前言
对于正常环境部署的harbor,可以外网拉取CVE,进行镜像扫描;但如果内网部署且无法连接外网,则必须做一些处理进行适配……
clair
harbor使用clair组件进行镜像扫描,clair是CoreOS开发的容器漏洞静态分析工具,原理如下:
Clair is an open source project for the static analysis of vulnerabilities in application containers (currently including appc and docker).
1.In regular intervals, Clair ingests vulnerability metadata from a configured set of sources and stores it in the database.
2.Clients use the Clair API to index their container images; this creates a list of features present in the image and stores them in the database.
3.Clients use the Clair API to query the database for vulnerabilities of a particular image; correlating vulnerabilities and features is done for each request, avoiding the need to rescan images.
4.When updates to vulnerability metadata occur, a notification can be sent to alert systems that a change has occurred.
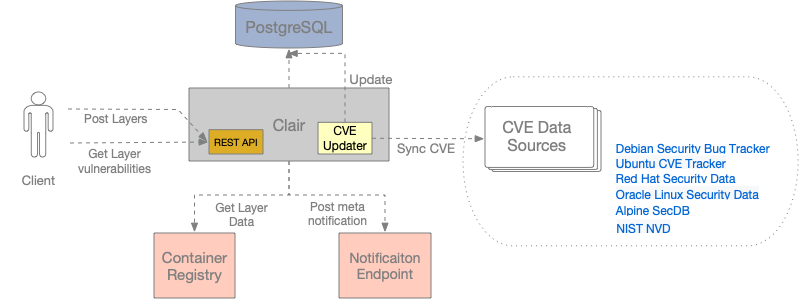
使用如下(Refers to static-analysis-of-docker-image-vulnerabilities-with-clair):
# POST image layers
$ POST http://localhost:6060/v1/layers
{
"Layer": {
"Name": "sha256:05d1a5232b461a4b35424129580054caa878cd56f100e34282510bd4b4082e4d",
"Path": "https://registry.mydomain.com/v2/debian/blobs/sha256:05d1a5232b461a4b35424129580054caa878cd56f100e34282510bd4b4082e4d",
"Headers": {
"Authorization": "xxx"
},
"Format": "Docker"
}
}
# GET result of found vulnerabilities in the image layer
$ GET http://localhost:6060/v1/layers/sha256:05d1a5232b461a4b35424129580054caa878cd56f100e34282510bd4b4082e4d?features&vulnerabilities
{
"Layer":{
"Name":"sha256:05d1a5232b461a4b35424129580054caa878cd56f100e34282510bd4b4082e4d",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"IndexedByVersion":3,
"Features":[
{
"Name":"systemd",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"VersionFormat":"dpkg",
"Version":"232-25+deb9u4",
"Vulnerabilities":[
{
"Name":"CVE-2017-1000082",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"Description":"systemd v233 and earlier fails to safely parse usernames starting with a numeric digit (e.g. \"0day\"), running the service in question with root privileges rather than the user intended.",
"Link":"https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2017-1000082",
"Severity":"Negligible"
},
{
"Name":"CVE-2013-4392",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"Description":"systemd, when updating file permissions, allows local users to change the permissions and SELinux security contexts for arbitrary files via a symlink attack on unspecified files.",
"Link":"https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2013-4392",
"Severity":"Negligible"
},
{
"Name":"CVE-2017-18078",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"Description":"systemd-tmpfiles in systemd before 237 attempts to support ownership/permission changes on hardlinked files even if the fs.protected_hardlinks sysctl is turned off, which allows local users to bypass intended access restrictions via vectors involving a hard link to a file for which the user lacks write access, as demonstrated by changing the ownership of the /etc/passwd file.",
"Link":"https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2017-18078",
"Severity":"Negligible"
},
{
"Name":"CVE-2018-1049",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"Description":"In systemd prior to 234 a race condition exists between .mount and .automount units such that automount requests from kernel may not be serviced by systemd resulting in kernel holding the mountpoint and any processes that try to use said mount will hang. A race condition like this may lead to denial of service, until mount points are unmounted.",
"Link":"https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2018-1049",
"Severity":"Medium"
},
{
"Name":"CVE-2018-6954",
"NamespaceName":"debian:9",
"Description":"systemd-tmpfiles in systemd through 237 mishandles symlinks present in non-terminal path components, which allows local users to obtain ownership of arbitrary files via vectors involving creation of a directory and a file under that directory, and later replacing that directory with a symlink. This occurs even if the fs.protected_symlinks sysctl is turned on.",
"Link":"https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2018-6954",
"Severity":"High"
}
],
"AddedBy":"sha256:05d1a5232b461a4b35424129580054caa878cd56f100e34282510bd4b4082e4d"
}
]
}
}
clair默认需要联网下载CVE库,而官方目前也并不支持在无网络情况下的执行方案。但是根据#401的讨论,对于本地镜像扫描的需求,一种方案是修改clair代码,将CVE urls设置为私有维护的CVE;另外一种方案是在外网部署一套clair,利用clair在启动时将CVE数据拉取到PostgreSQL数据库中,然后迁移到内网clair使用。这两种方案优缺点如下:
- 部署私有CVE
- Pros
- 理论上对于clair只需要修改一次,对harbor的影响也只有一次(部署第一次),后续只需要定期升级私有CVE就可以了,对harbor无感知(无损升级)
- Cons
- 需要修改clair且需要部署私有CVE,较为复杂
- Pros
- 迁移PostgreSQL
- Pros
- 对clair零侵入,无需维护私有CVE,较为简单
- Cons
- 需要定期生成PostgreSQL CVE镜像且升级后harbor镜像扫描的数据会丢失,需要重新执行一次镜像扫描(有损升级)
- Pros
这里我们采用第二种方案进行适配
迁移PostgreSQL
该方案原理图如下:
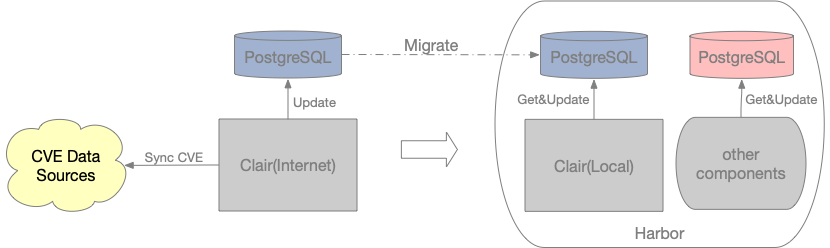
执行操作如下(参考clair-local-scan):
1、产生PostgreSQL镜像
$ docker build -t arminc/clair-local-scan --build-arg VERSION=v2.1.0 clair
$ docker pull postgres:11.1-alpine
$ docker run -d --name postgres -e 'PGDATA=/var/lib/postgresql/clair' -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=xxx postgres:11.1-alpine
$ docker run --rm -it --link postgres:postgres -e PGPASSWORD=xxx postgres:11.1-alpine pg_isready -U xxx -h postgres
$ docker run -d --name clair --link postgres:postgres arminc/clair-local-scan
$ docker logs clair|grep "update finished"
$ docker commit postgres arminc/clair-db:$(date +%Y-%m-%d)
2、备份CVE库
$ docker run --name postgres-cli -it --link postgres:postgres postgres:11.1-alpine bash
bash-4.4# pg_dump -h postgres -U xxx dbName > cve.bak
bash-4.4# exit
$ docker cp postgres-cli:/cve.bak ./
3、单独部署clair-db(clair 专用)
cat << EOF > clair-db.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: clair-db
labels:
app: clair-db
spec:
ports:
- port: xxx
selector:
app: clair-db
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: clair-db
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: clair-db # has to match .spec.template.metadata.labels
serviceName: "clair-db"
replicas: 1 # by default is 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: clair-db # has to match .spec.selector.matchLabels
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
initContainers:
- name: "remove-lost-found"
image: alpine
command: ["rm", "-Rf", "/var/lib/postgresql/data/lost+found"]
volumeMounts:
- name: database-data
mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
containers:
- name: clair-db
image: postgres:11.1-alpine
ports:
- containerPort: xxx
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: xxx
volumeMounts:
- name: database-data
mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: database-data
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
EOF
$ kubectl apply -f clair-db.yml
service/clair-db created
statefulset.apps/clair-db created
4、迁移数据(将CVE数据灌进Kubernetes pv)
$ kubectl run postgres-client --image=postgres:11.1-alpine -it --rm --restart=Never bash
bash-4.4# psql -h clair-db -U xxx
Password for user xxx:
psql (11.1)
Type "help" for help.
=# create database dbName;
CREATE DATABASE
# execute in another terminal
$ kubectl cp cve.bak postgres-client:/
# back postgres-client terminal
bash-4.4# psql -h clair-db -U xxx dbName < cve.bak
[...truncate...]
5、更新harbor clair配置
# update clair source to relevant values as below:
source: "postgres://xxx:xxx@clair-db:xxx/xxx?sslmode=disable"
# disable clair cve update
updater:
interval: 0
6、重启harbor clair
$ kubectl get pod | grep xxx | grep -v NAME|awk '{print $1}'| xargs kubectl delete pod
Refs
