spark.ui.proxyBase", "/proxy/" + _applicationId)
}
_ui.foreach(_.setAppId(_applicationId))
_env.blockManager.initialize(_applicationId)
// The metrics system for Driver need to be set spark.app.id to app ID.
// So it should start after we get app ID from the task scheduler and set spark.app.id.
_env.metricsSystem.start()
// Attach the driver metrics servlet handler to the web ui after the metrics system is started.
_env.metricsSystem.getServletHandlers.foreach(handler => ui.foreach(_.attachHandler(handler)))
_eventLogger =
if (isEventLogEnabled) {
val logger =
new EventLoggingListener(_applicationId, _applicationAttemptId, _eventLogDir.get,
_conf, _hadoopConfiguration)
logger.start()
listenerBus.addListener(logger)
Some(logger)
} else {
None
}
// Optionally scale number of executors dynamically based on workload. Exposed for testing.
val dynamicAllocationEnabled = Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(_conf)
_executorAllocationManager =
if (dynamicAllocationEnabled) {
schedulerBackend match {
case b: ExecutorAllocationClient =>
Some(new ExecutorAllocationManager(
schedulerBackend.asInstanceOf[ExecutorAllocationClient], listenerBus, _conf))
case _ =>
None
}
} else {
None
}
_executorAllocationManager.foreach(_.start())
_cleaner =
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.cleaner.referenceTracking", true)) {
Some(new ContextCleaner(this))
} else {
None
}
_cleaner.foreach(_.start())
setupAndStartListenerBus()
postEnvironmentUpdate()
postApplicationStart()
// Post init
_taskScheduler.postStartHook()
_env.metricsSystem.registerSource(_dagScheduler.metricsSource)
_env.metricsSystem.registerSource(new BlockManagerSource(_env.blockManager))
_executorAllocationManager.foreach { e =>
_env.metricsSystem.registerSource(e.executorAllocationManagerSource)
}
// Make sure the context is stopped if the user forgets about it. This avoids leaving
// unfinished event logs around after the JVM exits cleanly. It doesn't help if the JVM
// is killed, though.
logDebug("Adding shutdown hook") // force eager creation of logger
_shutdownHookRef = ShutdownHookManager.addShutdownHook(
ShutdownHookManager.SPARK_CONTEXT_SHUTDOWN_PRIORITY) { () =>
logInfo("Invoking stop() from shutdown hook")
stop()
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
logError("Error initializing SparkContext.", e)
try {
stop()
} catch {
case NonFatal(inner) =>
logError("Error stopping SparkContext after init error.", inner)
} finally {
throw e
}
}
createSparkEnv如下:
// This function allows components created by SparkEnv to be mocked in unit tests:
private[spark] def createSparkEnv(
conf: SparkConf,
isLocal: Boolean,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus): SparkEnv = {
SparkEnv.createDriverEnv(conf, isLocal, listenerBus, SparkContext.numDriverCores(master))
}
createDriverEnv如下:
/**
* Create a SparkEnv for the driver.
*/
private[spark] def createDriverEnv(
conf: SparkConf,
isLocal: Boolean,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus,
numCores: Int,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnv = {
assert(conf.contains(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS),
s"${DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS.key} is not set on the driver!")
assert(conf.contains("spark.driver.port"), "spark.driver.port is not set on the driver!")
val bindAddress = conf.get(DRIVER_BIND_ADDRESS)
val advertiseAddress = conf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS)
val port = conf.get("spark.driver.port").toInt
val ioEncryptionKey = if (conf.get(IO_ENCRYPTION_ENABLED)) {
Some(CryptoStreamUtils.createKey(conf))
} else {
None
}
create(
conf,
SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER,
bindAddress,
advertiseAddress,
port,
isLocal,
numCores,
ioEncryptionKey,
listenerBus = listenerBus,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator = mockOutputCommitCoordinator
)
}
create函数如下:
/**
* Helper method to create a SparkEnv for a driver or an executor.
*/
private def create(
conf: SparkConf,
executorId: String,
bindAddress: String,
advertiseAddress: String,
port: Int,
isLocal: Boolean,
numUsableCores: Int,
ioEncryptionKey: Option[Array[Byte]],
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus = null,
mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnv = {
val isDriver = executorId == SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER
// Listener bus is only used on the driver
if (isDriver) {
assert(listenerBus != null, "Attempted to create driver SparkEnv with null listener bus!")
}
val securityManager = new SecurityManager(conf, ioEncryptionKey)
ioEncryptionKey.foreach { _ =>
if (!securityManager.isSaslEncryptionEnabled()) {
logWarning("I/O encryption enabled without RPC encryption: keys will be visible on the " +
"wire.")
}
}
val systemName = if (isDriver) driverSystemName else executorSystemName
val rpcEnv = RpcEnv.create(systemName, bindAddress, advertiseAddress, port, conf,
securityManager, clientMode = !isDriver)
// Figure out which port RpcEnv actually bound to in case the original port is 0 or occupied.
// In the non-driver case, the RPC env's address may be null since it may not be listening
// for incoming connections.
if (isDriver) {
conf.set("spark.driver.port", rpcEnv.address.port.toString)
} else if (rpcEnv.address != null) {
conf.set("spark.executor.port", rpcEnv.address.port.toString)
logInfo(s"Setting spark.executor.port to: ${rpcEnv.address.port.toString}")
}
// Create an instance of the class with the given name, possibly initializing it with our conf
def instantiateClass[T](className: String): T = {
val cls = Utils.classForName(className)
// Look for a constructor taking a SparkConf and a boolean isDriver, then one taking just
// SparkConf, then one taking no arguments
try {
cls.getConstructor(classOf[SparkConf], java.lang.Boolean.TYPE)
.newInstance(conf, new java.lang.Boolean(isDriver))
.asInstanceOf[T]
} catch {
case _: NoSuchMethodException =>
try {
cls.getConstructor(classOf[SparkConf]).newInstance(conf).asInstanceOf[T]
} catch {
case _: NoSuchMethodException =>
cls.getConstructor().newInstance().asInstanceOf[T]
}
}
}
// Create an instance of the class named by the given SparkConf property, or defaultClassName
// if the property is not set, possibly initializing it with our conf
def instantiateClassFromConf[T](propertyName: String, defaultClassName: String): T = {
instantiateClass[T](conf.get(propertyName, defaultClassName))
}
val serializer = instantiateClassFromConf[Serializer](
"spark.serializer", "org.apache.spark.serializer.JavaSerializer")
logDebug(s"Using serializer: ${serializer.getClass}")
val serializerManager = new SerializerManager(serializer, conf, ioEncryptionKey)
val closureSerializer = new JavaSerializer(conf)
def registerOrLookupEndpoint(
name: String, endpointCreator: => RpcEndpoint):
RpcEndpointRef = {
if (isDriver) {
logInfo("Registering " + name)
rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(name, endpointCreator)
} else {
RpcUtils.makeDriverRef(name, conf, rpcEnv)
}
}
val broadcastManager = new BroadcastManager(isDriver, conf, securityManager)
val mapOutputTracker = if (isDriver) {
new MapOutputTrackerMaster(conf, broadcastManager, isLocal)
} else {
new MapOutputTrackerWorker(conf)
}
// Have to assign trackerEndpoint after initialization as MapOutputTrackerEndpoint
// requires the MapOutputTracker itself
mapOutputTracker.trackerEndpoint = registerOrLookupEndpoint(MapOutputTracker.ENDPOINT_NAME,
new MapOutputTrackerMasterEndpoint(
rpcEnv, mapOutputTracker.asInstanceOf[MapOutputTrackerMaster], conf))
// Let the user specify short names for shuffle managers
val shortShuffleMgrNames = Map(
"sort" -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName,
"tungsten-sort" -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName)
val shuffleMgrName = conf.get("spark.shuffle.manager", "sort")
val shuffleMgrClass = shortShuffleMgrNames.getOrElse(shuffleMgrName.toLowerCase, shuffleMgrName)
val shuffleManager = instantiateClass[ShuffleManager](shuffleMgrClass)
val useLegacyMemoryManager = conf.getBoolean("spark.memory.useLegacyMode", false)
val memoryManager: MemoryManager =
if (useLegacyMemoryManager) {
new StaticMemoryManager(conf, numUsableCores)
} else {
UnifiedMemoryManager(conf, numUsableCores)
}
val blockManagerPort = if (isDriver) {
conf.get(DRIVER_BLOCK_MANAGER_PORT)
} else {
conf.get(BLOCK_MANAGER_PORT)
}
val blockTransferService =
new NettyBlockTransferService(conf, securityManager, bindAddress, advertiseAddress,
blockManagerPort, numUsableCores)
val blockManagerMaster = new BlockManagerMaster(registerOrLookupEndpoint(
BlockManagerMaster.DRIVER_ENDPOINT_NAME,
new BlockManagerMasterEndpoint(rpcEnv, isLocal, conf, listenerBus)),
conf, isDriver)
// NB: blockManager is not valid until initialize() is called later.
val blockManager = new BlockManager(executorId, rpcEnv, blockManagerMaster,
serializerManager, conf, memoryManager, mapOutputTracker, shuffleManager,
blockTransferService, securityManager, numUsableCores)
val metricsSystem = if (isDriver) {
// Don't start metrics system right now for Driver.
// We need to wait for the task scheduler to give us an app ID.
// Then we can start the metrics system.
MetricsSystem.createMetricsSystem("driver", conf, securityManager)
} else {
// We need to set the executor ID before the MetricsSystem is created because sources and
// sinks specified in the metrics configuration file will want to incorporate this executor's
// ID into the metrics they report.
conf.set("spark.executor.id", executorId)
val ms = MetricsSystem.createMetricsSystem("executor", conf, securityManager)
ms.start()
ms
}
val outputCommitCoordinator = mockOutputCommitCoordinator.getOrElse {
new OutputCommitCoordinator(conf, isDriver)
}
val outputCommitCoordinatorRef = registerOrLookupEndpoint("OutputCommitCoordinator",
new OutputCommitCoordinatorEndpoint(rpcEnv, outputCommitCoordinator))
outputCommitCoordinator.coordinatorRef = Some(outputCommitCoordinatorRef)
val envInstance = new SparkEnv(
executorId,
rpcEnv,
serializer,
closureSerializer,
serializerManager,
mapOutputTracker,
shuffleManager,
broadcastManager,
blockManager,
securityManager,
metricsSystem,
memoryManager,
outputCommitCoordinator,
conf)
// Add a reference to tmp dir created by driver, we will delete this tmp dir when stop() is
// called, and we only need to do it for driver. Because driver may run as a service, and if we
// don't delete this tmp dir when sc is stopped, then will create too many tmp dirs.
if (isDriver) {
val sparkFilesDir = Utils.createTempDir(Utils.getLocalDir(conf), "userFiles").getAbsolutePath
envInstance.driverTmpDir = Some(sparkFilesDir)
}
envInstance
}
RpcEnv.create如下:
val rpcEnv = RpcEnv.create(systemName, bindAddress, advertiseAddress, port, conf,
securityManager, clientMode = !isDriver)
/**
* A RpcEnv implementation must have a [[RpcEnvFactory]] implementation with an empty constructor
* so that it can be created via Reflection.
*/
private[spark] object RpcEnv {
def create(
name: String,
host: String,
port: Int,
conf: SparkConf,
securityManager: SecurityManager,
clientMode: Boolean = false): RpcEnv = {
create(name, host, host, port, conf, securityManager, clientMode)
}
def create(
name: String,
bindAddress: String,
advertiseAddress: String,
port: Int,
conf: SparkConf,
securityManager: SecurityManager,
clientMode: Boolean): RpcEnv = {
val config = RpcEnvConfig(conf, name, bindAddress, advertiseAddress, port, securityManager,
clientMode)
new NettyRpcEnvFactory().create(config)
}
}
private[rpc] class NettyRpcEnvFactory extends RpcEnvFactory with Logging {
def create(config: RpcEnvConfig): RpcEnv = {
val sparkConf = config.conf
// Use JavaSerializerInstance in multiple threads is safe. However, if we plan to support
// KryoSerializer in future, we have to use ThreadLocal to store SerializerInstance
val javaSerializerInstance =
new JavaSerializer(sparkConf).newInstance().asInstanceOf[JavaSerializerInstance]
val nettyEnv =
new NettyRpcEnv(sparkConf, javaSerializerInstance, config.advertiseAddress,
config.securityManager)
if (!config.clientMode) {
val startNettyRpcEnv: Int => (NettyRpcEnv, Int) = { actualPort =>
nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)
(nettyEnv, nettyEnv.address.port)
}
try {
Utils.startServiceOnPort(config.port, startNettyRpcEnv, sparkConf, config.name)._1
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
nettyEnv.shutdown()
throw e
}
}
nettyEnv
}
}
val nettyEnv = new NettyRpcEnv(sparkConf, javaSerializerInstance, config.advertiseAddress, config.securityManager)如下:
private[netty] class NettyRpcEnv(
val conf: SparkConf,
javaSerializerInstance: JavaSerializerInstance,
host: String,
securityManager: SecurityManager) extends RpcEnv(conf) with Logging {
private[netty] val transportConf = SparkTransportConf.fromSparkConf(
conf.clone.set("spark.rpc.io.numConnectionsPerPeer", "1"),
"rpc",
conf.getInt("spark.rpc.io.threads", 0))
private val dispatcher: Dispatcher = new Dispatcher(this)
...
}
Dispatcher如下:
/**
* A message dispatcher, responsible for routing RPC messages to the appropriate endpoint(s).
*/
private[netty] class Dispatcher(nettyEnv: NettyRpcEnv) extends Logging {
private class EndpointData(
val name: String,
val endpoint: RpcEndpoint,
val ref: NettyRpcEndpointRef) {
val inbox = new Inbox(ref, endpoint)
}
private val endpoints: ConcurrentMap[String, EndpointData] =
new ConcurrentHashMap[String, EndpointData]
private val endpointRefs: ConcurrentMap[RpcEndpoint, RpcEndpointRef] =
new ConcurrentHashMap[RpcEndpoint, RpcEndpointRef]
// Track the receivers whose inboxes may contain messages.
private val receivers = new LinkedBlockingQueue[EndpointData]
/**
* True if the dispatcher has been stopped. Once stopped, all messages posted will be bounced
* immediately.
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
private var stopped = false
def registerRpcEndpoint(name: String, endpoint: RpcEndpoint): NettyRpcEndpointRef = {
val addr = RpcEndpointAddress(nettyEnv.address, name)
val endpointRef = new NettyRpcEndpointRef(nettyEnv.conf, addr, nettyEnv)
synchronized {
if (stopped) {
throw new IllegalStateException("RpcEnv has been stopped")
}
if (endpoints.putIfAbsent(name, new EndpointData(name, endpoint, endpointRef)) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"There is already an RpcEndpoint called $name")
}
val data = endpoints.get(name)
endpointRefs.put(data.endpoint, data.ref)
receivers.offer(data) // for the OnStart message
}
endpointRef
}
def getRpcEndpointRef(endpoint: RpcEndpoint): RpcEndpointRef = endpointRefs.get(endpoint)
def removeRpcEndpointRef(endpoint: RpcEndpoint): Unit = endpointRefs.remove(endpoint)
// Should be idempotent
private def unregisterRpcEndpoint(name: String): Unit = {
val data = endpoints.remove(name)
if (data != null) {
data.inbox.stop()
receivers.offer(data) // for the OnStop message
}
// Don't clean `endpointRefs` here because it's possible that some messages are being processed
// now and they can use `getRpcEndpointRef`. So `endpointRefs` will be cleaned in Inbox via
// `removeRpcEndpointRef`.
}
def stop(rpcEndpointRef: RpcEndpointRef): Unit = {
synchronized {
if (stopped) {
// This endpoint will be stopped by Dispatcher.stop() method.
return
}
unregisterRpcEndpoint(rpcEndpointRef.name)
}
}
/**
* Send a message to all registered [[RpcEndpoint]]s in this process.
*
* This can be used to make network events known to all end points (e.g. "a new node connected").
*/
def postToAll(message: InboxMessage): Unit = {
val iter = endpoints.keySet().iterator()
while (iter.hasNext) {
val name = iter.next
postMessage(name, message, (e) => logWarning(s"Message $message dropped. ${e.getMessage}"))
}
}
/** Posts a message sent by a remote endpoint. */
def postRemoteMessage(message: RequestMessage, callback: RpcResponseCallback): Unit = {
val rpcCallContext =
new RemoteNettyRpcCallContext(nettyEnv, callback, message.senderAddress)
val rpcMessage = RpcMessage(message.senderAddress, message.content, rpcCallContext)
postMessage(message.receiver.name, rpcMessage, (e) => callback.onFailure(e))
}
/** Posts a message sent by a local endpoint. */
def postLocalMessage(message: RequestMessage, p: Promise[Any]): Unit = {
val rpcCallContext =
new LocalNettyRpcCallContext(message.senderAddress, p)
val rpcMessage = RpcMessage(message.senderAddress, message.content, rpcCallContext)
postMessage(message.receiver.name, rpcMessage, (e) => p.tryFailure(e))
}
/** Posts a one-way message. */
def postOneWayMessage(message: RequestMessage): Unit = {
postMessage(message.receiver.name, OneWayMessage(message.senderAddress, message.content),
(e) => throw e)
}
/**
* Posts a message to a specific endpoint.
*
* @param endpointName name of the endpoint.
* @param message the message to post
* @param callbackIfStopped callback function if the endpoint is stopped.
*/
private def postMessage(
endpointName: String,
message: InboxMessage,
callbackIfStopped: (Exception) => Unit): Unit = {
val error = synchronized {
val data = endpoints.get(endpointName)
if (stopped) {
Some(new RpcEnvStoppedException())
} else if (data == null) {
Some(new SparkException(s"Could not find $endpointName."))
} else {
data.inbox.post(message)
receivers.offer(data)
None
}
}
// We don't need to call `onStop` in the `synchronized` block
error.foreach(callbackIfStopped)
}
def stop(): Unit = {
synchronized {
if (stopped) {
return
}
stopped = true
}
// Stop all endpoints. This will queue all endpoints for processing by the message loops.
endpoints.keySet().asScala.foreach(unregisterRpcEndpoint)
// Enqueue a message that tells the message loops to stop.
receivers.offer(PoisonPill)
threadpool.shutdown()
}
def awaitTermination(): Unit = {
threadpool.awaitTermination(Long.MaxValue, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
/**
* Return if the endpoint exists
*/
def verify(name: String): Boolean = {
endpoints.containsKey(name)
}
/** Thread pool used for dispatching messages. */
private val threadpool: ThreadPoolExecutor = {
val numThreads = nettyEnv.conf.getInt("spark.rpc.netty.dispatcher.numThreads",
math.max(2, Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors()))
val pool = ThreadUtils.newDaemonFixedThreadPool(numThreads, "dispatcher-event-loop")
for (i <- 0 until numThreads) {
pool.execute(new MessageLoop)
}
pool
}
/** Message loop used for dispatching messages. */
private class MessageLoop extends Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (true) {
try {
val data = receivers.take()
if (data == PoisonPill) {
// Put PoisonPill back so that other MessageLoops can see it.
receivers.offer(PoisonPill)
return
}
data.inbox.process(Dispatcher.this)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) => logError(e.getMessage, e)
}
}
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // exit
}
}
}
/** A poison endpoint that indicates MessageLoop should exit its message loop. */
private val PoisonPill = new EndpointData(null, null, null)
}
MessageLoop如下:
/** Message loop used for dispatching messages. */
private class MessageLoop extends Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (true) {
try {
val data = receivers.take()
if (data == PoisonPill) {
// Put PoisonPill back so that other MessageLoops can see it.
receivers.offer(PoisonPill)
return
}
data.inbox.process(Dispatcher.this)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) => logError(e.getMessage, e)
}
}
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException => // exit
}
}
}
/**
* Process stored messages.
*/
def process(dispatcher: Dispatcher): Unit = {
var message: InboxMessage = null
inbox.synchronized {
if (!enableConcurrent && numActiveThreads != 0) {
return
}
message = messages.poll()
if (message != null) {
numActiveThreads += 1
} else {
return
}
}
while (true) {
safelyCall(endpoint) {
message match {
case RpcMessage(_sender, content, context) =>
try {
endpoint.receiveAndReply(context).applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>
throw new SparkException(s"Unsupported message $message from ${_sender}")
})
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
context.sendFailure(e)
// Throw the exception -- this exception will be caught by the safelyCall function.
// The endpoint's onError function will be called.
throw e
}
case OneWayMessage(_sender, content) =>
endpoint.receive.applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>
throw new SparkException(s"Unsupported message $message from ${_sender}")
})
case OnStart =>
endpoint.onStart()
if (!endpoint.isInstanceOf[ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint]) {
inbox.synchronized {
if (!stopped) {
enableConcurrent = true
}
}
}
case OnStop =>
val activeThreads = inbox.synchronized { inbox.numActiveThreads }
assert(activeThreads == 1,
s"There should be only a single active thread but found $activeThreads threads.")
dispatcher.removeRpcEndpointRef(endpoint)
endpoint.onStop()
assert(isEmpty, "OnStop should be the last message")
case RemoteProcessConnected(remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onConnected(remoteAddress)
case RemoteProcessDisconnected(remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onDisconnected(remoteAddress)
case RemoteProcessConnectionError(cause, remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onNetworkError(cause, remoteAddress)
}
}
inbox.synchronized {
// "enableConcurrent" will be set to false after `onStop` is called, so we should check it
// every time.
if (!enableConcurrent && numActiveThreads != 1) {
// If we are not the only one worker, exit
numActiveThreads -= 1
return
}
message = messages.poll()
if (message == null) {
numActiveThreads -= 1
return
}
}
}
}
回到onDisconnected函数,如下:
protected val addressToExecutorId = new HashMap[RpcAddress, String]
override def onDisconnected(rpcAddress: RpcAddress): Unit = {
addressToExecutorId.get(rpcAddress).foreach { executorId =>
if (disableExecutor(executorId)) {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
runningExecutorsToPods.get(executorId).foreach { pod =>
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval.put(executorId, pod)
logInfo(s"executor $executorId Disconnected")
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* Address for an RPC environment, with hostname and port.
*/
private[spark] case class RpcAddress(host: String, port: Int) {
def hostPort: String = host + ":" + port
/** Returns a string in the form of "spark://host:port". */
def toSparkURL: String = "spark://" + hostPort
override def toString: String = hostPort
}
/**
* Stop making resource offers for the given executor. The executor is marked as lost with
* the loss reason still pending.
*
* @return Whether executor should be disabled
*/
protected def disableExecutor(executorId: String): Boolean = {
val shouldDisable = CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
if (executorIsAlive(executorId)) {
executorsPendingLossReason += executorId
true
} else {
// Returns true for explicitly killed executors, we also need to get pending loss reasons;
// For others return false.
executorsPendingToRemove.contains(executorId)
}
}
if (shouldDisable) {
logInfo(s"Disabling executor $executorId.")
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, LossReasonPending)
}
shouldDisable
}
private def executorIsAlive(executorId: String): Boolean = synchronized {
!executorsPendingToRemove.contains(executorId) &&
!executorsPendingLossReason.contains(executorId)
}
// Executors we have requested the cluster manager to kill that have not died yet; maps
// the executor ID to whether it was explicitly killed by the driver (and thus shouldn't
// be considered an app-related failure).
@GuardedBy("CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this")
private val executorsPendingToRemove = new HashMap[String, Boolean]
// Executors that have been lost, but for which we don't yet know the real exit reason.
protected val executorsPendingLossReason = new HashSet[String]
2、eventReceived作用是什么?
eventReceived函数watch executor Pod,并记录executor disconnected原因:podsWithKnownExitReasons(executorName,ExecutorExited)
3、整个处理逻辑是什么(总结+疑点解答)?
由于handleDisconnectedExecutors是SAR核心函数,我们从该函数整体分析流程,如下:
private val allocatorRunnable: Runnable = new Runnable {
// Maintains a map of executor id to count of checks performed to learn the loss reason
// for an executor.
private val executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts = new mutable.HashMap[String, Int]
override def run(): Unit = {
handleDisconnectedExecutors()
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
if (totalRegisteredExecutors.get() < runningExecutorsToPods.size) {
logDebug("Waiting for pending executors before scaling")
} else if (totalExpectedExecutors.get() <= runningExecutorsToPods.size) {
logDebug("Maximum allowed executor limit reached. Not scaling up further.")
} else {
for (i <- 0 until math.min(
totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorsToPods.size, podAllocationSize)) {
val (executorId, pod) = allocateNewExecutorPod()
runningExecutorsToPods.put(executorId, pod)
runningPodsToExecutors.put(pod.getMetadata.getName, executorId)
logInfo(
s"Requesting a new executor, total executors is now ${runningExecutorsToPods.size}")
}
}
}
}
def handleDisconnectedExecutors(): Unit = {
// For each disconnected executor, synchronize with the loss reasons that may have been found
// by the executor pod watcher. If the loss reason was discovered by the watcher,
// inform the parent class with removeExecutor.
val disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy =
Map.empty ++ disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemovalCopy.foreach { case (executorId, executorPod) =>
val knownExitReason = podsWithKnownExitReasons.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
knownExitReason.fold {
removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId)
} { executorExited =>
logDebug(s"Removing executor $executorId with loss reason " + executorExited.message)
removeExecutor(executorId, executorExited)
// We keep around executors that have exit conditions caused by the application. This
// allows them to be debugged later on. Otherwise, mark them as to be deleted from the
// the API server.
if (!executorExited.exitCausedByApp) {
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
}
}
}
}
def removeExecutorOrIncrementLossReasonCheckCount(executorId: String): Unit = {
val reasonCheckCount = executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts.getOrElse(executorId, 0)
if (reasonCheckCount >= MAX_EXECUTOR_LOST_REASON_CHECKS) {
removeExecutor(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor lost for unknown reasons."))
deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId)
} else {
executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts.put(executorId, reasonCheckCount + 1)
}
}
def deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures(executorId: String): Unit = {
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval -= executorId
executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts -= executorId
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
runningExecutorsToPods.remove(executorId).map { pod =>
kubernetesClient.pods().delete(pod)
runningPodsToExecutors.remove(pod.getMetadata.getName)
}.getOrElse(logWarning(s"Unable to remove pod for unknown executor $executorId"))
}
}
}
这些函数之间的关系是怎么样的:doKillExecutors、removeExecutor、onDisconnected以及deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures?
首先onDisconnected函数将disconnected executor添加到disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval(executorId,executorPod)中,也即它是负责监控disconnected executor作用
其次,deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures函数作用是将executorId对应的Pod从disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval、executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts、runningExecutorsToPods以及runningPodsToExecutors中剔除,同时将该Pod从集群中删除kubernetesClient.pods().delete(pod)
那么removeExecutor的作用具体是什么,和deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures有什么联系???
下面重点分析removeExecutor,如下:
...
removeExecutor(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor lost for unknown reasons."))
...
/**
* Called by subclasses when notified of a lost worker. It just fires the message and returns
* at once.
*/
protected def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
// Only log the failure since we don't care about the result.
driverEndpoint.ask[Boolean](RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason)).onFailure { case t =>
logError(t.getMessage, t)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
...
case class RemoveExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason)
extends CoarseGrainedClusterMessage
...
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {
executorRef.send(RegisterExecutorFailed("Duplicate executor ID: " + executorId))
context.reply(true)
} else {
// If the executor's rpc env is not listening for incoming connections, `hostPort`
// will be null, and the client connection should be used to contact the executor.
val executorAddress = if (executorRef.address != null) {
executorRef.address
} else {
context.senderAddress
}
logInfo(s"Registered executor $executorRef ($executorAddress) with ID $executorId")
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorId
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorRef.address, hostname,
cores, cores, logUrls)
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)
if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {
currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt
}
if (numPendingExecutors > 0) {
numPendingExecutors -= 1
logDebug(s"Decremented number of pending executors ($numPendingExecutors left)")
}
}
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the map
context.reply(true)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))
makeOffers()
}
case StopDriver =>
context.reply(true)
stop()
case StopExecutors =>
logInfo("Asking each executor to shut down")
for ((_, executorData) <- executorDataMap) {
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor)
}
context.reply(true)
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
// We will remove the executor's state and cannot restore it. However, the connection
// between the driver and the executor may be still alive so that the executor won't exit
// automatically, so try to tell the executor to stop itself. See SPARK-13519.
executorDataMap.get(executorId).foreach(_.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor))
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
context.reply(true)
case RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId) =>
val reply = SparkAppConfig(sparkProperties,
SparkEnv.get.securityManager.getIOEncryptionKey())
context.reply(reply)
}
重点分析receiveAndReply的case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason),如下:
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
// We will remove the executor's state and cannot restore it. However, the connection
// between the driver and the executor may be still alive so that the executor won't exit
// automatically, so try to tell the executor to stop itself. See SPARK-13519.
executorDataMap.get(executorId).foreach(_.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor))
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
context.reply(true)
...
// Accessing `executorDataMap` in `DriverEndpoint.receive/receiveAndReply` doesn't need any
// protection. But accessing `executorDataMap` out of `DriverEndpoint.receive/receiveAndReply`
// must be protected by `CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this`. Besides, `executorDataMap` should
// only be modified in `DriverEndpoint.receive/receiveAndReply` with protection by
// `CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this`.
private val executorDataMap = new HashMap[String, ExecutorData]
...
/**
* Grouping of data for an executor used by CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.
*
* @param executorEndpoint The RpcEndpointRef representing this executor
* @param executorAddress The network address of this executor
* @param executorHost The hostname that this executor is running on
* @param freeCores The current number of cores available for work on the executor
* @param totalCores The total number of cores available to the executor
*/
private[cluster] class ExecutorData(
val executorEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef,
val executorAddress: RpcAddress,
override val executorHost: String,
var freeCores: Int,
override val totalCores: Int,
override val logUrlMap: Map[String, String]
) extends ExecutorInfo(executorHost, totalCores, logUrlMap)
1、executorDataMap.get(executorId).foreach(_.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor))向executor发送了StopExecutor消息,使executor停止自己(stop itself),对应处理如下:
private[spark] class CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(
override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv,
driverUrl: String,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
cores: Int,
userClassPath: Seq[URL],
env: SparkEnv)
extends ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint with ExecutorBackend with Logging {
private[this] val stopping = new AtomicBoolean(false)
var executor: Executor = null
@volatile var driver: Option[RpcEndpointRef] = None
// If this CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend is changed to support multiple threads, then this may need
// to be changed so that we don't share the serializer instance across threads
private[this] val ser: SerializerInstance = env.closureSerializer.newInstance()
override def onStart() {
logInfo("Connecting to driver: " + driverUrl)
rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
driver = Some(ref)
ref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls))
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
case Success(msg) =>
// Always receive `true`. Just ignore it
case Failure(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e, notifyDriver = false)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
def extractLogUrls: Map[String, String] = {
val prefix = "SPARK_LOG_URL_"
sys.env.filterKeys(_.startsWith(prefix))
.map(e => (e._1.substring(prefix.length).toLowerCase, e._2))
}
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisteredExecutor =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")
try {
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)
}
case RegisterExecutorFailed(message) =>
exitExecutor(1, "Slave registration failed: " + message)
case LaunchTask(data) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received LaunchTask command but executor was null")
} else {
val taskDesc = ser.deserialize[TaskDescription](data.value)
logInfo("Got assigned task " + taskDesc.taskId)
executor.launchTask(this, taskId = taskDesc.taskId, attemptNumber = taskDesc.attemptNumber,
taskDesc.name, taskDesc.serializedTask)
}
case KillTask(taskId, _, interruptThread) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received KillTask command but executor was null")
} else {
executor.killTask(taskId, interruptThread)
}
case StopExecutor =>
stopping.set(true)
logInfo("Driver commanded a shutdown")
// Cannot shutdown here because an ack may need to be sent back to the caller. So send
// a message to self to actually do the shutdown.
self.send(Shutdown)
case Shutdown =>
stopping.set(true)
new Thread("CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend-stop-executor") {
override def run(): Unit = {
// executor.stop() will call `SparkEnv.stop()` which waits until RpcEnv stops totally.
// However, if `executor.stop()` runs in some thread of RpcEnv, RpcEnv won't be able to
// stop until `executor.stop()` returns, which becomes a dead-lock (See SPARK-14180).
// Therefore, we put this line in a new thread.
executor.stop()
}
}.start()
}
override def onDisconnected(remoteAddress: RpcAddress): Unit = {
if (stopping.get()) {
logInfo(s"Driver from $remoteAddress disconnected during shutdown")
} else if (driver.exists(_.address == remoteAddress)) {
exitExecutor(1, s"Driver $remoteAddress disassociated! Shutting down.", null,
notifyDriver = false)
} else {
logWarning(s"An unknown ($remoteAddress) driver disconnected.")
}
}
override def statusUpdate(taskId: Long, state: TaskState, data: ByteBuffer) {
val msg = StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data)
driver match {
case Some(driverRef) => driverRef.send(msg)
case None => logWarning(s"Drop $msg because has not yet connected to driver")
}
}
/**
* This function can be overloaded by other child classes to handle
* executor exits differently. For e.g. when an executor goes down,
* back-end may not want to take the parent process down.
*/
protected def exitExecutor(code: Int,
reason: String,
throwable: Throwable = null,
notifyDriver: Boolean = true) = {
val message = "Executor self-exiting due to : " + reason
if (throwable != null) {
logError(message, throwable)
} else {
logError(message)
}
if (notifyDriver && driver.nonEmpty) {
driver.get.ask[Boolean](
RemoveExecutor(executorId, new ExecutorLossReason(reason))
).onFailure { case e =>
logWarning(s"Unable to notify the driver due to " + e.getMessage, e)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
System.exit(code)
}
}
...
private[this] val stopping = new AtomicBoolean(false)
var executor: Executor = null
...
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
...
def stop(): Unit = {
env.metricsSystem.report()
heartbeater.shutdown()
heartbeater.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
threadPool.shutdown()
if (!isLocal) {
env.stop()
}
}
...
// Start worker thread pool
private val threadPool = ThreadUtils.newDaemonCachedThreadPool("Executor task launch worker")
2、执行removeExecutor(executorId, reason),如下:
// Remove a disconnected slave from the cluster
private def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
logDebug(s"Asked to remove executor $executorId with reason $reason")
executorDataMap.get(executorId) match {
case Some(executorInfo) =>
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
val killed = CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
addressToExecutorId -= executorInfo.executorAddress
executorDataMap -= executorId
executorsPendingLossReason -= executorId
executorsPendingToRemove.remove(executorId).getOrElse(false)
}
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(-executorInfo.totalCores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(-1)
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, if (killed) ExecutorKilled else reason)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorRemoved(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, reason.toString))
case None =>
// SPARK-15262: If an executor is still alive even after the scheduler has removed
// its metadata, we may receive a heartbeat from that executor and tell its block
// manager to reregister itself. If that happens, the block manager master will know
// about the executor, but the scheduler will not. Therefore, we should remove the
// executor from the block manager when we hit this case.
scheduler.sc.env.blockManager.master.removeExecutorAsync(executorId)
logInfo(s"Asked to remove non-existent executor $executorId")
}
}
...
// Executors that have been lost, but for which we don't yet know the real exit reason.
protected val executorsPendingLossReason = new HashSet[String]
...
// Executors we have requested the cluster manager to kill that have not died yet; maps
// the executor ID to whether it was explicitly killed by the driver (and thus shouldn't
// be considered an app-related failure).
@GuardedBy("CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this")
private val executorsPendingToRemove = new HashMap[String, Boolean]
...
/**
* Grouping of data for an executor used by CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.
*
* @param executorEndpoint The RpcEndpointRef representing this executor
* @param executorAddress The network address of this executor
* @param executorHost The hostname that this executor is running on
* @param freeCores The current number of cores available for work on the executor
* @param totalCores The total number of cores available to the executor
*/
private[cluster] class ExecutorData(
val executorEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef,
val executorAddress: RpcAddress,
override val executorHost: String,
var freeCores: Int,
override val totalCores: Int,
override val logUrlMap: Map[String, String]
) extends ExecutorInfo(executorHost, totalCores, logUrlMap)
要弄清楚这个先看receiveAndReply的RegisterExecutor消息处理逻辑:
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {
executorRef.send(RegisterExecutorFailed("Duplicate executor ID: " + executorId))
context.reply(true)
} else {
// If the executor's rpc env is not listening for incoming connections, `hostPort`
// will be null, and the client connection should be used to contact the executor.
val executorAddress = if (executorRef.address != null) {
executorRef.address
} else {
context.senderAddress
}
logInfo(s"Registered executor $executorRef ($executorAddress) with ID $executorId")
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorId
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorRef.address, hostname,
cores, cores, logUrls)
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)
if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {
currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt
}
if (numPendingExecutors > 0) {
numPendingExecutors -= 1
logDebug(s"Decremented number of pending executors ($numPendingExecutors left)")
}
}
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the map
context.reply(true)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))
makeOffers()
}
...
// The num of current max ExecutorId used to re-register appMaster
@volatile protected var currentExecutorIdCounter = 0
// Number of executors requested from the cluster manager that have not registered yet
@GuardedBy("CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this")
private var numPendingExecutors = 0
RegisterExecutor逻辑如下:
- 1、添加信息到
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress,executorId):addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorId - 2、增加
totalCoreCount:totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)——增加总核数 - 3、增加totalRegisteredExecutors:
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)——增加总注册executor数量 - 4、构造
ExecutorData:val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorRef.address, hostname, cores, cores, logUrls) - 5、添加
(executorId,ExecutorData)到executorDataMap中:executorDataMap.put(executorId, data) - 6、更新
currentExecutorIdCounter - 7、减少
numPendingExecutors:numPendingExecutors -= 1 - 8、向
executorRef发送RegisteredExecutor消息:executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
removeExecutor逻辑如下:
- 1、从
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress,executorId)中剔除executorAddress:addressToExecutorId -= executorInfo.executorAddress - 2、从
executorDataMap(executorId,ExecutorData)中剔除executorId:executorDataMap -= executorId - 3、从
executorsPendingLossReason(executorId)中剔除executorId:executorsPendingLossReason -= executorId - 4、从
executorsPendingToRemove(executorId,bool)中剔除executorId:executorsPendingToRemove.remove(executorId).getOrElse(false) - 5、减少
totalCoreCount:totalCoreCount.addAndGet(-executorInfo.totalCores)——减少总核数 - 6、减少
totalRegisteredExecutors:totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(-1)——减少总注册executor数量 - 7、执行
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, if (killed) ExecutorKilled else reason),clean upexecutor上执行的任务,如下:
override def executorLost(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = {
var failedExecutor: Option[String] = None
synchronized {
if (executorIdToRunningTaskIds.contains(executorId)) {
val hostPort = executorIdToHost(executorId)
logExecutorLoss(executorId, hostPort, reason)
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
failedExecutor = Some(executorId)
} else {
executorIdToHost.get(executorId) match {
case Some(hostPort) =>
// If the host mapping still exists, it means we don't know the loss reason for the
// executor. So call removeExecutor() to update tasks running on that executor when
// the real loss reason is finally known.
logExecutorLoss(executorId, hostPort, reason)
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
case None =>
// We may get multiple executorLost() calls with different loss reasons. For example,
// one may be triggered by a dropped connection from the slave while another may be a
// report of executor termination from Mesos. We produce log messages for both so we
// eventually report the termination reason.
logError(s"Lost an executor $executorId (already removed): $reason")
}
}
}
// Call dagScheduler.executorLost without holding the lock on this to prevent deadlock
if (failedExecutor.isDefined) {
dagScheduler.executorLost(failedExecutor.get, reason)
backend.reviveOffers()
}
}
// IDs of the tasks running on each executor
private val executorIdToRunningTaskIds = new HashMap[String, HashSet[Long]]
// The set of executors we have on each host; this is used to compute hostsAlive, which
// in turn is used to decide when we can attain data locality on a given host
protected val hostToExecutors = new HashMap[String, HashSet[String]]
protected val hostsByRack = new HashMap[String, HashSet[String]]
protected val executorIdToHost = new HashMap[String, String]
...
private def logExecutorLoss(
executorId: String,
hostPort: String,
reason: ExecutorLossReason): Unit = reason match {
case LossReasonPending =>
logDebug(s"Executor $executorId on $hostPort lost, but reason not yet known.")
case ExecutorKilled =>
logInfo(s"Executor $executorId on $hostPort killed by driver.")
case _ =>
logError(s"Lost executor $executorId on $hostPort: $reason")
}
...
/**
* Remove an executor from all our data structures and mark it as lost. If the executor's loss
* reason is not yet known, do not yet remove its association with its host nor update the status
* of any running tasks, since the loss reason defines whether we'll fail those tasks.
*/
private def removeExecutor(executorId: String, reason: ExecutorLossReason) {
// The tasks on the lost executor may not send any more status updates (because the executor
// has been lost), so they should be cleaned up here.
executorIdToRunningTaskIds.remove(executorId).foreach { taskIds =>
logDebug("Cleaning up TaskScheduler state for tasks " +
s"${taskIds.mkString("[", ",", "]")} on failed executor $executorId")
// We do not notify the TaskSetManager of the task failures because that will
// happen below in the rootPool.executorLost() call.
taskIds.foreach(cleanupTaskState)
}
val host = executorIdToHost(executorId)
val execs = hostToExecutors.getOrElse(host, new HashSet)
execs -= executorId
if (execs.isEmpty) {
hostToExecutors -= host
for (rack <- getRackForHost(host); hosts <- hostsByRack.get(rack)) {
hosts -= host
if (hosts.isEmpty) {
hostsByRack -= rack
}
}
}
if (reason != LossReasonPending) {
executorIdToHost -= executorId
rootPool.executorLost(executorId, host, reason)
}
}
再看doKillExecutors函数:
override def doKillExecutors(executorIds: Seq[String]): Future[Boolean] = Future[Boolean] {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
for (executor <- executorIds) {
val maybeRemovedExecutor = runningExecutorsToPods.remove(executor)
maybeRemovedExecutor.foreach { executorPod =>
kubernetesClient.pods().delete(executorPod)
disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval(executor) = executorPod
runningPodsToExecutors.remove(executorPod.getMetadata.getName)
}
if (maybeRemovedExecutor.isEmpty) {
logWarning(s"Unable to remove pod for unknown executor $executor")
}
}
}
true
}
和deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures函数作用类似:是将executorId对应的Pod从disconnectedPodsByExecutorIdPendingRemoval、runningExecutorsToPods以及runningPodsToExecutors中剔除,同时将该Pod从集群中删除kubernetesClient.pods().delete(executorPod),但是executorReasonCheckAttemptCounts并没有删除
那么什么时候调用doKillExecutors函数呢?
/**
* Request that the cluster manager kill the specified executors.
*
* When asking the executor to be replaced, the executor loss is considered a failure, and
* killed tasks that are running on the executor will count towards the failure limits. If no
* replacement is being requested, then the tasks will not count towards the limit.
*
* @param executorIds identifiers of executors to kill
* @param replace whether to replace the killed executors with new ones
* @param force whether to force kill busy executors
* @return whether the kill request is acknowledged. If list to kill is empty, it will return
* false.
*/
final def killExecutors(
executorIds: Seq[String],
replace: Boolean,
force: Boolean): Seq[String] = {
logInfo(s"Requesting to kill executor(s) ${executorIds.mkString(", ")}")
val response = synchronized {
val (knownExecutors, unknownExecutors) = executorIds.partition(executorDataMap.contains)
unknownExecutors.foreach { id =>
logWarning(s"Executor to kill $id does not exist!")
}
// If an executor is already pending to be removed, do not kill it again (SPARK-9795)
// If this executor is busy, do not kill it unless we are told to force kill it (SPARK-9552)
val executorsToKill = knownExecutors
.filter { id => !executorsPendingToRemove.contains(id) }
.filter { id => force || !scheduler.isExecutorBusy(id) }
executorsToKill.foreach { id => executorsPendingToRemove(id) = !replace }
logInfo(s"Actual list of executor(s) to be killed is ${executorsToKill.mkString(", ")}")
// If we do not wish to replace the executors we kill, sync the target number of executors
// with the cluster manager to avoid allocating new ones. When computing the new target,
// take into account executors that are pending to be added or removed.
val adjustTotalExecutors =
if (!replace) {
doRequestTotalExecutors(
numExistingExecutors + numPendingExecutors - executorsPendingToRemove.size)
} else {
numPendingExecutors += knownExecutors.size
Future.successful(true)
}
val killExecutors: Boolean => Future[Boolean] =
if (!executorsToKill.isEmpty) {
_ => doKillExecutors(executorsToKill)
} else {
_ => Future.successful(false)
}
val killResponse = adjustTotalExecutors.flatMap(killExecutors)(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
killResponse.flatMap(killSuccessful =>
Future.successful (if (killSuccessful) executorsToKill else Seq.empty[String])
)(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
defaultAskTimeout.awaitResult(response)
}
/**
* Request that the cluster manager kill the specified executor without adjusting the
* application resource requirements.
*
* The effect is that a new executor will be launched in place of the one killed by
* this request. This assumes the cluster manager will automatically and eventually
* fulfill all missing application resource requests.
*
* @note The replace is by no means guaranteed; another application on the same cluster
* can steal the window of opportunity and acquire this application's resources in the
* mean time.
*
* @return whether the request is received.
*/
private[spark] def killAndReplaceExecutor(executorId: String): Boolean = {
schedulerBackend match {
case b: CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend =>
b.killExecutors(Seq(executorId), replace = true, force = true).nonEmpty
case _ =>
logWarning("Killing executors is only supported in coarse-grained mode")
false
}
}
private def expireDeadHosts(): Unit = {
logTrace("Checking for hosts with no recent heartbeats in HeartbeatReceiver.")
val now = clock.getTimeMillis()
for ((executorId, lastSeenMs) <- executorLastSeen) {
if (now - lastSeenMs > executorTimeoutMs) {
logWarning(s"Removing executor $executorId with no recent heartbeats: " +
s"${now - lastSeenMs} ms exceeds timeout $executorTimeoutMs ms")
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor heartbeat " +
s"timed out after ${now - lastSeenMs} ms"))
// Asynchronously kill the executor to avoid blocking the current thread
killExecutorThread.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
// Note: we want to get an executor back after expiring this one,
// so do not simply call `sc.killExecutor` here (SPARK-8119)
sc.killAndReplaceExecutor(executorId)
}
})
executorLastSeen.remove(executorId)
}
}
}
...
/**
* Lives in the driver to receive heartbeats from executors..
*/
private[spark] class HeartbeatReceiver(sc: SparkContext, clock: Clock)
extends SparkListener with ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint with Logging {
def this(sc: SparkContext) {
this(sc, new SystemClock)
}
sc.addSparkListener(this)
override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv = sc.env.rpcEnv
private[spark] var scheduler: TaskScheduler = null
// executor ID -> timestamp of when the last heartbeat from this executor was received
private val executorLastSeen = new mutable.HashMap[String, Long]
// "spark.network.timeout" uses "seconds", while `spark.storage.blockManagerSlaveTimeoutMs` uses
// "milliseconds"
private val slaveTimeoutMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsMs("spark.storage.blockManagerSlaveTimeoutMs", "120s")
private val executorTimeoutMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsSeconds("spark.network.timeout", s"${slaveTimeoutMs}ms") * 1000
// "spark.network.timeoutInterval" uses "seconds", while
// "spark.storage.blockManagerTimeoutIntervalMs" uses "milliseconds"
private val timeoutIntervalMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsMs("spark.storage.blockManagerTimeoutIntervalMs", "60s")
private val checkTimeoutIntervalMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsSeconds("spark.network.timeoutInterval", s"${timeoutIntervalMs}ms") * 1000
private var timeoutCheckingTask: ScheduledFuture[_] = null
// "eventLoopThread" is used to run some pretty fast actions. The actions running in it should not
// block the thread for a long time.
private val eventLoopThread =
ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadScheduledExecutor("heartbeat-receiver-event-loop-thread")
private val killExecutorThread = ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadExecutor("kill-executor-thread")
override def onStart(): Unit = {
timeoutCheckingTask = eventLoopThread.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
Option(self).foreach(_.ask[Boolean](ExpireDeadHosts))
}
}, 0, checkTimeoutIntervalMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
// Messages sent and received locally
case ExecutorRegistered(executorId) =>
executorLastSeen(executorId) = clock.getTimeMillis()
context.reply(true)
case ExecutorRemoved(executorId) =>
executorLastSeen.remove(executorId)
context.reply(true)
case TaskSchedulerIsSet =>
scheduler = sc.taskScheduler
context.reply(true)
case ExpireDeadHosts =>
expireDeadHosts()
context.reply(true)
// Messages received from executors
case heartbeat @ Heartbeat(executorId, accumUpdates, blockManagerId) =>
if (scheduler != null) {
if (executorLastSeen.contains(executorId)) {
executorLastSeen(executorId) = clock.getTimeMillis()
eventLoopThread.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
val unknownExecutor = !scheduler.executorHeartbeatReceived(
executorId, accumUpdates, blockManagerId)
val response = HeartbeatResponse(reregisterBlockManager = unknownExecutor)
context.reply(response)
}
})
} else {
// This may happen if we get an executor's in-flight heartbeat immediately
// after we just removed it. It's not really an error condition so we should
// not log warning here. Otherwise there may be a lot of noise especially if
// we explicitly remove executors (SPARK-4134).
logDebug(s"Received heartbeat from unknown executor $executorId")
context.reply(HeartbeatResponse(reregisterBlockManager = true))
}
} else {
// Because Executor will sleep several seconds before sending the first "Heartbeat", this
// case rarely happens. However, if it really happens, log it and ask the executor to
// register itself again.
logWarning(s"Dropping $heartbeat because TaskScheduler is not ready yet")
context.reply(HeartbeatResponse(reregisterBlockManager = true))
}
}
...
}
也即driver端心跳线程:heartbeat-receiver-event-loop-thread定期给自己发送ExpireDeadHosts消息,而ExpireDeadHosts消息对应的处理函数为expireDeadHosts如下:
private def expireDeadHosts(): Unit = {
logTrace("Checking for hosts with no recent heartbeats in HeartbeatReceiver.")
val now = clock.getTimeMillis()
for ((executorId, lastSeenMs) <- executorLastSeen) {
if (now - lastSeenMs > executorTimeoutMs) {
logWarning(s"Removing executor $executorId with no recent heartbeats: " +
s"${now - lastSeenMs} ms exceeds timeout $executorTimeoutMs ms")
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor heartbeat " +
s"timed out after ${now - lastSeenMs} ms"))
// Asynchronously kill the executor to avoid blocking the current thread
killExecutorThread.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
// Note: we want to get an executor back after expiring this one,
// so do not simply call `sc.killExecutor` here (SPARK-8119)
sc.killAndReplaceExecutor(executorId)
}
})
executorLastSeen.remove(executorId)
}
}
}
// executor ID -> timestamp of when the last heartbeat from this executor was received
private val executorLastSeen = new mutable.HashMap[String, Long]
主要完成心跳超时检测,对于心跳超时的executor执行scheduler.executorLost(executorId, SlaveLost("Executor heartbeat " + s"timed out after ${now - lastSeenMs} ms"))以及sc.killAndReplaceExecutor(executorId),转而执行b.killExecutors(Seq(executorId), replace = true, force = true).nonEmpty:
/**
* Request that the cluster manager kill the specified executors.
*
* When asking the executor to be replaced, the executor loss is considered a failure, and
* killed tasks that are running on the executor will count towards the failure limits. If no
* replacement is being requested, then the tasks will not count towards the limit.
*
* @param executorIds identifiers of executors to kill
* @param replace whether to replace the killed executors with new ones
* @param force whether to force kill busy executors
* @return whether the kill request is acknowledged. If list to kill is empty, it will return
* false.
*/
final def killExecutors(
executorIds: Seq[String],
replace: Boolean,
force: Boolean): Seq[String] = {
logInfo(s"Requesting to kill executor(s) ${executorIds.mkString(", ")}")
val response = synchronized {
val (knownExecutors, unknownExecutors) = executorIds.partition(executorDataMap.contains)
unknownExecutors.foreach { id =>
logWarning(s"Executor to kill $id does not exist!")
}
// If an executor is already pending to be removed, do not kill it again (SPARK-9795)
// If this executor is busy, do not kill it unless we are told to force kill it (SPARK-9552)
val executorsToKill = knownExecutors
.filter { id => !executorsPendingToRemove.contains(id) }
.filter { id => force || !scheduler.isExecutorBusy(id) }
executorsToKill.foreach { id => executorsPendingToRemove(id) = !replace }
logInfo(s"Actual list of executor(s) to be killed is ${executorsToKill.mkString(", ")}")
// If we do not wish to replace the executors we kill, sync the target number of executors
// with the cluster manager to avoid allocating new ones. When computing the new target,
// take into account executors that are pending to be added or removed.
val adjustTotalExecutors =
if (!replace) {
doRequestTotalExecutors(
numExistingExecutors + numPendingExecutors - executorsPendingToRemove.size)
} else {
numPendingExecutors += knownExecutors.size
Future.successful(true)
}
val killExecutors: Boolean => Future[Boolean] =
if (!executorsToKill.isEmpty) {
_ => doKillExecutors(executorsToKill)
} else {
_ => Future.successful(false)
}
val killResponse = adjustTotalExecutors.flatMap(killExecutors)(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
killResponse.flatMap(killSuccessful =>
Future.successful (if (killSuccessful) executorsToKill else Seq.empty[String])
)(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
defaultAskTimeout.awaitResult(response)
}
// Executors we have requested the cluster manager to kill that have not died yet; maps
// the executor ID to whether it was explicitly killed by the driver (and thus shouldn't
// be considered an app-related failure).
@GuardedBy("CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this")
private val executorsPendingToRemove = new HashMap[String, Boolean]
...
override def doRequestTotalExecutors(requestedTotal: Int): Future[Boolean] = Future[Boolean] {
totalExpectedExecutors.set(requestedTotal)
true
}
- 1、从
executorIds序列中分离出executorDataMap中包含的executor和不包含的executor:val (knownExecutors, unknownExecutors) = executorIds.partition(executorDataMap.contains) - 2、从
knownExecutors中剔除If an executor is already pending to be removed, do not kill it again (SPARK-9795)和If this executor is busy, do not kill it unless we are told to force kill it (SPARK-9552),构造executorsToKill - 3、从
executorsToKill中根据replace设置executorsPendingToRemove:executorsToKill.foreach { id => executorsPendingToRemove(id) = !replace } - 4、如果希望替换(
replace=true)则同步totalExpectedExecutors:doRequestTotalExecutors(numExistingExecutors + numPendingExecutors - executorsPendingToRemove.size);否则增加numPendingExecutors:numPendingExecutors += knownExecutors.size - 5、对
executorsToKill执行doKillExecutors:doKillExecutors(executorsToKill) - 6、最后如果
doKillExecutors(executorsToKill)执行成功则返回executorsToKill;否则返回Seq.empty[String]
这里有一个疑问:removeExecutor和killExecutors有什么区别???
改进方案测试
初步测试见github issue
测试疑问:
1、We can see that Job still aborts even though the executor 3 is created when executor 1 is deleted.
2、And if i don’t use SAR(Static Allocation Recover), the spark application runs normally even though one executor has been deleted !!!
3、Also, another question bothers me is that some spark applications still can’t recover for lots of reasons, such as data loss and so on, even though new executors have been produced. How about this problem? Is there any thoughts to solve this problem?
修正方案
按照上述分析,有一些疑问:
- 1、正常Pod产生错误,Pod状态(
pod.getStatus.getPhase)为Failed,这在上述中不会得到处理 - 2、有一些处理函数的作用以及它们之间的联系没搞清楚:
doKillExecutors、removeExecutor以及新添加的onDisconnected? - 3、这里有一个疑问:
removeExecutor和killExecutors有什么区别??? - 4、这里保留一个疑问:
executorExited.exitCausedByApp具体可能是哪些?同时!executorExited.exitCausedByApp具体可能又是哪些? - 5、那
么removeExecutor的作用具体是什么,和deleteExecutorFromClusterAndDataStructures有什么联系??? - 6、
k8s master重启会导致任务失败?(测试发现k8s master重启不会导致任务失败,但是会导致Executor pod watch closed)
修正方案需要完成SAR如下目标:
- 1、如果
executor挂掉,则driver不会产生新的 替换executor - 2、如果
executor全部挂掉,driver依然运行——bug(原因待查……) - 3、
executor产生过程存在问题——如果某些executor因为某些原因始终无法起来,则driver不会继续产生新的executor
最终想要的结果是在spark应用程序正确的情况下,始终产生并维持用户指定数目的executor数目,并采用某种机制保障(检测)运行的executor是"健康状态",最终保证应用程序的成功运行
针对上述问题,我们需要做如下优化:
- 1、添加Pod挂掉的处理逻辑,包括:
注册成功和注册失败的executor - 2、添加超时机制,对于
executor container一直不起来(因为某些外部的原因,例如:rbd挂载失败)的情况能够超时发现并处理
修正方案测试
测试如下:
- 测试一:
executor运行过程中挂掉
k8s 1.5版本集群测试发现:手动kill掉executor 1进程,driver会发现并产生新的executor 3,并能正常运行完成(spark.executor.instances=2):
# kubectl get pods -n=xxx -a -o wide|grep spark-debug-sar-test6
spark-debug-sar-test6 0/1 Completed 0 4m 192.168.25.90 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test6-exec-1 0/1 Error 0 4m 192.168.25.92 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test6-exec-2 0/1 Completed 0 4m 192.168.25.91 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test6-exec-3 0/1 Completed 0 3m 192.168.25.93 x.x.x.x
这种情况下pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Failed"且action == Action.MODIFIED且pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null
- 测试二:
executor产生过程中挂掉(还没有register itself successfully)
k8s 1.5版本集群测试发现:executor 3、4、5还没有注册成功就失败了,driver会发现并产生新的executor,并能正常运行完成(spark.executor.instances=10):
# kubectl get pods -n=xxx -a -o wide|grep spark-debug-sar-test8
spark-debug-sar-test8 1/1 Completed 0 3m 192.168.25.92 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-1 1/1 Completed 0 3m 192.168.25.94 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-10 1/1 Completed 0 48s 192.168.25.96 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-11 1/1 Completed 0 28s 192.168.25.104 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-12 1/1 Completed 0 27s 192.168.25.101 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-13 1/1 Completed 0 27s 192.168.25.100 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-2 1/1 Completed 0 3m 192.168.25.93 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-3 0/1 Error 0 3m 192.168.11.31 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-4 0/1 Error 0 3m 192.168.11.37 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-5 0/1 Error 0 3m 192.168.11.44 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-6 1/1 Completed 0 48s 192.168.25.99 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-7 1/1 Completed 0 48s 192.168.25.95 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-8 1/1 Completed 0 48s 192.168.25.97 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test8-exec-9 1/1 Completed 0 48s 192.168.25.98 x.x.x.x
这种情况下pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Failed"且action == Action.MODIFIED且pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null
- 测试三:
deleteexecutor
手动delete掉executor 1,driver产生新的executor 3;再手动delete掉executor 2,driver产生新的executor 4,并能成功运行完成(spark.executor.instances=2):
# kubectl get pods -n=xxx -a -o wide|grep spark-debug-sar-test9
spark-debug-sar-test9 0/1 Completed 0 5m 192.168.25.100 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test9-exec-3 0/1 Completed 0 4m 192.168.25.105 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test9-exec-4 0/1 Completed 0 3m 192.168.25.106 x.x.x.x
这种情况下action == Action.DELETED
- 测试四:
executor container一直起不来(例如挂载rbd一直有问题、pull镜像失败)
这种情况下任务会挂住:
# kubectl get pods -n=xxx -a -o wide|grep spark-debug-sar-test10
spark-debug-sar-test10 1/1 Running 0 46m 192.168.25.108 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test10-exec-1 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 46m 192.168.25.109 x.x.x.x
spark-debug-sar-test10-exec-2 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 46m 192.168.25.110 x.x.x.x
这种情况后续再优化处理……
结论
修正后的方案基本可以满足Spark SAR需求,还需要优化如下:
- 1、添加超时机制,对于
executor container一直不起来(因为某些外部的原因,例如:rbd挂载失败)的情况能够超时发现并处理 - 2、k8s 1.5与1.8版本区别(升级版本带来的差异)?
Refs
- Changes to support executor recovery behavior during static allocation.
- Code enhancement: Replaced explicit synchronized access to a hashmap …
- Unit Tests for KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend
- Spark driver should exit and report a failure when all executors get killed/fail
- Spark behavior on k8s vs yarn on executor failures
- Scala Runnable
- Scala - for Loops
- GET /api/v1/watch/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}
- scala中的flatMap详解
- WatchConnectionManager closes when k8s master restarts