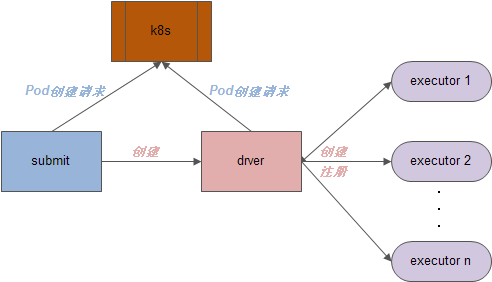
本文分析Spark on k8s项目集群调度流程(相关源码可能不是最新,仅供参考)
一、submit传递相关参数
启动submit,如下:
bin/spark-submit \
--deploy-mode cluster \
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--master k8s://https://<k8s-apiserver-host>:<k8s-apiserver-port> \
--kubernetes-namespace default \
--conf spark.driver.memory=3G \
--conf spark.driver.cores=2 \
--conf spark.executor.instances=2 \
--conf spark.executor.memory=3G \
--conf spark.executor.cores=2 \
--conf spark.app.name=spark-pi \
--conf spark.kubernetes.driver.docker.image=kubespark/spark-driver:v2.2.0-kubernetes-0.3.0 \
--conf spark.kubernetes.executor.docker.image=kubespark/spark-executor:v2.2.0-kubernetes-0.3.0 \
--conf spark.kubernetes.initcontainer.docker.image=kubespark/spark-init:v2.2.0-kubernetes-0.3.0 \
local:///opt/spark/examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.2.0-k8s-0.3.0.jar
spark-submit脚本如下:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
# disable randomized hash for string in Python 3.3+
export PYTHONHASHSEED=0
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
SparkSubmit对象main函数如下:
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val appArgs = new SparkSubmitArguments(args)
if (appArgs.verbose) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(appArgs)
// scalastyle:on println
}
appArgs.action match {
case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)
}
}
submit函数如下:
/**
* Submit the application using the provided parameters.
*
* This runs in two steps. First, we prepare the launch environment by setting up
* the appropriate classpath, system properties, and application arguments for
* running the child main class based on the cluster manager and the deploy mode.
* Second, we use this launch environment to invoke the main method of the child
* main class.
*/
@tailrec
private def submit(args: SparkSubmitArguments): Unit = {
val (childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
def doRunMain(): Unit = {
if (args.proxyUser != null) {
val proxyUser = UserGroupInformation.createProxyUser(args.proxyUser,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser())
try {
proxyUser.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {
override def run(): Unit = {
runMain(childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass, args.verbose)
}
})
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
// Hadoop's AuthorizationException suppresses the exception's stack trace, which
// makes the message printed to the output by the JVM not very helpful. Instead,
// detect exceptions with empty stack traces here, and treat them differently.
if (e.getStackTrace().length == 0) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(s"ERROR: ${e.getClass().getName()}: ${e.getMessage()}")
// scalastyle:on println
exitFn(1)
} else {
throw e
}
}
} else {
runMain(childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass, args.verbose)
}
}
// In standalone cluster mode, there are two submission gateways:
// (1) The traditional RPC gateway using o.a.s.deploy.Client as a wrapper
// (2) The new REST-based gateway introduced in Spark 1.3
// The latter is the default behavior as of Spark 1.3, but Spark submit will fail over
// to use the legacy gateway if the master endpoint turns out to be not a REST server.
if (args.isStandaloneCluster && args.useRest) {
try {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println("Running Spark using the REST application submission protocol.")
// scalastyle:on println
doRunMain()
} catch {
// Fail over to use the legacy submission gateway
case e: SubmitRestConnectionException =>
printWarning(s"Master endpoint ${args.master} was not a REST server. " +
"Falling back to legacy submission gateway instead.")
args.useRest = false
submit(args)
}
// In all other modes, just run the main class as prepared
} else {
doRunMain()
}
}
运行runMain函数,如下:
/**
* Run the main method of the child class using the provided launch environment.
*
* Note that this main class will not be the one provided by the user if we're
* running cluster deploy mode or python applications.
*/
private def runMain(
childArgs: Seq[String],
childClasspath: Seq[String],
sysProps: Map[String, String],
childMainClass: String,
verbose: Boolean): Unit = {
// scalastyle:off println
if (verbose) {
printStream.println(s"Main class:\n$childMainClass")
printStream.println(s"Arguments:\n${childArgs.mkString("\n")}")
printStream.println(s"System properties:\n${sysProps.mkString("\n")}")
printStream.println(s"Classpath elements:\n${childClasspath.mkString("\n")}")
printStream.println("\n")
}
// scalastyle:on println
val loader =
if (sysProps.getOrElse("spark.driver.userClassPathFirst", "false").toBoolean) {
new ChildFirstURLClassLoader(new Array[URL](0),
Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
} else {
new MutableURLClassLoader(new Array[URL](0),
Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
}
Thread.currentThread.setContextClassLoader(loader)
for (jar <- childClasspath) {
addJarToClasspath(jar, loader)
}
for ((key, value) <- sysProps) {
System.setProperty(key, value)
}
var mainClass: Class[_] = null
try {
mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)
} catch {
case e: ClassNotFoundException =>
e.printStackTrace(printStream)
if (childMainClass.contains("thriftserver")) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(s"Failed to load main class $childMainClass.")
printStream.println("You need to build Spark with -Phive and -Phive-thriftserver.")
// scalastyle:on println
}
System.exit(CLASS_NOT_FOUND_EXIT_STATUS)
case e: NoClassDefFoundError =>
e.printStackTrace(printStream)
if (e.getMessage.contains("org/apache/hadoop/hive")) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(s"Failed to load hive class.")
printStream.println("You need to build Spark with -Phive and -Phive-thriftserver.")
// scalastyle:on println
}
System.exit(CLASS_NOT_FOUND_EXIT_STATUS)
}
// SPARK-4170
if (classOf[scala.App].isAssignableFrom(mainClass)) {
printWarning("Subclasses of scala.App may not work correctly. Use a main() method instead.")
}
val mainMethod = mainClass.getMethod("main", new Array[String](0).getClass)
if (!Modifier.isStatic(mainMethod.getModifiers)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main method in the given main class must be static")
}
@tailrec
def findCause(t: Throwable): Throwable = t match {
case e: UndeclaredThrowableException =>
if (e.getCause() != null) findCause(e.getCause()) else e
case e: InvocationTargetException =>
if (e.getCause() != null) findCause(e.getCause()) else e
case e: Throwable =>
e
}
try {
mainMethod.invoke(null, childArgs.toArray)
} catch {
case t: Throwable =>
findCause(t) match {
case SparkUserAppException(exitCode) =>
System.exit(exitCode)
case t: Throwable =>
throw t
}
}
}
也即执行:mainMethod.invoke(null, childArgs.toArray)
再看submit函数中的val (childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)语句:
/**
* Prepare the environment for submitting an application.
* This returns a 4-tuple:
* (1) the arguments for the child process,
* (2) a list of classpath entries for the child,
* (3) a map of system properties, and
* (4) the main class for the child
* Exposed for testing.
*/
private[deploy] def prepareSubmitEnvironment(args: SparkSubmitArguments)
: (Seq[String], Seq[String], Map[String, String], String) = {
// Return values
val childArgs = new ArrayBuffer[String]()
val childClasspath = new ArrayBuffer[String]()
val sysProps = new HashMap[String, String]()
var childMainClass = ""
// Set the cluster manager
val clusterManager: Int = args.master match {
case "yarn" => YARN
case "yarn-client" | "yarn-cluster" =>
printWarning(s"Master ${args.master} is deprecated since 2.0." +
" Please use master \"yarn\" with specified deploy mode instead.")
YARN
case m if m.startsWith("spark") => STANDALONE
case m if m.startsWith("mesos") => MESOS
case m if m.startsWith("k8s") => KUBERNETES
case m if m.startsWith("local") => LOCAL
case _ =>
printErrorAndExit("Master must either be yarn or start with spark, mesos, k8s, or local")
-1
}
// Set the deploy mode; default is client mode
var deployMode: Int = args.deployMode match {
case "client" | null => CLIENT
case "cluster" => CLUSTER
case _ => printErrorAndExit("Deploy mode must be either client or cluster"); -1
}
// Because the deprecated way of specifying "yarn-cluster" and "yarn-client" encapsulate both
// the master and deploy mode, we have some logic to infer the master and deploy mode
// from each other if only one is specified, or exit early if they are at odds.
if (clusterManager == YARN) {
(args.master, args.deployMode) match {
case ("yarn-cluster", null) =>
deployMode = CLUSTER
args.master = "yarn"
case ("yarn-cluster", "client") =>
printErrorAndExit("Client deploy mode is not compatible with master \"yarn-cluster\"")
case ("yarn-client", "cluster") =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is not compatible with master \"yarn-client\"")
case (_, mode) =>
args.master = "yarn"
}
// Make sure YARN is included in our build if we're trying to use it
if (!Utils.classIsLoadable("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client") && !Utils.isTesting) {
printErrorAndExit(
"Could not load YARN classes. " +
"This copy of Spark may not have been compiled with YARN support.")
}
}
// Update args.deployMode if it is null. It will be passed down as a Spark property later.
(args.deployMode, deployMode) match {
case (null, CLIENT) => args.deployMode = "client"
case (null, CLUSTER) => args.deployMode = "cluster"
case _ =>
}
val isYarnCluster = clusterManager == YARN && deployMode == CLUSTER
val isMesosCluster = clusterManager == MESOS && deployMode == CLUSTER
val isKubernetesCluster = clusterManager == KUBERNETES && deployMode == CLUSTER
// Resolve maven dependencies if there are any and add classpath to jars. Add them to py-files
// too for packages that include Python code
val exclusions: Seq[String] =
if (!StringUtils.isBlank(args.packagesExclusions)) {
args.packagesExclusions.split(",")
} else {
Nil
}
val resolvedMavenCoordinates = SparkSubmitUtils.resolveMavenCoordinates(args.packages,
Option(args.repositories), Option(args.ivyRepoPath), exclusions = exclusions)
if (!StringUtils.isBlank(resolvedMavenCoordinates)) {
args.jars = mergeFileLists(args.jars, resolvedMavenCoordinates)
if (args.isPython) {
args.pyFiles = mergeFileLists(args.pyFiles, resolvedMavenCoordinates)
}
}
// install any R packages that may have been passed through --jars or --packages.
// Spark Packages may contain R source code inside the jar.
if (args.isR && !StringUtils.isBlank(args.jars)) {
RPackageUtils.checkAndBuildRPackage(args.jars, printStream, args.verbose)
}
// Require all python files to be local, so we can add them to the PYTHONPATH
// In YARN cluster mode, python files are distributed as regular files, which can be non-local.
// In Mesos cluster mode, non-local python files are automatically downloaded by Mesos.
if (args.isPython && !isYarnCluster && !isMesosCluster) {
if (Utils.nonLocalPaths(args.primaryResource).nonEmpty) {
printErrorAndExit(s"Only local python files are supported: ${args.primaryResource}")
}
val nonLocalPyFiles = Utils.nonLocalPaths(args.pyFiles).mkString(",")
if (nonLocalPyFiles.nonEmpty) {
printErrorAndExit(s"Only local additional python files are supported: $nonLocalPyFiles")
}
}
// Require all R files to be local
if (args.isR && !isYarnCluster && !isMesosCluster) {
if (Utils.nonLocalPaths(args.primaryResource).nonEmpty) {
printErrorAndExit(s"Only local R files are supported: ${args.primaryResource}")
}
}
// The following modes are not supported or applicable
(clusterManager, deployMode) match {
case (KUBERNETES, CLIENT) =>
printErrorAndExit("Client mode is currently not supported for Kubernetes.")
case (KUBERNETES, CLUSTER) if args.isPython || args.isR =>
printErrorAndExit("Kubernetes does not currently support python or R applications.")
case (STANDALONE, CLUSTER) if args.isPython =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is currently not supported for python " +
"applications on standalone clusters.")
case (STANDALONE, CLUSTER) if args.isR =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is currently not supported for R " +
"applications on standalone clusters.")
case (LOCAL, CLUSTER) =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is not compatible with master \"local\"")
case (_, CLUSTER) if isShell(args.primaryResource) =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is not applicable to Spark shells.")
case (_, CLUSTER) if isSqlShell(args.mainClass) =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is not applicable to Spark SQL shell.")
case (_, CLUSTER) if isThriftServer(args.mainClass) =>
printErrorAndExit("Cluster deploy mode is not applicable to Spark Thrift server.")
case _ =>
}
// If we're running a python app, set the main class to our specific python runner
if (args.isPython && deployMode == CLIENT) {
if (args.primaryResource == PYSPARK_SHELL) {
args.mainClass = "org.apache.spark.api.python.PythonGatewayServer"
} else {
// If a python file is provided, add it to the child arguments and list of files to deploy.
// Usage: PythonAppRunner <main python file> <extra python files> [app arguments]
args.mainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner"
args.childArgs = ArrayBuffer(args.primaryResource, args.pyFiles) ++ args.childArgs
if (clusterManager != YARN) {
// The YARN backend distributes the primary file differently, so don't merge it.
args.files = mergeFileLists(args.files, args.primaryResource)
}
}
if (clusterManager != YARN) {
// The YARN backend handles python files differently, so don't merge the lists.
args.files = mergeFileLists(args.files, args.pyFiles)
}
if (args.pyFiles != null) {
sysProps("spark.submit.pyFiles") = args.pyFiles
}
}
// In YARN mode for an R app, add the SparkR package archive and the R package
// archive containing all of the built R libraries to archives so that they can
// be distributed with the job
if (args.isR && clusterManager == YARN) {
val sparkRPackagePath = RUtils.localSparkRPackagePath
if (sparkRPackagePath.isEmpty) {
printErrorAndExit("SPARK_HOME does not exist for R application in YARN mode.")
}
val sparkRPackageFile = new File(sparkRPackagePath.get, SPARKR_PACKAGE_ARCHIVE)
if (!sparkRPackageFile.exists()) {
printErrorAndExit(s"$SPARKR_PACKAGE_ARCHIVE does not exist for R application in YARN mode.")
}
val sparkRPackageURI = Utils.resolveURI(sparkRPackageFile.getAbsolutePath).toString
// Distribute the SparkR package.
// Assigns a symbol link name "sparkr" to the shipped package.
args.archives = mergeFileLists(args.archives, sparkRPackageURI + "#sparkr")
// Distribute the R package archive containing all the built R packages.
if (!RUtils.rPackages.isEmpty) {
val rPackageFile =
RPackageUtils.zipRLibraries(new File(RUtils.rPackages.get), R_PACKAGE_ARCHIVE)
if (!rPackageFile.exists()) {
printErrorAndExit("Failed to zip all the built R packages.")
}
val rPackageURI = Utils.resolveURI(rPackageFile.getAbsolutePath).toString
// Assigns a symbol link name "rpkg" to the shipped package.
args.archives = mergeFileLists(args.archives, rPackageURI + "#rpkg")
}
}
// TODO: Support distributing R packages with standalone cluster
if (args.isR && clusterManager == STANDALONE && !RUtils.rPackages.isEmpty) {
printErrorAndExit("Distributing R packages with standalone cluster is not supported.")
}
// TODO: Support distributing R packages with mesos cluster
if (args.isR && clusterManager == MESOS && !RUtils.rPackages.isEmpty) {
printErrorAndExit("Distributing R packages with mesos cluster is not supported.")
}
// If we're running an R app, set the main class to our specific R runner
if (args.isR && deployMode == CLIENT) {
if (args.primaryResource == SPARKR_SHELL) {
args.mainClass = "org.apache.spark.api.r.RBackend"
} else {
// If an R file is provided, add it to the child arguments and list of files to deploy.
// Usage: RRunner <main R file> [app arguments]
args.mainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner"
args.childArgs = ArrayBuffer(args.primaryResource) ++ args.childArgs
args.files = mergeFileLists(args.files, args.primaryResource)
}
}
if (isYarnCluster && args.isR) {
// In yarn-cluster mode for an R app, add primary resource to files
// that can be distributed with the job
args.files = mergeFileLists(args.files, args.primaryResource)
}
// Special flag to avoid deprecation warnings at the client
sysProps("SPARK_SUBMIT") = "true"
// A list of rules to map each argument to system properties or command-line options in
// each deploy mode; we iterate through these below
val options = List[OptionAssigner](
// All cluster managers
OptionAssigner(args.master, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.master"),
OptionAssigner(args.deployMode, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.submit.deployMode"),
OptionAssigner(args.name, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.app.name"),
OptionAssigner(args.ivyRepoPath, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, CLIENT, sysProp = "spark.jars.ivy"),
OptionAssigner(args.driverMemory, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, CLIENT,
sysProp = "spark.driver.memory"),
OptionAssigner(args.driverExtraClassPath, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.driver.extraClassPath"),
OptionAssigner(args.driverExtraJavaOptions, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.driver.extraJavaOptions"),
OptionAssigner(args.driverExtraLibraryPath, ALL_CLUSTER_MGRS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.driver.extraLibraryPath"),
// Yarn only
OptionAssigner(args.queue, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.yarn.queue"),
OptionAssigner(args.numExecutors, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.executor.instances"),
OptionAssigner(args.jars, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.yarn.dist.jars"),
OptionAssigner(args.files, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.yarn.dist.files"),
OptionAssigner(args.archives, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.yarn.dist.archives"),
OptionAssigner(args.principal, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.yarn.principal"),
OptionAssigner(args.keytab, YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES, sysProp = "spark.yarn.keytab"),
OptionAssigner(args.kubernetesNamespace, KUBERNETES, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.kubernetes.namespace"),
// Other options
OptionAssigner(args.executorCores, STANDALONE | YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.executor.cores"),
OptionAssigner(args.executorMemory, STANDALONE | MESOS | YARN, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.executor.memory"),
OptionAssigner(args.totalExecutorCores, STANDALONE | MESOS, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.cores.max"),
OptionAssigner(args.files, LOCAL | STANDALONE | MESOS | KUBERNETES, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.files"),
OptionAssigner(args.jars, LOCAL, CLIENT, sysProp = "spark.jars"),
OptionAssigner(args.jars, STANDALONE | MESOS | KUBERNETES, ALL_DEPLOY_MODES,
sysProp = "spark.jars"),
OptionAssigner(args.driverMemory, STANDALONE | MESOS | YARN, CLUSTER,
sysProp = "spark.driver.memory"),
OptionAssigner(args.driverCores, STANDALONE | MESOS | YARN, CLUSTER,
sysProp = "spark.driver.cores"),
OptionAssigner(args.supervise.toString, STANDALONE | MESOS, CLUSTER,
sysProp = "spark.driver.supervise"),
OptionAssigner(args.ivyRepoPath, STANDALONE, CLUSTER, sysProp = "spark.jars.ivy")
)
// In client mode, launch the application main class directly
// In addition, add the main application jar and any added jars (if any) to the classpath
if (deployMode == CLIENT) {
childMainClass = args.mainClass
if (isUserJar(args.primaryResource)) {
childClasspath += args.primaryResource
}
if (args.jars != null) { childClasspath ++= args.jars.split(",") }
if (args.childArgs != null) { childArgs ++= args.childArgs }
}
// Map all arguments to command-line options or system properties for our chosen mode
for (opt <- options) {
if (opt.value != null &&
(deployMode & opt.deployMode) != 0 &&
(clusterManager & opt.clusterManager) != 0) {
if (opt.clOption != null) { childArgs += (opt.clOption, opt.value) }
if (opt.sysProp != null) { sysProps.put(opt.sysProp, opt.value) }
}
}
// Add the application jar automatically so the user doesn't have to call sc.addJar
// For YARN cluster mode, the jar is already distributed on each node as "app.jar"
// In Kubernetes cluster mode, the jar will be uploaded by the client separately.
// For python and R files, the primary resource is already distributed as a regular file
if (!isYarnCluster && !isKubernetesCluster && !args.isPython && !args.isR) {
var jars = sysProps.get("spark.jars").map(x => x.split(",").toSeq).getOrElse(Seq.empty)
if (isUserJar(args.primaryResource)) {
jars = jars ++ Seq(args.primaryResource)
}
sysProps.put("spark.jars", jars.mkString(","))
}
// In standalone cluster mode, use the REST client to submit the application (Spark 1.3+).
// All Spark parameters are expected to be passed to the client through system properties.
if (args.isStandaloneCluster) {
if (args.useRest) {
childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.rest.RestSubmissionClient"
childArgs += (args.primaryResource, args.mainClass)
} else {
// In legacy standalone cluster mode, use Client as a wrapper around the user class
childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.Client"
if (args.supervise) { childArgs += "--supervise" }
Option(args.driverMemory).foreach { m => childArgs += ("--memory", m) }
Option(args.driverCores).foreach { c => childArgs += ("--cores", c) }
childArgs += "launch"
childArgs += (args.master, args.primaryResource, args.mainClass)
}
if (args.childArgs != null) {
childArgs ++= args.childArgs
}
}
// Let YARN know it's a pyspark app, so it distributes needed libraries.
if (clusterManager == YARN) {
if (args.isPython) {
sysProps.put("spark.yarn.isPython", "true")
}
if (args.pyFiles != null) {
sysProps("spark.submit.pyFiles") = args.pyFiles
}
}
// assure a keytab is available from any place in a JVM
if (clusterManager == YARN || clusterManager == LOCAL) {
if (args.principal != null) {
require(args.keytab != null, "Keytab must be specified when principal is specified")
if (!new File(args.keytab).exists()) {
throw new SparkException(s"Keytab file: ${args.keytab} does not exist")
} else {
// Add keytab and principal configurations in sysProps to make them available
// for later use; e.g. in spark sql, the isolated class loader used to talk
// to HiveMetastore will use these settings. They will be set as Java system
// properties and then loaded by SparkConf
sysProps.put("spark.yarn.keytab", args.keytab)
sysProps.put("spark.yarn.principal", args.principal)
UserGroupInformation.loginUserFromKeytab(args.principal, args.keytab)
}
}
}
// In yarn-cluster mode, use yarn.Client as a wrapper around the user class
if (isYarnCluster) {
childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client"
if (args.isPython) {
childArgs += ("--primary-py-file", args.primaryResource)
childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner")
} else if (args.isR) {
val mainFile = new Path(args.primaryResource).getName
childArgs += ("--primary-r-file", mainFile)
childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner")
} else {
if (args.primaryResource != SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE) {
childArgs += ("--jar", args.primaryResource)
}
childArgs += ("--class", args.mainClass)
}
if (args.childArgs != null) {
args.childArgs.foreach { arg => childArgs += ("--arg", arg) }
}
}
if (isMesosCluster) {
assert(args.useRest, "Mesos cluster mode is only supported through the REST submission API")
childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.rest.RestSubmissionClient"
if (args.isPython) {
// Second argument is main class
childArgs += (args.primaryResource, "")
if (args.pyFiles != null) {
sysProps("spark.submit.pyFiles") = args.pyFiles
}
} else if (args.isR) {
// Second argument is main class
childArgs += (args.primaryResource, "")
} else {
childArgs += (args.primaryResource, args.mainClass)
}
if (args.childArgs != null) {
childArgs ++= args.childArgs
}
}
if (isKubernetesCluster) {
childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.kubernetes.submit.Client"
childArgs += args.primaryResource
childArgs += args.mainClass
childArgs ++= args.childArgs
}
// Load any properties specified through --conf and the default properties file
for ((k, v) <- args.sparkProperties) {
sysProps.getOrElseUpdate(k, v)
}
// Ignore invalid spark.driver.host in cluster modes.
if (deployMode == CLUSTER) {
sysProps -= "spark.driver.host"
}
// Resolve paths in certain spark properties
val pathConfigs = Seq(
"spark.jars",
"spark.files",
"spark.yarn.dist.files",
"spark.yarn.dist.archives",
"spark.yarn.dist.jars")
pathConfigs.foreach { config =>
// Replace old URIs with resolved URIs, if they exist
sysProps.get(config).foreach { oldValue =>
sysProps(config) = Utils.resolveURIs(oldValue)
}
}
// Resolve and format python file paths properly before adding them to the PYTHONPATH.
// The resolving part is redundant in the case of --py-files, but necessary if the user
// explicitly sets `spark.submit.pyFiles` in his/her default properties file.
sysProps.get("spark.submit.pyFiles").foreach { pyFiles =>
val resolvedPyFiles = Utils.resolveURIs(pyFiles)
val formattedPyFiles = if (!isYarnCluster && !isMesosCluster) {
PythonRunner.formatPaths(resolvedPyFiles).mkString(",")
} else {
// Ignoring formatting python path in yarn and mesos cluster mode, these two modes
// support dealing with remote python files, they could distribute and add python files
// locally.
resolvedPyFiles
}
sysProps("spark.submit.pyFiles") = formattedPyFiles
}
(childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass)
}
看到childMainClass在k8s集群模式下设置为:childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.kubernetes.submit.Client
再看runMain函数,如下:
mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)
...
val mainMethod = mainClass.getMethod("main", new Array[String](0).getClass)
...
mainMethod.invoke(null, childArgs.toArray)
执行org.apache.spark.deploy.kubernetes.submit.Client的main函数:
private[spark] object Client {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf(true)
val mainAppResource = args(0)
val mainClass = args(1)
val appArgs = args.drop(2)
run(sparkConf, mainAppResource, mainClass, appArgs)
}
def run(
sparkConf: SparkConf,
mainAppResource: String,
mainClass: String,
appArgs: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkJars = sparkConf.getOption("spark.jars")
.map(_.split(","))
.getOrElse(Array.empty[String]) ++
Option(mainAppResource)
.filterNot(_ == SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE)
.toSeq
val launchTime = System.currentTimeMillis
val sparkFiles = sparkConf.getOption("spark.files")
.map(_.split(","))
.getOrElse(Array.empty[String])
val appName = sparkConf.getOption("spark.app.name")
.getOrElse("spark")
val kubernetesAppId = sparkConf.getOption("spark.kubernetes.driver.pod.name")
.getOrElse(s"$appName-$launchTime".toLowerCase.replaceAll("\\.", "-"))
val namespace = sparkConf.get(KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE)
val master = resolveK8sMaster(sparkConf.get("spark.master"))
val sslOptionsProvider = new ResourceStagingServerSslOptionsProviderImpl(sparkConf)
val initContainerComponentsProvider = new DriverInitContainerComponentsProviderImpl(
sparkConf,
kubernetesAppId,
namespace,
sparkJars,
sparkFiles,
sslOptionsProvider.getSslOptions)
Utils.tryWithResource(SparkKubernetesClientFactory.createKubernetesClient(
master,
Some(namespace),
APISERVER_AUTH_SUBMISSION_CONF_PREFIX,
sparkConf,
None,
None)) { kubernetesClient =>
val kubernetesCredentialsMounterProvider =
new DriverPodKubernetesCredentialsMounterProviderImpl(sparkConf, kubernetesAppId)
val waitForAppCompletion = sparkConf.get(WAIT_FOR_APP_COMPLETION)
val loggingInterval = Option(sparkConf.get(REPORT_INTERVAL))
.filter( _ => waitForAppCompletion)
val loggingPodStatusWatcher = new LoggingPodStatusWatcherImpl(
kubernetesAppId, loggingInterval)
new Client(
appName,
kubernetesAppId,
mainClass,
sparkConf,
appArgs,
sparkJars,
sparkFiles,
waitForAppCompletion,
kubernetesClient,
initContainerComponentsProvider,
kubernetesCredentialsMounterProvider,
loggingPodStatusWatcher).run()
}
}
}
创建Client对象并执行run函数如下:
def run(): Unit = {
validateNoDuplicateFileNames(sparkJars)
validateNoDuplicateFileNames(sparkFiles)
val parsedCustomLabels = ConfigurationUtils.parseKeyValuePairs(
customLabels, KUBERNETES_DRIVER_LABELS.key, "labels")
require(!parsedCustomLabels.contains(SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL), s"Label with key " +
s" $SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL is not allowed as it is reserved for Spark bookkeeping operations.")
require(!parsedCustomLabels.contains(SPARK_APP_NAME_LABEL), s"Label with key" +
s" $SPARK_APP_NAME_LABEL is not allowed as it is reserved for Spark bookkeeping operations.")
val allLabels = parsedCustomLabels ++ Map(
SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL -> kubernetesAppId,
SPARK_APP_NAME_LABEL -> appName,
SPARK_ROLE_LABEL -> "driver")
val parsedCustomAnnotations = ConfigurationUtils.parseKeyValuePairs(
customAnnotations, KUBERNETES_DRIVER_ANNOTATIONS.key, "annotations")
val driverExtraClasspathEnv = driverExtraClasspath.map { classPath =>
new EnvVarBuilder()
.withName(ENV_SUBMIT_EXTRA_CLASSPATH)
.withValue(classPath)
.build()
}
val driverCpuQuantity = new QuantityBuilder(false)
.withAmount(driverCpuCores)
.build()
val driverMemoryQuantity = new QuantityBuilder(false)
.withAmount(s"${driverMemoryMb}M")
.build()
val driverMemoryLimitQuantity = new QuantityBuilder(false)
.withAmount(s"${driverContainerMemoryWithOverhead}M")
.build()
val driverContainer = new ContainerBuilder()
.withName(DRIVER_CONTAINER_NAME)
.withImage(driverDockerImage)
.withImagePullPolicy("IfNotPresent")
.addToEnv(driverExtraClasspathEnv.toSeq: _*)
.addNewEnv()
.withName(ENV_DRIVER_MEMORY)
.withValue(driverContainerMemoryWithOverhead + "m")
.endEnv()
.addNewEnv()
.withName(ENV_DRIVER_MAIN_CLASS)
.withValue(mainClass)
.endEnv()
.addNewEnv()
.withName(ENV_DRIVER_ARGS)
.withValue(appArgs.mkString(" "))
.endEnv()
.withNewResources()
.addToRequests("cpu", driverCpuQuantity)
.addToLimits("cpu", driverCpuQuantity)
.addToRequests("memory", driverMemoryQuantity)
.addToLimits("memory", driverMemoryLimitQuantity)
.endResources()
.build()
val basePod = new PodBuilder()
.withNewMetadata()
.withName(kubernetesDriverPodName)
.addToLabels(allLabels.asJava)
.addToAnnotations(parsedCustomAnnotations.asJava)
.endMetadata()
.withNewSpec()
.withRestartPolicy("Never")
.addToContainers(driverContainer)
.endSpec()
val maybeSubmittedDependencyUploader = initContainerComponentsProvider
.provideInitContainerSubmittedDependencyUploader(allLabels)
val maybeSubmittedResourceIdentifiers = maybeSubmittedDependencyUploader.map { uploader =>
SubmittedResources(uploader.uploadJars(), uploader.uploadFiles())
}
val maybeSecretBuilder = initContainerComponentsProvider
.provideSubmittedDependenciesSecretBuilder(
maybeSubmittedResourceIdentifiers.map(_.secrets()))
val maybeSubmittedDependenciesSecret = maybeSecretBuilder.map(_.build())
val initContainerConfigMap = initContainerComponentsProvider
.provideInitContainerConfigMapBuilder(maybeSubmittedResourceIdentifiers.map(_.ids()))
.build()
val podWithInitContainer = initContainerComponentsProvider
.provideInitContainerBootstrap()
.bootstrapInitContainerAndVolumes(driverContainer.getName, basePod)
val containerLocalizedFilesResolver = initContainerComponentsProvider
.provideContainerLocalizedFilesResolver()
val resolvedSparkJars = containerLocalizedFilesResolver.resolveSubmittedSparkJars()
val resolvedSparkFiles = containerLocalizedFilesResolver.resolveSubmittedSparkFiles()
val executorInitContainerConfiguration = initContainerComponentsProvider
.provideExecutorInitContainerConfiguration()
val sparkConfWithExecutorInit = executorInitContainerConfiguration
.configureSparkConfForExecutorInitContainer(sparkConf)
val credentialsMounter = kubernetesCredentialsMounterProvider
.getDriverPodKubernetesCredentialsMounter()
val credentialsSecret = credentialsMounter.createCredentialsSecret()
val podWithInitContainerAndMountedCreds = credentialsMounter.mountDriverKubernetesCredentials(
podWithInitContainer, driverContainer.getName, credentialsSecret)
val resolvedSparkConf = credentialsMounter.setDriverPodKubernetesCredentialLocations(
sparkConfWithExecutorInit)
if (resolvedSparkJars.nonEmpty) {
resolvedSparkConf.set("spark.jars", resolvedSparkJars.mkString(","))
}
if (resolvedSparkFiles.nonEmpty) {
resolvedSparkConf.set("spark.files", resolvedSparkFiles.mkString(","))
}
resolvedSparkConf.setIfMissing(KUBERNETES_DRIVER_POD_NAME, kubernetesDriverPodName)
resolvedSparkConf.set("spark.app.id", kubernetesAppId)
// We don't need this anymore since we just set the JVM options on the environment
resolvedSparkConf.remove(org.apache.spark.internal.config.DRIVER_JAVA_OPTIONS)
val resolvedLocalClasspath = containerLocalizedFilesResolver
.resolveSubmittedAndRemoteSparkJars()
val resolvedDriverJavaOpts = resolvedSparkConf.getAll.map {
case (confKey, confValue) => s"-D$confKey=$confValue"
}.mkString(" ") + driverJavaOptions.map(" " + _).getOrElse("")
val resolvedDriverPod = podWithInitContainerAndMountedCreds.editSpec()
.editMatchingContainer(new ContainerNameEqualityPredicate(driverContainer.getName))
.addNewEnv()
.withName(ENV_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH)
.withValue(resolvedLocalClasspath.mkString(File.pathSeparator))
.endEnv()
.addNewEnv()
.withName(ENV_DRIVER_JAVA_OPTS)
.withValue(resolvedDriverJavaOpts)
.endEnv()
.endContainer()
.endSpec()
.build()
Utils.tryWithResource(
kubernetesClient
.pods()
.withName(resolvedDriverPod.getMetadata.getName)
.watch(loggingPodStatusWatcher)) { _ =>
val createdDriverPod = kubernetesClient.pods().create(resolvedDriverPod)
try {
val driverOwnedResources = Seq(initContainerConfigMap) ++
maybeSubmittedDependenciesSecret.toSeq ++
credentialsSecret.toSeq
val driverPodOwnerReference = new OwnerReferenceBuilder()
.withName(createdDriverPod.getMetadata.getName)
.withApiVersion(createdDriverPod.getApiVersion)
.withUid(createdDriverPod.getMetadata.getUid)
.withKind(createdDriverPod.getKind)
.withController(true)
.build()
driverOwnedResources.foreach { resource =>
val originalMetadata = resource.getMetadata
originalMetadata.setOwnerReferences(Collections.singletonList(driverPodOwnerReference))
}
kubernetesClient.resourceList(driverOwnedResources: _*).createOrReplace()
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
kubernetesClient.pods().delete(createdDriverPod)
throw e
}
if (waitForAppCompletion) {
logInfo(s"Waiting for application $kubernetesAppId to finish...")
loggingPodStatusWatcher.awaitCompletion()
logInfo(s"Application $kubernetesAppId finished.")
} else {
logInfo(s"Deployed Spark application $kubernetesAppId into Kubernetes.")
}
}
}
val createdDriverPod = kubernetesClient.pods().create(resolvedDriverPod)创建driver pod如下:
Utils.tryWithResource(
kubernetesClient
.pods()
.withName(resolvedDriverPod.getMetadata.getName)
.watch(loggingPodStatusWatcher)) { _ =>
val createdDriverPod = kubernetesClient.pods().create(resolvedDriverPod)
try {
val driverOwnedResources = Seq(initContainerConfigMap) ++
maybeSubmittedDependenciesSecret.toSeq ++
credentialsSecret.toSeq
val driverPodOwnerReference = new OwnerReferenceBuilder()
.withName(createdDriverPod.getMetadata.getName)
.withApiVersion(createdDriverPod.getApiVersion)
.withUid(createdDriverPod.getMetadata.getUid)
.withKind(createdDriverPod.getKind)
.withController(true)
.build()
driverOwnedResources.foreach { resource =>
val originalMetadata = resource.getMetadata
originalMetadata.setOwnerReferences(Collections.singletonList(driverPodOwnerReference))
}
kubernetesClient.resourceList(driverOwnedResources: _*).createOrReplace()
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
kubernetesClient.pods().delete(createdDriverPod)
throw e
}
if (waitForAppCompletion) {
logInfo(s"Waiting for application $kubernetesAppId to finish...")
loggingPodStatusWatcher.awaitCompletion()
logInfo(s"Application $kubernetesAppId finished.")
} else {
logInfo(s"Deployed Spark application $kubernetesAppId into Kubernetes.")
}
}
最后直接退出或者等待driver运行结束:
if (waitForAppCompletion) {
logInfo(s"Waiting for application $kubernetesAppId to finish...")
loggingPodStatusWatcher.awaitCompletion()
logInfo(s"Application $kubernetesAppId finished.")
} else {
logInfo(s"Deployed Spark application $kubernetesAppId into Kubernetes.")
}
至此,submit运行流程完毕
二、driver创建executors
driver dockerfile如下:
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
FROM openjdk:8-alpine
# If this docker file is being used in the context of building your images from a Spark distribution, the docker build
# command should be invoked from the top level directory of the Spark distribution. E.g.:
# docker build -t spark-driver:latest -f dockerfiles/driver/Dockerfile .
RUN apk upgrade --update
RUN apk add --update bash tini
RUN mkdir -p /opt/spark
RUN touch /opt/spark/RELEASE
ADD jars /opt/spark/jars
ADD examples /opt/spark/examples
ADD bin /opt/spark/bin
ADD sbin /opt/spark/sbin
ADD conf /opt/spark/conf
ENV SPARK_HOME /opt/spark
WORKDIR /opt/spark
CMD SPARK_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/jars/*" && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH+x} ]; then SPARK_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH:$SPARK_CLASSPATH"; fi && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_SUBMIT_EXTRA_CLASSPATH+x} ]; then SPARK_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_SUBMIT_EXTRA_CLASSPATH:$SPARK_CLASSPATH"; fi && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_EXTRA_CLASSPATH+x} ]; then SPARK_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_EXTRA_CLASSPATH:$SPARK_CLASSPATH"; fi && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_MOUNTED_FILES_DIR} ]; then cp -R "$SPARK_MOUNTED_FILES_DIR/." .; fi && \
exec /sbin/tini -- ${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java $SPARK_DRIVER_JAVA_OPTS -cp $SPARK_CLASSPATH -Xms$SPARK_DRIVER_MEMORY -Xmx$SPARK_DRIVER_MEMORY $SPARK_DRIVER_CLASS $SPARK_DRIVER_ARGS
根据Dockerfile内容,driver容器启动后会运行用户指定的driver class,也即前面submit传递的org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi参数,而Spark中无论什么类都会调用SparkContext,如下:
/**
* Main entry point for Spark functionality. A SparkContext represents the connection to a Spark
* cluster, and can be used to create RDDs, accumulators and broadcast variables on that cluster.
*
* Only one SparkContext may be active per JVM. You must `stop()` the active SparkContext before
* creating a new one. This limitation may eventually be removed; see SPARK-2243 for more details.
*
* @param config a Spark Config object describing the application configuration. Any settings in
* this config overrides the default configs as well as system properties.
*/
class SparkContext(config: SparkConf) extends Logging {
...
构造函数执行如下:
try {
_conf = config.clone()
_conf.validateSettings()
if (!_conf.contains("spark.master")) {
throw new SparkException("A master URL must be set in your configuration")
}
if (!_conf.contains("spark.app.name")) {
throw new SparkException("An application name must be set in your configuration")
}
// System property spark.yarn.app.id must be set if user code ran by AM on a YARN cluster
if (master == "yarn" && deployMode == "cluster" && !_conf.contains("spark.yarn.app.id")) {
throw new SparkException("Detected yarn cluster mode, but isn't running on a cluster. " +
"Deployment to YARN is not supported directly by SparkContext. Please use spark-submit.")
}
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.logConf", false)) {
logInfo("Spark configuration:\n" + _conf.toDebugString)
}
// Set Spark driver host and port system properties. This explicitly sets the configuration
// instead of relying on the default value of the config constant.
_conf.set(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS, _conf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS))
_conf.setIfMissing("spark.driver.port", "0")
_conf.set("spark.executor.id", SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER)
_jars = Utils.getUserJars(_conf)
_files = _conf.getOption("spark.files").map(_.split(",")).map(_.filter(_.nonEmpty))
.toSeq.flatten
_eventLogDir =
if (isEventLogEnabled) {
val unresolvedDir = conf.get("spark.eventLog.dir", EventLoggingListener.DEFAULT_LOG_DIR)
.stripSuffix("/")
Some(Utils.resolveURI(unresolvedDir))
} else {
None
}
_eventLogCodec = {
val compress = _conf.getBoolean("spark.eventLog.compress", false)
if (compress && isEventLogEnabled) {
Some(CompressionCodec.getCodecName(_conf)).map(CompressionCodec.getShortName)
} else {
None
}
}
if (master == "yarn" && deployMode == "client") System.setProperty("SPARK_YARN_MODE", "true")
// "_jobProgressListener" should be set up before creating SparkEnv because when creating
// "SparkEnv", some messages will be posted to "listenerBus" and we should not miss them.
_jobProgressListener = new JobProgressListener(_conf)
listenerBus.addListener(jobProgressListener)
// Create the Spark execution environment (cache, map output tracker, etc)
_env = createSparkEnv(_conf, isLocal, listenerBus)
SparkEnv.set(_env)
// If running the REPL, register the repl's output dir with the file server.
_conf.getOption("spark.repl.class.outputDir").foreach { path =>
val replUri = _env.rpcEnv.fileServer.addDirectory("/classes", new File(path))
_conf.set("spark.repl.class.uri", replUri)
}
_statusTracker = new SparkStatusTracker(this)
_progressBar =
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.showConsoleProgress", true) && !log.isInfoEnabled) {
Some(new ConsoleProgressBar(this))
} else {
None
}
_ui =
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.enabled", true)) {
Some(SparkUI.createLiveUI(this, _conf, listenerBus, _jobProgressListener,
_env.securityManager, appName, startTime = startTime))
} else {
// For tests, do not enable the UI
None
}
// Bind the UI before starting the task scheduler to communicate
// the bound port to the cluster manager properly
_ui.foreach(_.bind())
_hadoopConfiguration = SparkHadoopUtil.get.newConfiguration(_conf)
// Add each JAR given through the constructor
if (jars != null) {
jars.foreach(addJar)
}
if (files != null) {
files.foreach(addFile)
}
_executorMemory = _conf.getOption("spark.executor.memory")
.orElse(Option(System.getenv("SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY")))
.orElse(Option(System.getenv("SPARK_MEM"))
.map(warnSparkMem))
.map(Utils.memoryStringToMb)
.getOrElse(1024)
// Convert java options to env vars as a work around
// since we can't set env vars directly in sbt.
for { (envKey, propKey) <- Seq(("SPARK_TESTING", "spark.testing"))
value <- Option(System.getenv(envKey)).orElse(Option(System.getProperty(propKey)))} {
executorEnvs(envKey) = value
}
Option(System.getenv("SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES")).foreach { v =>
executorEnvs("SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES") = v
}
// The Mesos scheduler backend relies on this environment variable to set executor memory.
// TODO: Set this only in the Mesos scheduler.
executorEnvs("SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY") = executorMemory + "m"
executorEnvs ++= _conf.getExecutorEnv
executorEnvs("SPARK_USER") = sparkUser
// We need to register "HeartbeatReceiver" before "createTaskScheduler" because Executor will
// retrieve "HeartbeatReceiver" in the constructor. (SPARK-6640)
_heartbeatReceiver = env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(
HeartbeatReceiver.ENDPOINT_NAME, new HeartbeatReceiver(this))
// Create and start the scheduler
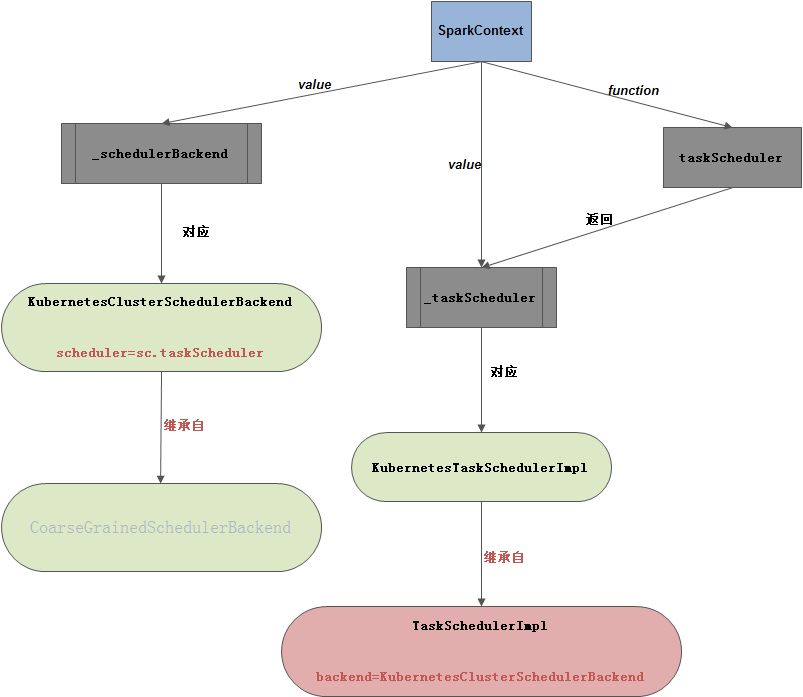
val (sched, ts) = SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master, deployMode)
_schedulerBackend = sched
_taskScheduler = ts
_dagScheduler = new DAGScheduler(this)
_heartbeatReceiver.ask[Boolean](TaskSchedulerIsSet)
// start TaskScheduler after taskScheduler sets DAGScheduler reference in DAGScheduler's
// constructor
_taskScheduler.start()
_applicationId = _taskScheduler.applicationId()
_applicationAttemptId = taskScheduler.applicationAttemptId()
_conf.set("spark.app.id", _applicationId)
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.reverseProxy", false)) {
System.setProperty("spark.ui.proxyBase", "/proxy/" + _applicationId)
}
_ui.foreach(_.setAppId(_applicationId))
_env.blockManager.initialize(_applicationId)
// The metrics system for Driver need to be set spark.app.id to app ID.
// So it should start after we get app ID from the task scheduler and set spark.app.id.
_env.metricsSystem.start()
// Attach the driver metrics servlet handler to the web ui after the metrics system is started.
_env.metricsSystem.getServletHandlers.foreach(handler => ui.foreach(_.attachHandler(handler)))
_eventLogger =
if (isEventLogEnabled) {
val logger =
new EventLoggingListener(_applicationId, _applicationAttemptId, _eventLogDir.get,
_conf, _hadoopConfiguration)
logger.start()
listenerBus.addListener(logger)
Some(logger)
} else {
None
}
// Optionally scale number of executors dynamically based on workload. Exposed for testing.
val dynamicAllocationEnabled = Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(_conf)
_executorAllocationManager =
if (dynamicAllocationEnabled) {
schedulerBackend match {
case b: ExecutorAllocationClient =>
Some(new ExecutorAllocationManager(
schedulerBackend.asInstanceOf[ExecutorAllocationClient], listenerBus, _conf))
case _ =>
None
}
} else {
None
}
_executorAllocationManager.foreach(_.start())
_cleaner =
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.cleaner.referenceTracking", true)) {
Some(new ContextCleaner(this))
} else {
None
}
_cleaner.foreach(_.start())
setupAndStartListenerBus()
postEnvironmentUpdate()
postApplicationStart()
// Post init
_taskScheduler.postStartHook()
_env.metricsSystem.registerSource(_dagScheduler.metricsSource)
_env.metricsSystem.registerSource(new BlockManagerSource(_env.blockManager))
_executorAllocationManager.foreach { e =>
_env.metricsSystem.registerSource(e.executorAllocationManagerSource)
}
// Make sure the context is stopped if the user forgets about it. This avoids leaving
// unfinished event logs around after the JVM exits cleanly. It doesn't help if the JVM
// is killed, though.
logDebug("Adding shutdown hook") // force eager creation of logger
_shutdownHookRef = ShutdownHookManager.addShutdownHook(
ShutdownHookManager.SPARK_CONTEXT_SHUTDOWN_PRIORITY) { () =>
logInfo("Invoking stop() from shutdown hook")
stop()
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
logError("Error initializing SparkContext.", e)
try {
stop()
} catch {
case NonFatal(inner) =>
logError("Error stopping SparkContext after init error.", inner)
} finally {
throw e
}
}
val (sched, ts) = SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master, deployMode)语句执行如下:
/**
* Create a task scheduler based on a given master URL.
* Return a 2-tuple of the scheduler backend and the task scheduler.
*/
private def createTaskScheduler(
sc: SparkContext,
master: String,
deployMode: String): (SchedulerBackend, TaskScheduler) = {
import SparkMasterRegex._
// When running locally, don't try to re-execute tasks on failure.
val MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES = 1
master match {
case "local" =>
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true)
val backend = new LocalSchedulerBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, 1)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
case LOCAL_N_REGEX(threads) =>
def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors()
// local[*] estimates the number of cores on the machine; local[N] uses exactly N threads.
val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt
if (threadCount <= 0) {
throw new SparkException(s"Asked to run locally with $threadCount threads")
}
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true)
val backend = new LocalSchedulerBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
case LOCAL_N_FAILURES_REGEX(threads, maxFailures) =>
def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors()
// local[*, M] means the number of cores on the computer with M failures
// local[N, M] means exactly N threads with M failures
val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, maxFailures.toInt, isLocal = true)
val backend = new LocalSchedulerBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
case SPARK_REGEX(sparkUrl) =>
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc)
val masterUrls = sparkUrl.split(",").map("spark://" + _)
val backend = new StandaloneSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
(backend, scheduler)
case LOCAL_CLUSTER_REGEX(numSlaves, coresPerSlave, memoryPerSlave) =>
// Check to make sure memory requested <= memoryPerSlave. Otherwise Spark will just hang.
val memoryPerSlaveInt = memoryPerSlave.toInt
if (sc.executorMemory > memoryPerSlaveInt) {
throw new SparkException(
"Asked to launch cluster with %d MB RAM / worker but requested %d MB/worker".format(
memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.executorMemory))
}
val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc)
val localCluster = new LocalSparkCluster(
numSlaves.toInt, coresPerSlave.toInt, memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.conf)
val masterUrls = localCluster.start()
val backend = new StandaloneSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls)
scheduler.initialize(backend)
backend.shutdownCallback = (backend: StandaloneSchedulerBackend) => {
localCluster.stop()
}
(backend, scheduler)
case masterUrl =>
val cm = getClusterManager(masterUrl) match {
case Some(clusterMgr) => clusterMgr
case None => throw new SparkException("Could not parse Master URL: '" + master + "'")
}
try {
val scheduler = cm.createTaskScheduler(sc, masterUrl)
val backend = cm.createSchedulerBackend(sc, masterUrl, scheduler)
cm.initialize(scheduler, backend)
(backend, scheduler)
} catch {
case se: SparkException => throw se
case NonFatal(e) =>
throw new SparkException("External scheduler cannot be instantiated", e)
}
}
}
getClusterManager获取集群信息:
private def getClusterManager(url: String): Option[ExternalClusterManager] = {
val loader = Utils.getContextOrSparkClassLoader
val serviceLoaders =
ServiceLoader.load(classOf[ExternalClusterManager], loader).asScala.filter(_.canCreate(url))
if (serviceLoaders.size > 1) {
throw new SparkException(
s"Multiple external cluster managers registered for the url $url: $serviceLoaders")
}
serviceLoaders.headOption
}
由于集群是k8s:--master k8s://https://<k8s-apiserver-host>:<k8s-apiserver-port>,则对应KubernetesClusterManager
1、运行KubernetesClusterManager的createTaskScheduler函数,如下:
override def createTaskScheduler(sc: SparkContext, masterURL: String): TaskScheduler = {
val scheduler = new KubernetesTaskSchedulerImpl(sc)
sc.taskScheduler = scheduler
scheduler
}
KubernetesTaskSchedulerImpl类如下:
private[spark] class KubernetesTaskSchedulerImpl(sc: SparkContext) extends TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) {
override def createTaskSetManager(taskSet: TaskSet, maxTaskFailures: Int): TaskSetManager = {
new KubernetesTaskSetManager(this, taskSet, maxTaskFailures)
}
}
该类继承自TaskSchedulerImpl类
2、再看val backend = cm.createSchedulerBackend(sc, masterUrl, scheduler)语句,如下:
override def createSchedulerBackend(sc: SparkContext, masterURL: String, scheduler: TaskScheduler)
: SchedulerBackend = {
val sparkConf = sc.getConf
val maybeConfigMap = sparkConf.get(EXECUTOR_INIT_CONTAINER_CONFIG_MAP)
val maybeConfigMapKey = sparkConf.get(EXECUTOR_INIT_CONTAINER_CONFIG_MAP_KEY)
val maybeExecutorInitContainerSecretName =
sparkConf.get(EXECUTOR_INIT_CONTAINER_SECRET)
val maybeExecutorInitContainerSecretMount =
sparkConf.get(EXECUTOR_INIT_CONTAINER_SECRET_MOUNT_DIR)
val executorInitContainerSecretVolumePlugin = for {
initContainerSecretName <- maybeExecutorInitContainerSecretName
initContainerSecretMountPath <- maybeExecutorInitContainerSecretMount
} yield {
new InitContainerResourceStagingServerSecretPluginImpl(
initContainerSecretName,
initContainerSecretMountPath)
}
// Only set up the bootstrap if they've provided both the config map key and the config map
// name. Note that we generally expect both to have been set from spark-submit V2, but for
// testing developers may simply run the driver JVM locally, but the config map won't be set
// then.
val bootStrap = for {
configMap <- maybeConfigMap
configMapKey <- maybeConfigMapKey
} yield {
new SparkPodInitContainerBootstrapImpl(
sparkConf.get(INIT_CONTAINER_DOCKER_IMAGE),
sparkConf.get(INIT_CONTAINER_JARS_DOWNLOAD_LOCATION),
sparkConf.get(INIT_CONTAINER_FILES_DOWNLOAD_LOCATION),
sparkConf.get(INIT_CONTAINER_MOUNT_TIMEOUT),
configMap,
configMapKey,
executorInitContainerSecretVolumePlugin)
}
if (maybeConfigMap.isEmpty) {
logWarning("The executor's init-container config map was not specified. Executors will" +
" therefore not attempt to fetch remote or submitted dependencies.")
}
if (maybeConfigMapKey.isEmpty) {
logWarning("The executor's init-container config map key was not specified. Executors will" +
" therefore not attempt to fetch remote or submitted dependencies.")
}
val kubernetesClient = SparkKubernetesClientFactory.createKubernetesClient(
KUBERNETES_MASTER_INTERNAL_URL,
Some(sparkConf.get(KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE)),
APISERVER_AUTH_DRIVER_MOUNTED_CONF_PREFIX,
sparkConf,
Some(new File(Config.KUBERNETES_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_TOKEN_PATH)),
Some(new File(Config.KUBERNETES_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_CA_CRT_PATH)))
new KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend(
sc.taskScheduler.asInstanceOf[TaskSchedulerImpl], sc, bootStrap, kubernetesClient)
}
返回KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend对象,该类继承CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend类
3、再看KubernetesClusterManager的initialize函数,如下:
override def initialize(scheduler: TaskScheduler, backend: SchedulerBackend): Unit = {
scheduler.asInstanceOf[TaskSchedulerImpl].initialize(backend)
}
调用TaskSchedulerImpl的initialize函数,如下:
def initialize(backend: SchedulerBackend) {
this.backend = backend
// temporarily set rootPool name to empty
rootPool = new Pool("", schedulingMode, 0, 0)
schedulableBuilder = {
schedulingMode match {
case SchedulingMode.FIFO =>
new FIFOSchedulableBuilder(rootPool)
case SchedulingMode.FAIR =>
new FairSchedulableBuilder(rootPool, conf)
case _ =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"Unsupported spark.scheduler.mode: $schedulingMode")
}
}
schedulableBuilder.buildPools()
}
createTaskScheduler函数最后返回(backend, scheduler),如下:
try {
val scheduler = cm.createTaskScheduler(sc, masterUrl)
val backend = cm.createSchedulerBackend(sc, masterUrl, scheduler)
cm.initialize(scheduler, backend)
(backend, scheduler)
} catch {
case se: SparkException => throw se
case NonFatal(e) =>
throw new SparkException("External scheduler cannot be instantiated", e)
}
关系图示如下:
再看如下代码:
// start TaskScheduler after taskScheduler sets DAGScheduler reference in DAGScheduler's
// constructor
_taskScheduler.start()
运行TaskSchedulerImpl的start函数,如下:
override def start() {
backend.start()
if (!isLocal && conf.getBoolean("spark.speculation", false)) {
logInfo("Starting speculative execution thread")
speculationScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryOrStopSparkContext(sc) {
checkSpeculatableTasks()
}
}, SPECULATION_INTERVAL_MS, SPECULATION_INTERVAL_MS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
}
运行backend.start(),也即运行KubernetesClusterSchedulerBackend的start函数,如下:
override def start(): Unit = {
super.start()
executorWatchResource.set(kubernetesClient.pods().withLabel(SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL, applicationId())
.watch(new ExecutorPodsWatcher()))
allocator.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
allocatorRunnable, 0, podAllocationInterval, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
if (!Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(sc.conf)) {
doRequestTotalExecutors(initialExecutors)
} else {
shufflePodCache = shuffleServiceConfig
.map { config => new ShufflePodCache(
kubernetesClient, config.shuffleNamespace, config.shuffleLabels) }
shufflePodCache.foreach(_.start())
kubernetesExternalShuffleClient.foreach(_.init(applicationId()))
}
}
1、运行CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend的start函数,如下:
override def start() {
val properties = new ArrayBuffer[(String, String)]
for ((key, value) <- scheduler.sc.conf.getAll) {
if (key.startsWith("spark.")) {
properties += ((key, value))
}
}
// TODO (prashant) send conf instead of properties
driverEndpoint = createDriverEndpointRef(properties)
}
2、watch具有如下labels:spark-app-id:spark.kubernetes.driver.pod.name的Pod状态:
executorWatchResource.set(kubernetesClient.pods().withLabel(SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL, applicationId())
.watch(new ExecutorPodsWatcher()))
ExecutorPodsWatcher类如下:
private class ExecutorPodsWatcher extends Watcher[Pod] {
override def eventReceived(action: Action, pod: Pod): Unit = {
if (action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getStatus.getPhase == "Running"
&& pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp == null) {
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
val clusterNodeName = pod.getSpec.getNodeName
logDebug(s"Executor pod $pod ready, launched at $clusterNodeName as IP $podIP.")
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs += ((podIP, pod))
}
} else if ((action == Action.MODIFIED && pod.getMetadata.getDeletionTimestamp != null) ||
action == Action.DELETED || action == Action.ERROR) {
val podName = pod.getMetadata.getName
val podIP = pod.getStatus.getPodIP
logDebug(s"Executor pod $podName at IP $podIP was at $action.")
if (podIP != null) {
EXECUTOR_PODS_BY_IPS_LOCK.synchronized {
executorPodsByIPs -= podIP
}
}
}
}
override def onClose(cause: KubernetesClientException): Unit = {
logDebug("Executor pod watch closed.", cause)
}
}
3、在static allocation配置下(默认配置),执行doRequestTotalExecutors(initialExecutors)函数,设置totalExpectedExecutors为参数spark.executor.instances,如下:
protected var totalExpectedExecutors = new AtomicInteger(0)
override def doRequestTotalExecutors(requestedTotal: Int): Future[Boolean] = Future[Boolean] {
totalExpectedExecutors.set(requestedTotal)
true
}
private val initialExecutors = getInitialTargetExecutorNumber(1)
private def getInitialTargetExecutorNumber(defaultNumExecutors: Int = 1): Int = {
if (Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(conf)) {
val minNumExecutors = conf.getInt("spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors", 0)
val initialNumExecutors = Utils.getDynamicAllocationInitialExecutors(conf)
val maxNumExecutors = conf.getInt("spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors", 1)
require(initialNumExecutors >= minNumExecutors && initialNumExecutors <= maxNumExecutors,
s"initial executor number $initialNumExecutors must between min executor number " +
s"$minNumExecutors and max executor number $maxNumExecutors")
initialNumExecutors
} else {
conf.getInt("spark.executor.instances", defaultNumExecutors)
}
}
4、运行allocatorRunnable批量创建executorPod,如下:
private val runningExecutorPods = new mutable.HashMap[String, Pod] // Indexed by executor IDs.
// Total number of executors that are currently registered
protected val totalRegisteredExecutors = new AtomicInteger(0)
private val allocatorRunnable: Runnable = new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
if (totalRegisteredExecutors.get() < runningExecutorPods.size) {
logDebug("Waiting for pending executors before scaling")
} else if (totalExpectedExecutors.get() <= runningExecutorPods.size) {
logDebug("Maximum allowed executor limit reached. Not scaling up further.")
} else {
RUNNING_EXECUTOR_PODS_LOCK.synchronized {
for (i <- 0 until math.min(
totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorPods.size, podAllocationSize)) {
runningExecutorPods += allocateNewExecutorPod()
logInfo(
s"Requesting a new executor, total executors is now ${runningExecutorPods.size}")
}
}
}
}
}
这是创建executor的主要函数,逻辑很简单:
- 1、若已经成功创建的
executorpod数量(totalRegisteredExecutors) < 已经发出创建请求的数量(runningExecutorPods),则等待k8s创建executorpod,直到两者相等为止 - 2、若需要创建的
executorpod数量(totalExpectedExecutors)= 已经发出创建请求的数量(runningExecutorPods),则不再发出新的创建请求 - 3、否则,按照策略:
math.min(totalExpectedExecutors.get - runningExecutorPods.size, podAllocationSize)批量发出executorpod 创建请求,并同时增加runningExecutorPods数值
podAllocationSize数值如下:
private val podAllocationSize = conf.get(KUBERNETES_ALLOCATION_BATCH_SIZE)
private[spark] val KUBERNETES_ALLOCATION_BATCH_SIZE =
ConfigBuilder("spark.kubernetes.allocation.batch.size")
.doc("Number of pods to launch at once in each round of dynamic allocation. ")
.intConf
.createWithDefault(5)
其中,当每个executor pod被成功创建后,executor会调用CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend的receiveAndReply函数进行executor注册,同时相应地增加totalRegisteredExecutors数值,这个后续会详细说明
创建executor pod的具体逻辑在函数allocateNewExecutorPod中,如下:
private def allocateNewExecutorPod(): (String, Pod) = {
val executorId = EXECUTOR_ID_COUNTER.incrementAndGet().toString
val name = s"${applicationId()}-exec-$executorId"
// hostname must be no longer than 63 characters, so take the last 63 characters of the pod
// name as the hostname. This preserves uniqueness since the end of name contains
// executorId and applicationId
val hostname = name.substring(Math.max(0, name.length - 63))
val resolvedExecutorLabels = Map(
SPARK_EXECUTOR_ID_LABEL -> executorId,
SPARK_APP_ID_LABEL -> applicationId(),
SPARK_ROLE_LABEL -> "executor") ++
executorLabels
val executorMemoryQuantity = new QuantityBuilder(false)
.withAmount(s"${executorMemoryMb}M")
.build()
val executorMemoryLimitQuantity = new QuantityBuilder(false)
.withAmount(s"${executorMemoryWithOverhead}M")
.build()
val executorCpuQuantity = new QuantityBuilder(false)
.withAmount(executorCores)
.build()
val executorExtraClasspathEnv = executorExtraClasspath.map { cp =>
new EnvVarBuilder()
.withName(ENV_EXECUTOR_EXTRA_CLASSPATH)
.withValue(cp)
.build()
}
val requiredEnv = Seq(
(ENV_EXECUTOR_PORT, executorPort.toString),
(ENV_DRIVER_URL, driverUrl),
(ENV_EXECUTOR_CORES, executorCores),
(ENV_EXECUTOR_MEMORY, executorMemoryString),
(ENV_APPLICATION_ID, applicationId()),
(ENV_EXECUTOR_ID, executorId),
(ENV_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH, s"$executorJarsDownloadDir/*"))
.map(env => new EnvVarBuilder()
.withName(env._1)
.withValue(env._2)
.build()
) ++ Seq(
new EnvVarBuilder()
.withName(ENV_EXECUTOR_POD_IP)
.withValueFrom(new EnvVarSourceBuilder()
.withNewFieldRef("v1", "status.podIP")
.build())
.build()
)
val requiredPorts = Seq(
(EXECUTOR_PORT_NAME, executorPort),
(BLOCK_MANAGER_PORT_NAME, blockmanagerPort))
.map(port => {
new ContainerPortBuilder()
.withName(port._1)
.withContainerPort(port._2)
.build()
})
val basePodBuilder = new PodBuilder()
.withNewMetadata()
.withName(name)
.withLabels(resolvedExecutorLabels.asJava)
.withAnnotations(executorAnnotations.asJava)
.withOwnerReferences()
.addNewOwnerReference()
.withController(true)
.withApiVersion(driverPod.getApiVersion)
.withKind(driverPod.getKind)
.withName(driverPod.getMetadata.getName)
.withUid(driverPod.getMetadata.getUid)
.endOwnerReference()
.endMetadata()
.withNewSpec()
.withRestartPolicy("Never")
.withHostname(hostname)
.addNewContainer()
.withName(s"executor")
.withImage(executorDockerImage)
.withImagePullPolicy("IfNotPresent")
.withNewResources()
.addToRequests("memory", executorMemoryQuantity)
.addToLimits("memory", executorMemoryLimitQuantity)
.addToRequests("cpu", executorCpuQuantity)
.addToLimits("cpu", executorCpuQuantity)
.endResources()
.addAllToEnv(requiredEnv.asJava)
.addToEnv(executorExtraClasspathEnv.toSeq: _*)
.withPorts(requiredPorts.asJava)
.endContainer()
.endSpec()
val withMaybeShuffleConfigPodBuilder = shuffleServiceConfig
.map { config =>
config.shuffleDirs.foldLeft(basePodBuilder) { (builder, dir) =>
builder
.editSpec()
.addNewVolume()
.withName(FilenameUtils.getBaseName(dir))
.withNewHostPath()
.withPath(dir)
.endHostPath()
.endVolume()
.editFirstContainer()
.addNewVolumeMount()
.withName(FilenameUtils.getBaseName(dir))
.withMountPath(dir)
.endVolumeMount()
.endContainer()
.endSpec()
}
}.getOrElse(basePodBuilder)
val resolvedExecutorPod = executorInitContainerBootstrap.map { bootstrap =>
bootstrap.bootstrapInitContainerAndVolumes(
"executor",
withMaybeShuffleConfigPodBuilder)
}.getOrElse(withMaybeShuffleConfigPodBuilder)
try {
(executorId, kubernetesClient.pods.create(resolvedExecutorPod.build()))
} catch {
case throwable: Throwable =>
logError("Failed to allocate executor pod.", throwable)
throw throwable
}
}
返回创建的executor pod的id和Pod对象实例(这个时候k8s不一定成功创建了相应的Pod)
三、executor与driver交互(executor注册)
如下是executor Dockerfile内容:
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
FROM openjdk:8-alpine
# If this docker file is being used in the context of building your images from a Spark distribution, the docker build
# command should be invoked from the top level directory of the Spark distribution. E.g.:
# docker build -t spark-executor:latest -f dockerfiles/executor/Dockerfile .
RUN apk upgrade --update
RUN apk add --update bash tini
RUN mkdir -p /opt/spark
RUN touch /opt/spark/RELEASE
ADD jars /opt/spark/jars
ADD examples /opt/spark/examples
ADD bin /opt/spark/bin
ADD sbin /opt/spark/sbin
ADD conf /opt/spark/conf
ENV SPARK_HOME /opt/spark
WORKDIR /opt/spark
# TODO support spark.executor.extraClassPath
CMD SPARK_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/jars/*" && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH}+x} ]; then SPARK_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_MOUNTED_CLASSPATH:$SPARK_CLASSPATH"; fi && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_EXECUTOR_EXTRA_CLASSPATH+x} ]; then SPARK_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_EXECUTOR_EXTRA_CLASSPATH:$SPARK_CLASSPATH"; fi && \
if ! [ -z ${SPARK_MOUNTED_FILES_DIR} ]; then cp -R "$SPARK_MOUNTED_FILES_DIR/." .; fi && \
exec /sbin/tini -- ${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java -Dspark.executor.port=$SPARK_EXECUTOR_PORT -Xms$SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY -Xmx$SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY -cp $SPARK_CLASSPATH org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend --driver-url $SPARK_DRIVER_URL --executor-id $SPARK_EXECUTOR_ID --cores $SPARK_EXECUTOR_CORES --app-id $SPARK_APPLICATION_ID --hostname $SPARK_EXECUTOR_POD_IP
根据Dockerfile内容,可以知道在executor容器起来后会执行org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend,如下:
private[spark] object CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend extends Logging {
private def run(
driverUrl: String,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
cores: Int,
appId: String,
workerUrl: Option[String],
userClassPath: Seq[URL]) {
Utils.initDaemon(log)
SparkHadoopUtil.get.runAsSparkUser { () =>
// Debug code
Utils.checkHost(hostname)
// Bootstrap to fetch the driver's Spark properties.
val executorConf = new SparkConf
val port = executorConf.getInt("spark.executor.port", 0)
val fetcher = RpcEnv.create(
"driverPropsFetcher",
hostname,
port,
executorConf,
new SecurityManager(executorConf),
clientMode = true)
val driver = fetcher.setupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl)
val cfg = driver.askWithRetry[SparkAppConfig](RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId))
val props = cfg.sparkProperties ++ Seq[(String, String)](("spark.app.id", appId))
fetcher.shutdown()
// Create SparkEnv using properties we fetched from the driver.
val driverConf = new SparkConf()
for ((key, value) <- props) {
// this is required for SSL in standalone mode
if (SparkConf.isExecutorStartupConf(key)) {
driverConf.setIfMissing(key, value)
} else {
driverConf.set(key, value)
}
}
if (driverConf.contains("spark.yarn.credentials.file")) {
logInfo("Will periodically update credentials from: " +
driverConf.get("spark.yarn.credentials.file"))
SparkHadoopUtil.get.startCredentialUpdater(driverConf)
}
val env = SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv(
driverConf, executorId, hostname, port, cores, cfg.ioEncryptionKey, isLocal = false)
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor", new CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(
env.rpcEnv, driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, userClassPath, env))
workerUrl.foreach { url =>
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("WorkerWatcher", new WorkerWatcher(env.rpcEnv, url))
}
env.rpcEnv.awaitTermination()
SparkHadoopUtil.get.stopCredentialUpdater()
}
}
def main(args: Array[String]) {
var driverUrl: String = null
var executorId: String = null
var hostname: String = null
var cores: Int = 0
var appId: String = null
var workerUrl: Option[String] = None
val userClassPath = new mutable.ListBuffer[URL]()
var argv = args.toList
while (!argv.isEmpty) {
argv match {
case ("--driver-url") :: value :: tail =>
driverUrl = value
argv = tail
case ("--executor-id") :: value :: tail =>
executorId = value
argv = tail
case ("--hostname") :: value :: tail =>
hostname = value
argv = tail
case ("--cores") :: value :: tail =>
cores = value.toInt
argv = tail
case ("--app-id") :: value :: tail =>
appId = value
argv = tail
case ("--worker-url") :: value :: tail =>
// Worker url is used in spark standalone mode to enforce fate-sharing with worker
workerUrl = Some(value)
argv = tail
case ("--user-class-path") :: value :: tail =>
userClassPath += new URL(value)
argv = tail
case Nil =>
case tail =>
// scalastyle:off println
System.err.println(s"Unrecognized options: ${tail.mkString(" ")}")
// scalastyle:on println
printUsageAndExit()
}
}
if (driverUrl == null || executorId == null || hostname == null || cores <= 0 ||
appId == null) {
printUsageAndExit()
}
run(driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, appId, workerUrl, userClassPath)
System.exit(0)
}
private def printUsageAndExit() = {
// scalastyle:off println
System.err.println(
"""
|Usage: CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend [options]
|
| Options are:
| --driver-url <driverUrl>
| --executor-id <executorId>
| --hostname <hostname>
| --cores <cores>
| --app-id <appid>
| --worker-url <workerUrl>
| --user-class-path <url>
|""".stripMargin)
// scalastyle:on println
System.exit(1)
}
}
解析参数后执行run(driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, appId, workerUrl, userClassPath),如下:
1、Bootstrap to fetch the driver's Spark properties,如下:
// Bootstrap to fetch the driver's Spark properties.
val executorConf = new SparkConf
val port = executorConf.getInt("spark.executor.port", 0)
val fetcher = RpcEnv.create(
"driverPropsFetcher",
hostname,
port,
executorConf,
new SecurityManager(executorConf),
clientMode = true)
val driver = fetcher.setupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl)
val cfg = driver.askWithRetry[SparkAppConfig](RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId))
val props = cfg.sparkProperties ++ Seq[(String, String)](("spark.app.id", appId))
fetcher.shutdown()
2、Create SparkEnv using properties we fetched from the driver,如下:
// Create SparkEnv using properties we fetched from the driver.
val driverConf = new SparkConf()
for ((key, value) <- props) {
// this is required for SSL in standalone mode
if (SparkConf.isExecutorStartupConf(key)) {
driverConf.setIfMissing(key, value)
} else {
driverConf.set(key, value)
}
}
if (driverConf.contains("spark.yarn.credentials.file")) {
logInfo("Will periodically update credentials from: " +
driverConf.get("spark.yarn.credentials.file"))
SparkHadoopUtil.get.startCredentialUpdater(driverConf)
}
3、construct CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend,如下:
val env = SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv(
driverConf, executorId, hostname, port, cores, cfg.ioEncryptionKey, isLocal = false)
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor", new CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(
env.rpcEnv, driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, userClassPath, env))
workerUrl.foreach { url =>
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("WorkerWatcher", new WorkerWatcher(env.rpcEnv, url))
}
env.rpcEnv.awaitTermination()
SparkHadoopUtil.get.stopCredentialUpdater()
CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend类如下:
private[spark] class CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(
override val rpcEnv: RpcEnv,
driverUrl: String,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
cores: Int,
userClassPath: Seq[URL],
env: SparkEnv)
extends ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint with ExecutorBackend with Logging {
private[this] val stopping = new AtomicBoolean(false)
var executor: Executor = null
@volatile var driver: Option[RpcEndpointRef] = None
// If this CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend is changed to support multiple threads, then this may need
// to be changed so that we don't share the serializer instance across threads
private[this] val ser: SerializerInstance = env.closureSerializer.newInstance()
override def onStart() {
logInfo("Connecting to driver: " + driverUrl)
rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
driver = Some(ref)
ref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls))
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
case Success(msg) =>
// Always receive `true`. Just ignore it
case Failure(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e, notifyDriver = false)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
def extractLogUrls: Map[String, String] = {
val prefix = "SPARK_LOG_URL_"
sys.env.filterKeys(_.startsWith(prefix))
.map(e => (e._1.substring(prefix.length).toLowerCase, e._2))
}
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisteredExecutor =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")
try {
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)
}
case RegisterExecutorFailed(message) =>
exitExecutor(1, "Slave registration failed: " + message)
case LaunchTask(data) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received LaunchTask command but executor was null")
} else {
val taskDesc = ser.deserialize[TaskDescription](data.value)
logInfo("Got assigned task " + taskDesc.taskId)
executor.launchTask(this, taskId = taskDesc.taskId, attemptNumber = taskDesc.attemptNumber,
taskDesc.name, taskDesc.serializedTask)
}
case KillTask(taskId, _, interruptThread) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received KillTask command but executor was null")
} else {
executor.killTask(taskId, interruptThread)
}
case StopExecutor =>
stopping.set(true)
logInfo("Driver commanded a shutdown")
// Cannot shutdown here because an ack may need to be sent back to the caller. So send
// a message to self to actually do the shutdown.
self.send(Shutdown)
case Shutdown =>
stopping.set(true)
new Thread("CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend-stop-executor") {
override def run(): Unit = {
// executor.stop() will call `SparkEnv.stop()` which waits until RpcEnv stops totally.
// However, if `executor.stop()` runs in some thread of RpcEnv, RpcEnv won't be able to
// stop until `executor.stop()` returns, which becomes a dead-lock (See SPARK-14180).
// Therefore, we put this line in a new thread.
executor.stop()
}
}.start()
}
override def onDisconnected(remoteAddress: RpcAddress): Unit = {
if (stopping.get()) {
logInfo(s"Driver from $remoteAddress disconnected during shutdown")
} else if (driver.exists(_.address == remoteAddress)) {
exitExecutor(1, s"Driver $remoteAddress disassociated! Shutting down.", null,
notifyDriver = false)
} else {
logWarning(s"An unknown ($remoteAddress) driver disconnected.")
}
}
override def statusUpdate(taskId: Long, state: TaskState, data: ByteBuffer) {
val msg = StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data)
driver match {
case Some(driverRef) => driverRef.send(msg)
case None => logWarning(s"Drop $msg because has not yet connected to driver")
}
}
/**
* This function can be overloaded by other child classes to handle
* executor exits differently. For e.g. when an executor goes down,
* back-end may not want to take the parent process down.
*/
protected def exitExecutor(code: Int,
reason: String,
throwable: Throwable = null,
notifyDriver: Boolean = true) = {
val message = "Executor self-exiting due to : " + reason
if (throwable != null) {
logError(message, throwable)
} else {
logError(message)
}
if (notifyDriver && driver.nonEmpty) {
driver.get.ask[Boolean](
RemoveExecutor(executorId, new ExecutorLossReason(reason))
).onFailure { case e =>
logWarning(s"Unable to notify the driver due to " + e.getMessage, e)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
System.exit(code)
}
}
执行onStart函数注册自身,如下:
override def onStart() {
logInfo("Connecting to driver: " + driverUrl)
rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
driver = Some(ref)
ref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls))
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
case Success(msg) =>
// Always receive `true`. Just ignore it
case Failure(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e, notifyDriver = false)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
远程调用driver类CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend的RegisterExecutor函数,如下:
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {
executorRef.send(RegisterExecutorFailed("Duplicate executor ID: " + executorId))
context.reply(true)
} else {
// If the executor's rpc env is not listening for incoming connections, `hostPort`
// will be null, and the client connection should be used to contact the executor.
val executorAddress = if (executorRef.address != null) {
executorRef.address
} else {
context.senderAddress
}
logInfo(s"Registered executor $executorRef ($executorAddress) with ID $executorId")
addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorId
totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)
totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorRef.address, hostname,
cores, cores, logUrls)
// This must be synchronized because variables mutated
// in this block are read when requesting executors
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {
executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)
if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {
currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt
}
if (numPendingExecutors > 0) {
numPendingExecutors -= 1
logDebug(s"Decremented number of pending executors ($numPendingExecutors left)")
}
}
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the map
context.reply(true)
listenerBus.post(
SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))
makeOffers()
}
case StopDriver =>
context.reply(true)
stop()
case StopExecutors =>
logInfo("Asking each executor to shut down")
for ((_, executorData) <- executorDataMap) {
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor)
}
context.reply(true)
case RemoveExecutor(executorId, reason) =>
// We will remove the executor's state and cannot restore it. However, the connection
// between the driver and the executor may be still alive so that the executor won't exit
// automatically, so try to tell the executor to stop itself. See SPARK-13519.
executorDataMap.get(executorId).foreach(_.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor))
removeExecutor(executorId, reason)
context.reply(true)
case RetrieveSparkAppConfig(executorId) =>
val reply = SparkAppConfig(sparkProperties,
SparkEnv.get.securityManager.getIOEncryptionKey())
context.reply(reply)
}
driver在收到executor的Rpc RegisterExecutor调用后,便将executor的信息存放到executorDataMap中,如下:
val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorRef.address, hostname,cores, cores, logUrls)
...
executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)
...
最后向executor发送RegisteredExecutor消息,如下:
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the map
context.reply(true)
而executor在收到RegisteredExecutor消息后,执行如下代码段:
case RegisteredExecutor =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")
try {
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)
}
也即创建Executor实例,如下:
/**
* Spark executor, backed by a threadpool to run tasks.
*
* This can be used with Mesos, YARN, and the standalone scheduler.
* An internal RPC interface is used for communication with the driver,
* except in the case of Mesos fine-grained mode.
*/
private[spark] class Executor(
executorId: String,
executorHostname: String,
env: SparkEnv,
userClassPath: Seq[URL] = Nil,
isLocal: Boolean = false)
extends Logging {
logInfo(s"Starting executor ID $executorId on host $executorHostname")
...
这样从submit交付spark application到driver Pod产生,再到所有executor Pod产生就分析完毕了,大致图示如下: