前言
在企业生产环境,Kubernetes高可用是一个必不可少的特性,其中最通用的场景就是如何在Kubernetes集群宕机一个节点的情况下保障服务依旧可用
本文就针对这个场景下在实现集群和应用高可用过程中遇到的各种问题进行一个梳理和总结
整体架构
本文描述的高可用方案对应架构如下:
- control plane node
管理节点采用kubeadm搭建的3节点标准高可用方案(Stacked etcd topology):
该方案中,所有管理节点都部署kube-apiserver,kube-controller-manager,kube-scheduler,以及etcd等组件;kube-apiserver均与本地的etcd进行通信,etcd在三个节点间同步数据;而kube-controller-manager和kube-scheduler也只与本地的kube-apiserver进行通信(或者通过LB访问)
kube-apiserver前面顶一个LB;work节点kubelet以及kube-proxy组件对接LB访问apiserver
在这种架构中,如果其中任意一个master节点宕机了,由于kube-controller-manager以及kube-scheduler基于Leader Election Mechanism实现了高可用,可以认为管理集群不受影响,相关组件依旧正常运行(在分布式锁释放后)
- work node
工作节点上部署应用,应用按照反亲和部署多个副本,使副本调度在不同的work node上,这样如果其中一个副本所在的母机宕机了,理论上通过Kubernetes service可以把请求切换到另外副本上,使服务依旧可用
网络
针对上述架构,我们分析一下实际环境中节点宕机对网络层面带来的影响
service backend剔除
正如上文所述,工作节点上应用会按照反亲和部署。这里我们讨论最简单的情况:例如一个nginx服务,部署了两个副本,分别落在work node1和work node2上
集群中还部署了依赖nginx服务的应用A,如果某个时刻work node1宕机了,此时应用A访问nginx service会有问题吗?
这里答案是会有问题。因为service不会马上剔除掉宕机上对应的nginx pod,同时由于service常用的iptables代理模式没有实现retry with another backend特性,所以在一段时间内访问会出现间歇性问题(如果请求轮询到挂掉的nginx pod上),也就是说会存在一个访问失败间隔期
这个间隔期取决于service对应的endpoint什么时候踢掉宕机的pod。之后,kube-proxy会watch到endpoint变化,然后更新对应的iptables规则,使service访问后端列表恢复正常(也就是踢掉该pod)
要理解这个间隔,我们首先需要弄清楚Kubernetes节点心跳的概念:
每个node在kube-node-lease namespace下会对应一个Lease object,kubelet每隔node-status-update-frequency时间(默认10s)会更新对应node的Lease object
node-controller会每隔node-monitor-period时间(默认5s)检查Lease object是否更新,如果超过node-monitor-grace-period时间(默认40s)没有发生过更新,则认为这个node不健康,会更新NodeStatus(ConditionUnknown)。如果这样的状态在这之后持续了一段时间(默认5mins),则会驱逐(evict)该node上的pod
对于母机宕机的场景,node controller在node-monitor-grace-period时间段没有观察到心跳的情况下,会更新NodeStatus(ConditionUnknown),之后endpoint controller会从endpoint backend中踢掉该母机上的所有pod,最终服务访问正常,请求不会落在挂掉的pod上
也就是说在母机宕机后,在node-monitor-grace-period间隔内访问service会有间歇性问题,我们可以通过调整相关参数来缩小这个窗口期,如下:
(kubelet)node-status-update-frequency:default 10s
(kube-controller-manager)node-monitor-period:default 5s
(kube-controller-manager)node-monitor-grace-period:default 40s
- Amount of time which we allow running Node to be unresponsive before marking it unhealthy. Must be N times more than kubelet's nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, where N means number of retries allowed for kubelet to post node status.
- Currently nodeStatusUpdateRetry is constantly set to 5 in kubelet.go
连接复用(长连接)
对于使用长连接访问的应用来说(默认使用都是tcp长连接,无论HTTP/2还是HTTP/1),在没有设置合适请求timeout参数的情况下可能会出现15mins的超时问题,详情见Kubernetes Controller高可用诡异的15mins超时。解决方案如下:
通过上面的分析,可以知道是TCP的ARQ机制导致了Controller在母机宕机后15mins内一直超时重试,超时重试失败后,tcp socket关闭,应用重新创建连接
这个问题本质上不是Kubernetes的问题,而是应用在复用tcp socket(长连接)时没有考虑设置超时,导致了母机宕机后,tcp socket没有及时关闭,服务依旧使用失效连接导致异常
要解决这个问题,可以从两方面考虑:
- 应用层使用超时设置或者健康检查机制,从上层保障连接的健康状态 - 作用于该应用
- 底层调整TCP ARQ设置(/proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_retries2),缩小超时重试周期,作用于整个集群
由于应用层的超时或者健康检查机制无法使用统一的方案,这里只介绍如何采用系统配置的方式规避无效连接,如下:
# 0.2+0.4+0.8+1.6+3.2+6.4+12.8+25.6+51.2+102.4 = 222.6s $ echo 9 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_retries2
另外对于推送类的服务,比如Watch,在母机宕机后,可以通过tcp keepalive机制来关闭无效连接(这也是上面测试cluster-coredns-controller时其中一个连接5分钟(30+30*9=300s)断开的原因):
# 30 + 30*5 = 180s $ echo 30 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_keepalive_time $ echo 30 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_keepalive_intvl $ echo 5 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_keepalive_probes
注意:在Kubernetes环境中,容器不会直接继承母机tcp keepalive的配置(可以直接继承母机tcp超时重试的配置),因此必须通过一定方式进行适配。这里介绍其中一种方式,添加initContainers使配置生效:
- name: init-sysctl image: busybox command: - /bin/sh - -c - | sysctl -w net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time=30 sysctl -w net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl=30 sysctl -w net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes=5 securityContext: privileged: true
通过上述的TCP keepalive以及TCP ARQ配置,我们可以将无效连接断开时间缩短到4分钟以内,一定程度上解决了母机宕机导致的连接异常问题。不过最好的解决方案是在应用层设置超时或者健康检查机制及时关闭底层无效连接
节点驱逐
这里我们对节点驱逐分应用和存储两方面进行分析:
应用相关
pod驱逐可以使服务自动恢复副本数量。如上所述,node controller会在节点心跳超时之后一段时间(默认5mins)驱逐该节点上的pod,这个时间由如下参数决定:
(kube-apiserver)default-not-ready-toleration-seconds:default 300
(kube-apiserver)default-unreachable-toleration-seconds:default 300
Note: Kubernetes automatically adds a toleration for node.kubernetes.io/not-ready and node.kubernetes.io/unreachable with tolerationSeconds=300, unless you, or a controller, set those tolerations explicitly. These automatically-added tolerations mean that Pods remain bound to Nodes for 5 minutes after one of these problems is detected.
这里面涉及两个tolerations:
- node.kubernetes.io/not-ready: Node is not ready. This corresponds to the NodeCondition Ready being “False”.
- node.kubernetes.io/unreachable: Node is unreachable from the node controller. This corresponds to the NodeCondition Ready being “Unknown”.
tolerations:
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready
operator: Exists
tolerationSeconds: 300
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable
operator: Exists
tolerationSeconds: 300
当节点心跳超时(ConditionUnknown)之后,node controller会给该node添加如下taints:
spec:
...
taints:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable
timeAdded: "2020-07-02T03:50:47Z"
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable
timeAdded: "2020-07-02T03:50:53Z"
由于pod对node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute taint容忍时间为300s,因此node controller会在5mins之后驱逐该节点上的pod
这里面有比较特殊的情况,例如:statefulset,daemonset以及static pod。我们逐一说明:
- statefulset
pod删除存在两个阶段,第一个阶段是controller-manager设置pod的spec.deletionTimestamp字段为非nil值;第二个阶段是kubelet完成实际的pod删除操作(volume detach,container删除等)
当node宕机后,显然kubelet无法完成第二阶段的操作,因此controller-manager认为pod并没有被删除掉,在这种情况下statefulset工作负载形式的pod不会产生新的替换pod,并一直处于”Terminating”状态
Like a Deployment, a StatefulSet manages Pods that are based on an identical container spec. Unlike a Deployment, a StatefulSet maintains a sticky identity for each of their Pods. These pods are created from the same spec, but are not interchangeable: each has a persistent identifier that it maintains across any rescheduling.
In normal operation of a StatefulSet, there is never a need to force delete a StatefulSet Pod. The StatefulSet controller is responsible for creating, scaling and deleting members of the StatefulSet. It tries to ensure that the specified number of Pods from ordinal 0 through N-1 are alive and ready. StatefulSet ensures that, at any time, there is at most one Pod with a given identity running in a cluster. This is referred to as at most one semantics provided by a StatefulSet.
原因是statefulset为了保障at most one semantics,需要满足对于指定identity同时只有一个pod存在。在node shoudown后,虽然pod被驱逐了(“Terminating”),但是由于controller无法判断这个statefulset pod是否还在运行(因为并没有彻底删除),故不会产生替换容器,一定是要等到这个pod被完全删除干净(by kubelet),才会产生替换容器(deployment不需要满足这个条件,所以在驱逐pod时,controller会马上产生替换pod,而不需要等待kubelet删除pod)
- daemonset
daemonset则更加特殊,默认情况下daemonset pod会被设置多个tolerations,使其可以容忍节点几乎所有异常的状态,所以不会出现驱逐的情况。这也很好理解,因为daemonset本来就是一个node部署一个pod,如下:
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: dns
operator: Equal
value: "false"
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable
operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node.kubernetes.io/disk-pressure
operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node.kubernetes.io/memory-pressure
operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node.kubernetes.io/pid-pressure
operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node.kubernetes.io/unschedulable
operator: Exists
- static pod
static pod类型类似daemonset会设置tolerations容忍节点异常状态,如下:
tolerations:
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
因此在节点宕机后,static pod也不会发生驱逐
存储相关
当pod使用的volume只支持RWO读写模式时,如果pod所在母机宕机了,并且随后在其它母机上产生了替换副本,则该替换副本的创建会阻塞,如下所示:
$ kubectl get pods -o wide
nginx-7b4d5d9fd-bmc8g 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> 10.0.0.1 <none> <none>
nginx-7b4d5d9fd-nqgfz 1/1 Terminating 0 19m 192.28.1.165 10.0.0.2 <none> <none>
$ kubectl describe pods/nginx-7b4d5d9fd-bmc8g
[...truncate...]
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 3m5s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/nginx-7b4d5d9fd-bmc8g to 10.0.0.1
Warning FailedAttachVolume 3m5s attachdetach-controller Multi-Attach error for volume "pvc-7f68c087-9e56-11ea-a2ef-5254002f7cc9" Volume is already used by pod(s) nginx-7b4d5d9fd-nqgfz
Warning FailedMount 62s kubelet, 10.0.0.1 Unable to mount volumes for pod "nginx-7b4d5d9fd-bmc8g_default(bb5501ca-9fea-11ea-9730-5254002f7cc9)": timeout expired waiting for volumes to attach or mount for pod "default"/"nginx-7b4d5d9fd-nqgfz". list of unmounted volumes=[nginx-data]. list of unattached volumes=[root-certificate default-token-q2vft nginx-data]
这是因为只支持RWO(ReadWriteOnce – the volume can be mounted as read-write by a single node)的volume正常情况下在Kubernetes集群中只能被一个母机attach,由于宕机母机无法执行volume detach操作,其它母机上的pod如果使用相同的volume会被挂住,最终导致容器创建一直阻塞并报错:
Multi-Attach error for volume "pvc-7f68c087-9e56-11ea-a2ef-5254002f7cc9" Volume is already used by pod(s) nginx-7b4d5d9fd-nqgfz
解决办法是采用支持RWX(ReadWriteMany – the volume can be mounted as read-write by many nodes)读写模式的volume。另外如果必须采用只支持RWO模式的volume,则可以执行如下命令强制删除pod,如下:
$ kubectl delete pods/nginx-7b4d5d9fd-nqgfz --force --grace-period=0
之后,对于新创建的pod,attachDetachController会在6mins(代码写死)后强制detach volume,并正常attach,如下:
W0811 04:01:25.024422 1 reconciler.go:328] Multi-Attach error for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1" (UniqueName: "kubernetes.io/rbd/k8s:kubernetes-dynamic-pvc-f35fc6fa-d8a6-11ea-bd98-aeb6842de1e3") from node "10.0.0.3" Volume is already exclusively attached to node 10.0.0.2 and can't be attached to another
I0811 04:01:25.024480 1 event.go:209] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Pod", Namespace:"default", Name:"default-nginx-6584f7ddb7-jx9s2", UID:"5322240f-db87-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1", APIVersion:"v1", ResourceVersion:"28275287", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Warning' reason: 'FailedAttachVolume' Multi-Attach error for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1" Volume is already exclusively attached to one node and can't be attached to another
W0811 04:07:25.047767 1 reconciler.go:232] attacherDetacher.DetachVolume started for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1" (UniqueName: "kubernetes.io/rbd/k8s:kubernetes-dynamic-pvc-f35fc6fa-d8a6-11ea-bd98-aeb6842de1e3") on node "10.0.0.2" This volume is not safe to detach, but maxWaitForUnmountDuration 6m0s expired, force detaching
I0811 04:07:25.047860 1 operation_generator.go:500] DetachVolume.Detach succeeded for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1" (UniqueName: "kubernetes.io/rbd/k8s:kubernetes-dynamic-pvc-f35fc6fa-d8a6-11ea-bd98-aeb6842de1e3") on node "10.0.0.2"
I0811 04:07:25.148094 1 reconciler.go:288] attacherDetacher.AttachVolume started for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1" (UniqueName: "kubernetes.io/rbd/k8s:kubernetes-dynamic-pvc-f35fc6fa-d8a6-11ea-bd98-aeb6842de1e3") from node "10.0.0.3"
I0811 04:07:25.148180 1 operation_generator.go:377] AttachVolume.Attach succeeded for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1" (UniqueName: "kubernetes.io/rbd/k8s:kubernetes-dynamic-pvc-f35fc6fa-d8a6-11ea-bd98-aeb6842de1e3") from node "10.0.0.3"
I0811 04:07:25.148266 1 event.go:209] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Pod", Namespace:"default", Name:"default-nginx-6584f7ddb7-jx9s2", UID:"5322240f-db87-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1", APIVersion:"v1", ResourceVersion:"28275287", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'SuccessfulAttachVolume' AttachVolume.Attach succeeded for volume "pvc-e97c6ce6-d8a6-11ea-b832-7a866c097df1"
而默认的6mins对于生产环境来说太长了,而且Kubernetes并没有提供参数进行配置,因此我向官方提了一个PR用于解决这个问题,如下:
--attach-detach-reconcile-max-wait-unmount-duration duration maximum amount of time the attach detach controller will wait for a volume to be safely unmounted from its node. Once this time has expired, the controller will assume the node or kubelet are unresponsive and will detach the volume anyway. (default 6m0s)
通过配置attach-detach-reconcile-max-wait-unmount-duration,可以缩短替换pod成功运行的时间
另外,注意force detaching逻辑只会在pod被force delete的时候触发,正常delete不会触发该逻辑
存储
对于存储,可以分为Kubernetes系统存储和应用存储,系统存储专指etcd;而应用存储一般来说只考虑persistent volume
系统存储 - etcd
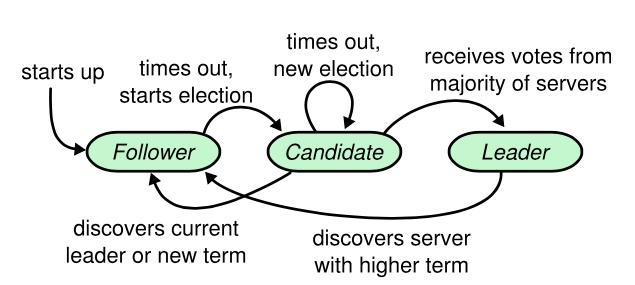
etcd使用Raft一致性算法(leader selection + log replication + safety)中的leader selection来实现节点宕机下的高可用问题,如下:
应用存储 - persistent volume
这里考虑存储是部署在集群外的情况(通常情况)。如果一个母机宕机了,由于没有对外部存储集群产生破坏,因此不会影响其它母机上应用访问pv存储
而对于Kubernetes存储本身组件功能(in-tree, flexVolume, external-storage以及csi)的影响实际上可以归纳为对存储插件应用的影响,这里以csi为例子进行说明:
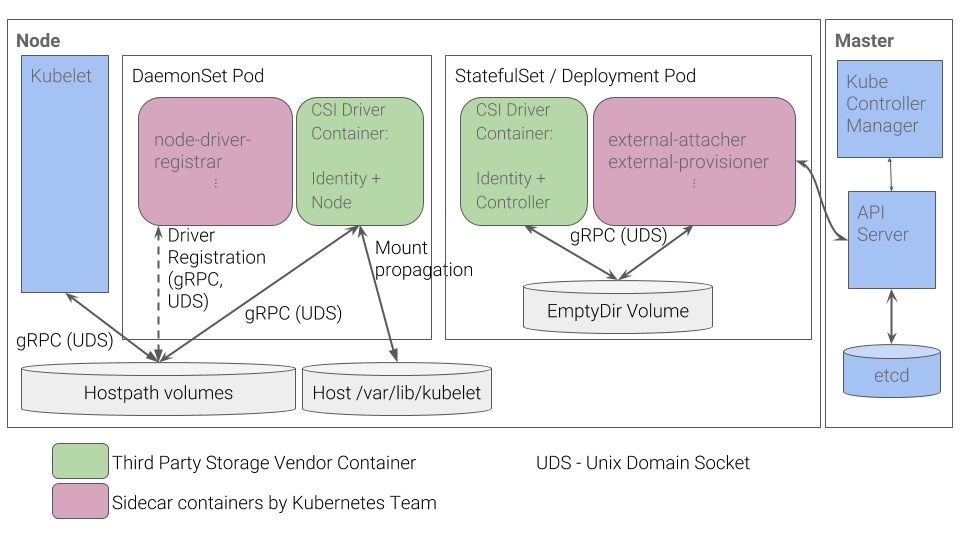
通过实现对上述StatefulSet/Deployment工作负载类型应用(CSI Driver+Identity Controller以及external-attacher+external-provisioner)的高可用即可
应用
Stateless Application
对于无状态的服务(通常部署为deployment工作负载),我们可以直接通过设置反亲和+多副本来实现高可用,例如nginx服务:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: web-server
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web-store
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web-store
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- web-store
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
containers:
- name: web-app
image: nginx:1.16-alpine
如果其中一个pod所在母机宕机了,则在endpoint controller踢掉该pod backend后,服务访问正常
这类服务通常依赖于其它有状态服务,例如:WebServer,APIServer等
Stateful Application
对于有状态的服务,可以按照高可用的实现类型分类如下:
- RWX Type
对于本身基于多副本实现高可用的应用来说,我们可以直接利用反亲和+多副本进行部署(一般部署为deployment类型),后接同一个存储(支持ReadWriteMany,例如:Cephfs or Ceph RGW),实现类似无状态服务的高可用模式
其中,docker distribution,helm chartmuseum以及harbor jobservice等都属于这种类型
- Special Type
对于特殊类型的应用,例如database,它们一般有自己定制的高可用方案,例如常用的主从模式
这类应用通常以statefulset的形式进行部署,每个副本对接一个pv,在母机宕机的情况下,由应用本身实现高可用(例如:master选举-主备切换)
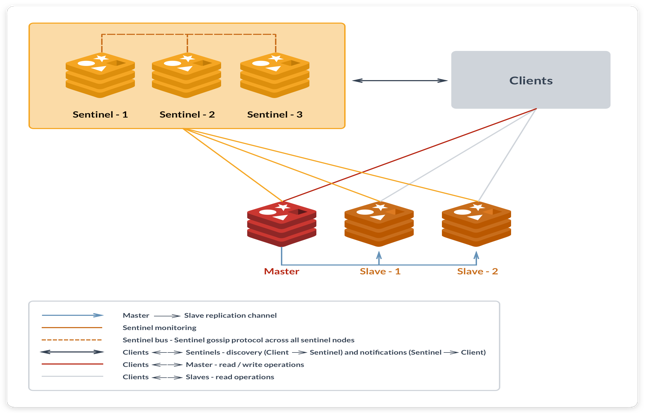
其中,redis,postgres,以及各类db都基本是这种模式,如下是redis一主两从三哨高可用方案:
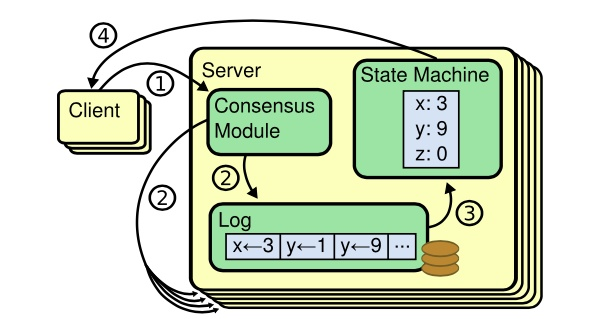
还有更加复杂的高可用方案,例如etcd的Raft一致性算法:
- Distributed Lock Type
Kubernetes Controller就是利用分布式锁实现高可用
这里归纳了一些应用常用的实现高可用的方案。当然了,各个应用可以定制适合自身的高可用方案,不可能完全一样
Conclusion
本文先介绍了Kubernetes集群高可用的整体架构,之后基于该架构从网络,存储,以及应用层面分析了当节点宕机时可能会出现的问题以及对应的解决方案,希望对Kubernetes高可用实践有所助益。实际生产环境需要综合上述因素全面考虑,将整体服务的恢复时间控制在一个可以接受的范围内

